Abstract
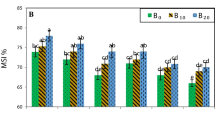
An experiment was conducted to determine the effect of water stress on nutritional changes in tolerant (DS-4 and Chakwal-86) and susceptible (DS-17 and Pavon) genotypes in lysimeters. The stress was imposed at different growth stages (pre-anthesis, post-anthesis, terminal drought). The biomass (dry weight) and Ca, Mg and P concentration decreased with water stress in all the wheat genotypes. However, the tolerant genotypes had less reduction than susceptible at all the treatments. Potassium increased in all wheat genotypes due to water stress and was higher in tolerant than susceptible genotypes. Sodium content was not affected by water stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M.Y., Azmi A.R., Khan A.H., Naqvi S.S.M., 1994. Water relations in different wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes under soil water deficits. Acta Physiol. Plant., 16(3):231–240.
Asraf M. Y., Khan A.H., Azmi A.R., 1992. Cell membrane stability and its relation with some physiological processes in wheat. Acta Agron. Hung., 41(3–4): 183–191.
Hsiao T.C., 1973. Plant responses to water stress. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol., 24: 519–570.
Kidambi S.P., Matches A.G., Bolger T.P., 1990. Mineral concentrations in alfalfa and sainfoin as influenced by soil moisture level. Agron. J., 82: 229–236.
Mbagwe I.S.C., Osuigwe., 1985. Effect of varying levels and frequencies of irrigation on growth, yield, nutrient uptake and water use efficiency of maize and cowpeas on a sandyloam soil. Plant and Soil., 84: 181–186.
Menzel C.M., Simpson D.R., 1986. Reduction in wheat leaves as affected by different types of water stress. Physiol. Plant. 46: 318–323.
Premachandra G.S., Saneoka H., Fujita., Orgata S., 1990. Cell membrane stability and leaf water relations as affected by phosphorus nutrition under water stress in maize. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 36(4): 661–666.
Premachandra G.S., Saneoka H., Fujita., Orgata S., 1990 a. Cell membrane stability and leaf water relations as affected by nitrogen nutrition under water stress in maize. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 36(4): 653–659.
Steel R.G.D., Torrie J.H., 1980. Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Tanguilig V.C., Yambao E.B., Toole J.C.O., Dedatta S., 1987. Water stress effects on leaf elongation leaf water potential, transpiration and nutrient uptake of rice, maize, and soybean. Plant and Soil. 103: 155–168.
Venekamp L., Lampe L.E.M., oot J.T.M., 1989. Organic acid as sources drought-induced proline synthesis in field bean (Vicia faba L.) J. Plant Physiol., 133: 654–659.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashraf, M.Y., Ala, S.A. & Bhatti, A.S. Nutritional imbalance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes grown at soil water stress. Acta Physiol Plant 20, 307–311 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-998-0063-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-998-0063-8