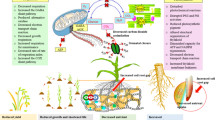
Abstract
Water deficit is a main abiotic factor that seriously influences the production of crop plants such as anise and the lack of effective selection criteria has made it difficult to develop tolerant genotypes. This experiment aimed to investigate the relationship between seed yield and related characteristics in anise to evaluate genotype × trait interaction emphasis genotype × water treatment interaction. According to this aim, 21 Iranian endemic anise genotypes were evaluated under both water deficit and control conditions in a nursery. Genotypic variance and correlation coefficients estimates calculated from pooled analysis of control and water deficit conditions were used in structural equation modeling (SEM) and genotype × trait (G × T) biplot analysis. The G × T biplot visually showed the interrelationships among traits and facilitate graphical comparison of genotypes. Based on the SEM, predictors used in the causal diagram could explain 97.6%, 93.9%, 78.7%, 69.8%, and 65.9% of the total variation in seed yield per plant (SYPP), thousand seed weight (TSW), seed number per plant (SNPP), net photosynthesis (NPh) and stomatal conductance (gs), respectively. The G × T biplots explained 77.5% of the total variation in control condition, 59.4% in water deficit stress and 64.6% in the pooled conditions. SNPP, TSW, NPh and gs must be regarded as a priority for developing new genotypes anise to get more tolerant and productive genotypes to water deficit and selection criteria. Also, G11 (tolerant) and G21 (susceptible) can be considered as parents in crossing schemes to genetic architecture studies and heritability for improvement in drought tolerance.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SEM:
-
Structural equation modeling
- G × T biplot:
-
Genotype × trait biplot
- RWC:
-
Relative water content
- Tchl:
-
Total chlorophyll
- LNPP:
-
Leaf number per plant
- BLN:
-
Basal leaf number
- LLL:
-
Longest leaf length
- BNPP:
-
Branch number per plant
- UNPP:
-
Umbel number per plant
- TSW:
-
Thousand seed weight
- DTF:
-
Days to flowering
- DTR:
-
Days to ripening
- SDW:
-
Shoot dry weight
- SNPP:
-
Seed number per plant
- SYPP:
-
Seed yield per plant
- PH:
-
Plant height at the end of the seed ripening stage
- SD:
-
Stem diameter
- F v /F m :
-
PSII maximum quantum yield
- NPh:
-
Net photosynthesis
- g s :
-
Stomatal conductance
- Tr:
-
Transpiration
- LT:
-
Leaf temperature
- CI:
-
Intercellular CO2 concentration
- SPAD index:
-
Leaf chlorophyll content
References
Akbarpour OA, Dehghani H, Rousta MJ (2015) Evaluation of salt stress of Iranian wheat germplasm under field conditions. Crop Pasture Sci 66(8):770–781. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP14286
Ambachew D, Mekbib F, Asfaw A, Beebe SE, Blair MW (2015) Trait associations in common bean genotypes grown under drought stress and field infestation by BSM bean fly. Crop J 3(4):305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2015.01.006
Andarwulan N, Shetty K (1999) Phenolic content in differentiated tissue cultures of untransformed and Agrobacterium-transformed roots of anise (Pimpinella anisum L.). J Agric Food Chem 47(4): 1776–1780. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf981214r
Arbuckle J (2011) Amos [computer program]. Version 20. 0. IBM SPSS Chicago, Ill. USA.
Arslan N, Gürbüz B, Sarihan EO, Bayrak A, Gümüşçü A (2004) Variation in essential oil content and composition in Turkish anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) populations. Turk J Agric For 28(3): 173–177.
