Abstract
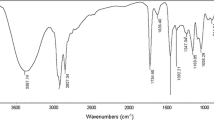
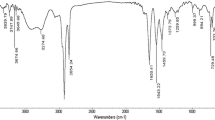
Three eco-friendly cationic surface active agents were synthesized from the chemical modification of vanillin. The chemical structures of these surfactants were confirmed using elemental analysis, IR and NMR spectra. The surface activity measurements showed their high tendency towards adsorption and micellization and their good surface tension reduction, low interfacial tension. The emulsion stability measurements showed acceptable efficiency as emulsifying agents for short term emulsions. The biodegradability tests revealed that these compounds are eco-friendly and had completely degraded in 30 days.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dikusar EA, Potkin VI, Kozlov NG (2009) Synthesis of water-soluble azomethines based on the substituted benzaldehydes of vanillin series and d−(+)-glucosamine hydrochloride. Russ J General Chem 79:2655–2657
Dikusar EA, Kozlov NG, Zhukovskaya NA (2004) Esters of vanillin and vanillal oximes. Chem Natur Comp 40:180–183
Dikusar EA, Potkin VI, Kozlov NG, Yuvchenko AP (2006) Synthesis of long-chain Schiff bases containing ether and ester moieties by condensation of octadecylamine with vanillin, vanillal, and esters derived therefrom. Russ J General Chem 76:1425–1430
Rosliza R, Noraaini A, Wan Nik WB (2010) Study on the effect of vanillin on the corrosion inhibition of aluminum alloy. J Appl Electrochem 40:833–840
Obot IB, Obi Egbedi NO (2009) Ipomoea involcrata as an eco-friendly inhibitor for aluminium in alkaline medium. Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta 27:517–524
Umoren SA, Obot IB, Obi Egbedi NO (2009) Raphia hookeri gum as a potential eco-friendly inhibitor for mild steel in sulfuric acid. J Mater Sci 44:274–279
Negm NA, Aiad IA (2007) Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional surfactants in oil-field protection applications. JSD 10:87–92
Aelony D (1954) Direct esterification of phenols with higher fatty acids. JAOCS 32:170–172
Negm NA, El-Farargy A, Zaki MF, Mahmoud SA, Abdel Rahman N (2008) Cationic Schiff base amphiphiles: 1. Synthesis, characterization and surface activities of cationic surfactants bearing Schiff base groups and their Mn(Ii), Cu(Ii) And Co(Ii) complexes. Egypt J Petrol 17:15–25
Negm NA (2007) Solubilization, surface active and thermodynamic parameters of gemini amphiphiles bearing nonionic hydrophilic spacer. JSD 8:71–80
Negm NA, Elkholy YM, Ghuiba FM, Zahran MK, Mahmoud SA, Tawfik SM (2011) Benzothiazol-3-ium cationic Schiff base surfactants: synthesis, surface activity and antimicrobial applications against pathogenic and sulfur reducing bacteria in oil fields. J Adsorp Sci Technol (Accepted manuscript, in press)
OECD Chemical group (1993) Ready biodegradability: modified screening test, method 301 D, OECD revised guidelines for ready biodegradability. OECD Paris, France
Bentiss F, Bouanis M, Mernari B, Traisnel M, Vezin H, Lagrenee M (2007) Understanding the adsorption of 4H–1,2,4-triazole derivatives on mild steel surface in molar hydrochloric acid. Appl Surf Sci 253:3696–3703
Rosen MJ (1992) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Oda R, Huc I, Candau SJ (1997) Gemini surfactants: the effect of hydrophobic chain length and dissymmetry. Chem Commun 21:6382–6389
Bai G, Wang J, Yan LZ, Thomas RK (2001) Thermodynamics of molecular self-assembly of cationic gemini and related double chain surfactants in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem 105:3105–3112
Leal JS, Gonzalez JJ, Kaiser KL, Palabrica VS, Comelles F, Garcıa MT (1994) On the toxicity and biodegradation of cationic surfactants (Über die Toxizität und den biologischen Abbau kationischer Tenside). Acta Hydrochim Hydrobiol 22:13–21
Ratledge C (1994). In: Ratledge C (ed) Biochemistry of microbial degradation. Kluwer, Amsterdam 89
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Negm, N.A., Kandile, N.G. & Mohamad, M.A. Synthesis, Characterization and Surface Activity of New Eco-friendly Schiff Bases Vanillin Derived Cationic Surfactants. J Surfact Deterg 14, 325–331 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-011-1249-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-011-1249-4