Abstract
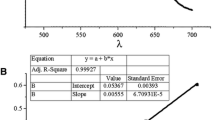
Alkylpolyglucosides (APG) prepared on the basis of renewable raw materials have been proven ultimately readily biodegradable. They are completely green surfactants. With the development of the petrochemical industry, APG prepared by oxo alcohol have been widely used recently. They have equal physicochemical properties with those prepared with renewable raw materials, but there is little information about their environmental compatibility. Primary aerobic biodegradability of linear alcohol and oxo alcohol APG was compared in this study. The results showed that oxo APG had similar good blodegradability with linear alcohol APG. In a shaking-flask test, more than 87% APG could be degraded after 21 d and are therefore completely green surfactants. The relationship between structure and biodegradability was studied. The hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups affected their biodegradation. Biodegradability deteriorated with increasing chain length and size of head groups. Branching did not affect their biodegradation. The degradation rate decreased with increasing head group size. Monoglucoside degraded faster than diglucosides, and diglucosides degraded faster than polyglucosides. Accordingly, a potential degradation pathway was proposed. APG were hydrolyzed to alcohol and polysaccharide in the first step, then the alcohol was oxidized to CO2 and H2O by β or α oxidation. The polysaccharide was hydrolyzed to glucose, and then the glucose was degraded by a glucose metabolism mechanism. This pathway provided a good explanation of the experiment results.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APG:
-
alkylpolyglucosides
- DP:
-
degree of polymerization
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- ISO:
-
international Standards Organization
References
Zhang, J., K. Xie, X. Dai, and G. Zhang, Differences Between Alkyl Polyglucosides of Natural Alcohol and Oxo Alcohol, J. Surfactants Detergents 6:253 (2003).
Garcia, M.T., I. Ribosa, E. Campos, and L.J. Sanchez, Ecological Properties of Alkylglucosides, Chemosphere 35:545 (1997).
Swisher, R.D., Surfactant Biodegradation, 2nd edn., Surfactant Science Series, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1988, Vol. 18, p. 156.
Qin, Y., G. Zhang, B. Kang, and Y. Zhao, Primary Areobic Biodegradation of Cationic and Amphoteric Surfactants, Journal of Surfactants and Detergents 8:55 (2005).
International Standards Organization, ISO 7827-1984(E), Water Quality—Evaluation in an Aqueous Medium of the Ultimate Aerobic Biodegradability of Organic Compounds—Methods by Analysis of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC), International Standards Organization, Geneva, 1984.
Buschmann, N., and S. Wodarczak, Analytical Methods for Alkylpolyglucosides Part: Colorimetric Determination, Tenside Surfactants Detergents 32:336 (1995).
Baker, J.A., B. Matthews, H. Suares, I. Krodkiewska, D. Neil Furlong, F. Grieser et al., Sugar Fatty Acid Surfactants: Structure and Ultimate Aerobic Biodegradability, J. Surfactants Detergents 3:1 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Zhang, G., Zhang, J. et al. Primary aerobic biodegradation of linear and oxo alcohol alkylpolyglucosides (APG). J Surfact Deterg 9, 227–230 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-006-5001-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-006-5001-4