Asfaw A, Ambachew D, Shah T, Blair MW (2017) Trait associations in diversity panels of the two common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) gene pools grown under well-watered and water-stress conditions. Front Plant Sci 8: 733. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00733
Bacher H, Sharaby Y, Walia H, Peleg Z (2022) Modifying root-to-shoot ratio improves root water influxes in wheat under drought stress. J Exp Bot 73(5):1643–1654. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erab500
Bernier J, Atlin GN, Serraj R, Kumar A, Spaner D (2008) Breeding upland rice for drought resistance. J Sci Food Agric 88(6):927–939. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.3153
Cechin I, Cardoso GS, Fumis TDF, Corniani N (2015) Nitric oxide reduces oxidative damage induced by water stress in sunflower plants. Bragantia 74:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4499.353
Chen X, Min D, Yasir TA, Hu YG (2012) Evaluation of 14 morphological, yield-related and physiological traits as indicators of drought tolerance in Chinese winter bread wheat revealed by analysis of the membership function value of drought tolerance (MFVD). Field Crops Res 137:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2012.09.008
Chenu K, Cooper M, Hammer GL, Mathews KL, Dreccer MF, Chapman SC (2011) Environment characterization as an aid to wheat improvement: interpreting genotype–environment interactions by modelling water-deficit patterns in North-Eastern Australia. J Exp Bot 62(6):1743–1755. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq459
da Silva PP, Soares L, da Costa JG, da Silva Viana L, de Andrade JCF, Gonçalves ER, dos Santos JM, de Souza Barbosa GV, Nascimento VX, Todaro AR, Riffel A, Grossi-de-Sa MF, Barbosa MHP, Sant’Ana AEG, Neto CER (2012) Path analysis for selection of drought tolerant sugarcane genotypes through physiological components. Ind Crops Prod 37(1): 11-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.11.015
Dehghani H, Omidi H, Sabaghnia N (2008) Graphic analysis of trait relations of rapeseed using the biplot method. Agron J 100(5):1443–1449. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2007.0275
Dolatabad SS, Choukan R, Hervan EM, Dehghani H (2010) Biplot analysis for multi-environment trials of maize (Zea mays L.) hybrids in Iran. Crop Pasture Sci 61(9): 700–707. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP09325
Elfadl E, Reinbrecht C, Claupein W (2010) Evaluation of phenotypic variation in a worldwide germplasm collection of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) grown under organic farming conditions in Germany. Genet Resour Crop Evol 57(2): 155–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-009-9458-7
Eynizadeh P, Dehghani H (2020) Selecting elite tomato genotypes through a modified analytical hierarchy process. Crop Pasture Sci 71(9):822–830. https://doi.org/10.1071/CP20116
Fischer RA, Maurer R (1978) Drought resistance in spring wheat cultivars. I. Grain yield responses. Aust J Agric Res 29(5): 897–912. https://doi.org/10.1071/AR9780897
Garshasbi P (2014) Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran. Jihad-Agriculture Minsitry, of the IR Iran, Iran.
GGEbiplot 2011 GGEbiplot. A statistical package. Ottawa, ON, Canada.
Gholizadeh A, Dehghani H, Khodadadi M (2019) Quantitative genetic analysis of water deficit tolerance in coriander through physiological traits. Plant Genet Resour 17(3):255–264. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1479262118000539
Golabadi M, Arzani A, Maibody SMM (2005) Evaluation of variation among durum wheat F3 families for grain yield and its components under normal and water-stress field conditions. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 41: 263–267. https://doi.org/10.17221/6188-CJGPB
Gonzalez A, Bermejo V, Gimeno BS (2010) Effect of different physiological traits on grain yield in barley grown under irrigated and terminal water deficit conditions. J Agric Sci 148(3):319–328. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859610000031
Gülçın İ, Oktay M, Kıreçcı E, Küfrevıoǧlu Öİ (2003) Screening of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) seed extracts. Food Chem 83(3): 371–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00098-0
Hanifei M, Mehravi S, Khodadadi M, Severn-Ellis AA, Edwards D, Batley J (2021) Detection of epistasis for seed and some phytochemical traits in coriander under different irrigation regimes. Agronomy 11(9):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11091891
Hosseini B, Dehghani H, Khodadadi M (2019) Root traits and transpiration efficiency in fenugreek ecotypes grown under different water treatments. J Agric Sci Technol 21(3): 715–727
Hui Z, ZhengBin Z, HongBo S, Ping X, Foulkes MJ (2008) Genetic correlation and path analysis of transpiration efficiency for wheat flag leaves. Environ Exp Bot 64(2):128–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.11.001
Hussain M, Farooq S, Hasan W, Ul-Allah S, Tanveer M, Farooq M, Nawaz A (2018) Drought stress in sunflower: Physiological effects and its management through breeding and agronomic alternatives. Agric Water Manag 201:152–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.01.028
SPSS INC (2011) SPSS 20. SPSS User’s guide. SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA.
