Abstract
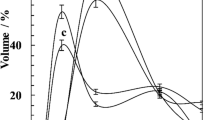
Soapstock was converted into a liquid soap from its acid oil and formulated with varying amounts of rosin. The characteristics of the acid oil and rosin were experimentally estimated. Liquid soaps were characterized by density, pH, total fatty matter, free caustic alkali, critical micelle concentration, foaming capacity, wetting power, and washing performance. The foaming results indicated that the liquid soap is best used as an ingredient in a washing-machine detergent. The dark aspect of a formulation with 10% rosin precluded higher substitution.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AV:
-
acid value
- CMC:
-
critical micelle concentration
- DDBS:
-
sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate
- ENCG:
-
Enterprise Nationale des Corps Gras
- IV:
-
iodine value
- STPP:
-
sodium tripolyphosphate
- SV:
-
saponification value
- TFM:
-
total fatty matter
- UM:
-
unsaponifiable matter
References
Kiefer, D.M., It Was All About Alkali, Today’s Chemist at Work 11:45 (2002).
Woollatt, E., The Manufacture of Soaps, Other Detergents and Glycerine, 1st edn., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1985.
Davidsohn, A.S., and M. Mildwidsky, Synthetic Detergents, 7th edn., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1987.
Suszkiw, J., Soapstock Waste May Yield New Product, ARS News Inf. (March 22, 1999).
Partridge, G.G., M. Findlay, and R.A. Fordyce, Fat Supplementation of Diets for Growing Rabbits, Animal Feed Sci. Technol. 16:109 (1986).
Sibbald, I.R., S.J. Slinger, and G.C. Ashton, The Utilization of a Number of Fats, Fatty Materials and Mixtures Thereof, Evaluated in Terms of Metabolizable Energy, Weight Gains, and Gain to Feed Ratios, Poultry Sci. 41:46 (1962).
Haas, M.J., S. Bloomer, and K. Scott, Simple, High-Efficiency Synthesis of Fatty Acid Methyl Esters from Soapstocks, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 77:373 (2000).
Haas, M.J., K.M. Scott, T.L. Alleman, and R.L. McCormick, Engine Performance of Biodiesel Fuel Prepared from Soybean Soapstocks: A High Quality Renewable Fuel Produced from a Waste Feedstock, Energy Fuels 15:127 (2001).
Norris, F.A., Fats and Fatty Acids, in Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 2nd edn., John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1965, Vol. 8.
Moulay, S., B. Halim, and A. Mohamed, Algerian Montmorillonite as a Builder in a Detergent Powder, J. Surfact. Deterg. 6:113 (2003).
British Standard Specifications, BS 9405:1969.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Moulay, S., Zenimi, A. & Dib, M. Rosin/acid oil-based liquid soap. J Surfact Deterg 8, 169–174 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-005-343-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11743-005-343-5