Jangpromma N, Songsri P, Thammasirirak S, Jaisil P (2010) Rapid assessment of chlorophyll content in sugarcane using a SPAD chlorophyll meter across different water stress conditions. Asian J Plant Sci 9(6):368–374. https://doi.org/10.3923/ajps.2010.368.374
Johnson HW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimates of genetic and environmental variability in soybeans. Agron J 47(7):314–318. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1955.00021962004700070009x
Khodadadi M, Dehghani H, Jalali-Javaran M, Rashidi-Monfared S, Christopher JT (2016) Numerical and graphical assessment of relationships between traits of the Iranian Coriandrum sativum L. core collection by considering genotype× irrigation interaction. Sci Hortic 200:73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2016.01.003
Khodadadi M, Dehghani H, Jalali Javaran M (2017) Quantitative genetic analysis reveals potential to genetically improve fruit yield and drought resistance simultaneously in coriander. Front Plant Sci 8:568. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00568
Khonghintaisong J, Songsri P, Toomsan B, Jongrungklang N (2018) Rooting and physiological trait responses to early drought stress of sugarcane cultivars. Sugar Tech 20(4):396–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-017-0564-0
Koonjah SS, Walker S, Singels A, Van Antwerpen R, Nayamuth AR (2006) A quantitative study of water stress effect on sugarcane photosynthesis. Proc S Afr Sug Technol Ass 80:148–158
Kumar A, Bernier J, Verulkar S, Lafitte HR, Atlin GN (2008) Breeding for drought tolerance: direct selection for yield, response to selection and use of drought-tolerant donors in upland and lowland-adapted populations. Field Crops Res 107(3):221–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2008.02.007
Lafitte R (2002) Relationship between leaf relative water content during reproductive stage water deficit and grain formation in rice. Field Crops Res 76(2–3):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4290(02)00037-0
Lal RK, Gupta P, Srivastva S, Chanotiya CS, Mishra A, Yadav A, Maurya R (2021) Delineating photosynthesis, essential oil yield performance, and their component traits under genotype×traits×environments interactions in Ocimum genotypes. S Afr J Bot 141:54–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2021.03.039
Lamb E, Shirtliffe S, May W (2011) Structural equation modeling in the plant sciences: an example using yield components in oat. Can J Plant Sci 91(4):603–619. https://doi.org/10.4141/cjps2010-035
Lawlor DW, Tezara W (2009) Causes of decreased photosynthetic rate and metabolic capacity in water-deficient leaf cells: a critical evaluation of mechanisms and integration of processes. Ann Bot 103(4):561–579. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcn244
Leal-Bertioli S, Bertioli DJ, Guimarães PM, Pereira TD, Galhardo I, Silva JP, Brasileiro ACM, Oliveira RS, Silva PÍ, Vadez V (2012) The effect of tetraploidization of wild Arachis on leaf morphology and other drought-related traits. Environ Exp Bot 84:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2012.04.005
Liu Q, Zhao X, Liu Y, Xie S, Xing Y, Dao J, Beilei W, Peng Y, Duan W, Wang Z (2021) Response of sugarcane rhizosphere bacterial community to drought stress. Front microb 12:716196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.716196
Maghsoudi K, Emam Y, Pessarakli M (2016) Effect of silicon on photosynthetic gas exchange, photosynthetic pigments, cell membrane stability and relative water content of different wheat cultivars under drought stress conditions. J Plant Nutr 39(7):1001–1015. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2015.1109108
Martínez-Vilalta J, Garcia-Forner N (2017) Water potential regulation, stomatal behaviour and hydraulic transport under drought: deconstructing the iso/anisohydric concept. Plant Cell Environ 40(6):962–976. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.12846
Mehraban A, Tobe A, Gholipouri A, Amiri E, Ghafari A, Rostaii M (2019) The effects of drought stress on yield, yield components, and yield stability at different growth stages in bread wheat cultivar (Triticum aestivum L.). Pol J Environ Syud 28(2): 739–746. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/85350
Mehravi S, Ranjbar GA, Mirzaghaderi G, Severn-Ellis AA, Scheben A, Edwards D, Batley J (2021) De novo SNP discovery and genotyping of Iranian Pimpinella species using ddRAD sequencing. Agron 11(7):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071342
Mehravi S, Ranjbar GA, Najafi-Zarrini H, Mirzaghaderi G, Hanifei M, Severn-Ellis AA, Edwards D, Batley J (2022) Karyology and genome size analyses of Iranian endemic Pimpinella (Apiaceae) species. Front Plant Sci 13: 898881. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.898881
Mohi-Ud-Din M, Hossain M, Rohman M, Uddin M, Haque M, Ahmed JU, Hossain A, Hassan MM, Mostofa MG (2021) Multivariate analysis of morpho-physiological traits reveals differential drought tolerance potential of bread wheat genotypes at the seedling stage. Plants 10(5):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050879
Mousavi SMN, Bojtor C, Illés Á, Nagy J (2021) Genotype by trait interaction (GT) in maize hybrids on complete fertilizer. Plants 10(11):2388. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10112388
Nazari L, Pakniyat H (2010) Assessment of drought tolerance in barley genotypes. J Appl Sci 10(2): 151–156. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2010.151.156 Source: DOAJ
Nazari A, Javidfar F, Attary AA (2002) Genetic variability, correlation and path analysis of yield and its components in winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Pak J Bot 34(2): 145–150.
Ongom PO, Volenec JJ, Ejeta G (2016) Selection for drought tolerance in sorghum using desiccants to simulate post-anthesis drought stress. Field Crops Res 198:312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2016.03.015
Paknejad F, Nasri M, Moghadam H T, Zahedi H, Alahmadi MJ (2007) Effects of drought stress on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, chlorophyll content and grain yield of wheat cultivars. J Biol Sci 7(6): 841–847. http://en.journals.sid.ir/ViewPaper.aspx?ID=103989
Rebey IB, Jabri-Karoui I, Hamrouni-Sellami I, Bourgou S, Limam F, Marzouk B (2012) Effect of drought on the biochemical composition and antioxidant activities of cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) seeds. Ind Crops Prod 36(1): 238–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2011.09.013
Robertson LA, Kleinschmidt CE, White DG, Payne GA, Maragos CM, Holland JB (2006) Heritabilities and correlations of Fusarium ear rot resistance and fumonisin contamination resistance in two maize populations. Crop Sci 46(1):353–361. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.0139
Rubio J, Cubero JI, Martin LM, Suso MJ, Flores F (2004) Biplot analysis of trait relations of white lupin in Spain. Euphytica 135(2):217–224. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000014911.70355.c9
Sabaghnia N, Dehghani H, Alizadeh B, Mohghaddam M (2010) Interrelationships between seed yield and 20 related traits of 49 canola (Brassica napus L.) genotypes in non-stressed and water-stressed environments. Span J Agric Res 2:356–370
Santos TDO, Amaral Junior ATD, Bispo RB, Lima VJD, Kamphorst SH, Leite JT, Santos Júnior DRD, Diniz Santos PHA, de Oliveira UA, Schmitt KFM, Campostrini E, Moulin MM, Pio Viana A, Gravina GDA, Corrêa CCG, Gonçalves GMB (2021) Phenotyping Latin American open-pollinated varieties of popcorn for environments with low water availability. Plants 10(6):1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10061211
SAS (2005) Statistical Analysis Software, Inc., Cary, NC.
Sato AM, Catuchi TA, Ribeiro RV, Souza GM (2010) The use of network analysis to uncover homeostatic responses of a drought-tolerant sugarcane cultivar under severe water deficit and phosphorus supply. Acta Physiol Plant 32(6):1145–1151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0506-x
Silva MDA, Jifon JL, da Silva JAG, dos Santos CM, Sharma V (2014) Relationships between physiological traits and productivity of sugarcane in response to water deficit. J Agric Sci 152(1):104–118. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859612000834
Songsri P, Jogloy S, Kesmala T, Vorasoot N, Akkasaeng C, Patanothai A, Holbrook CC (2008) Heritability of drought resistance traits and correlation of drought resistance and agronomic traits in peanut. Crop Sci 48(6):2245–2253. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2008.04.0228
Valente BD, Rosa GJ, Gianola D, Wu XL, Weigel K (2013) Is structural equation modeling advantageous for the genetic improvement of multiple traits? Genetics 194(3):561–572. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.113.151209
Venuprasad R, Lafitte HR, Atlin GN (2007) Response to direct selection for grain yield under drought stress in rice. Crop Sci 47(1):285–293. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2006.03.0181
Wright S (1921) Correlation and causation. J Agric Res 20:557–585
Yan W, Rajcan I (2002) Biplot analysis of test sites and trait relations of soybean in Ontario. Crop Sci 42(1):11–20. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2002.1100
Yan W, Tinker NA (2005) An integrated biplot analysis system for displaying, interpreting, and exploring genotype× environment interaction. Crop Sci 45(3):1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2004.0076
Yan W, Hunt LA, Sheng Q, Szlavnics Z (2000) Cultivar evaluation and mega-environment investigation based on the GGE biplot. Crop Sci 40(3):597–605. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2000.403597x
Yetisir H, Uygur V (2010) Responses of grafted watermelon onto different gourd species to salinity stress. J Plant Nutr 33(3):315–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904160903470372
Zaharieva M, Gaulin E, Havaux M, Acevedo E, Monneveux P (2001) Drought and heat responses in the wild wheat relative Aegilops geniculata Roth: potential interest for wheat improvement. Crop Sci 41(4):1321–1329. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2001.4141321x
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by University of Western Australia. The authors thank the Forests, Range and Watershed Management Organization, Tehran, Iran, for providing the seeds of anise genotypes.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Communicated by B. Zheng.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mehravi, S., Hanifei, M., Khodadadi, M. et al. Evaluation of relationships between traits of anise (Pimpinella anisum L.) genotypes in response to drought stress using the structural equation modeling and biplot method. Acta Physiol Plant 45, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03491-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-022-03491-7