Abstract
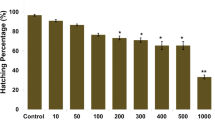
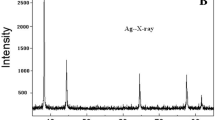
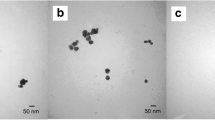
Silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs) are synthesized by several methods and are being widely used in various fields of science. In recent times, evaluation of their toxicological effects on environment, especially to the plant ecosystems has attained special attention. In this study, effect of synthesized AgNPs [chemically (S-AgNPs) and/or biologically (B-AgNPs)] on the growth and physiology of an aquatic plant water hyacinth—Eichhornia crassipes (Mart) Solms was evaluated. Water hyacinth plants were treated with S-AgNPs and B-AgNPs at different concentrations of 1, 10 and 100 mg L−1and growth was monitored for 5 days. Decreased growth of hyacinth was observed only on fifth day in treatments with S-AgNPs treatment alone but not for B-AgNPs. Further, the atomic absorption spectroscopy results (at 100 mg L−1 concentration) showed a higher accumulation of S-AgNPs over the B-AgNPs in various parts of the treated plants. Biochemical analysis on day five in B-AgNPs treated leaf extracts revealed an increase in carbohydrate and protein levels, and a decrease in phenol and chlorophyll content. In contrary, S-AgNPs treated leaf extracts did not show any significant changes in carbohydrate and protein levels, however, observed a significant increase in phenol and chlorophyll content. Interestingly, S-AgNP treatment increased the activities of antioxidative enzymes, such as catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. No significant differences were measured in plants treated with B-AgNPs when compared to normal plants which may reveal that these B-AgNPs instead enhanced the plant growth with a fewer minor effects on water hyacinth plants over S-AgNPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- AgNPs:
-
Silver nanoparticles
- AgNO3 :
-
Silver nitrate
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- CHL:
-
Chlorophyll
- CAT:
-
Catalase
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126
Angel BM, Batley GE, Jarolimek CV, Rogers NJ (2013) The impact of size on the fate and toxicity of nanoparticulate silver in aquatic systems. Chemosphere 93(2):359–365
Benn TM, Westerhoff P (2008) Nanoparticle silver released into water from commercially available sock fabrics. Environ Sci Technol 42:4133–4139
Beyer WF, Fridovich I (1987) Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal Biochem 161:559–566
Chance B, Maehly AC (1955) Assay of catalase and peroxidase. Meth Enzymol 2:764–775
Chernousova S, Epple M (2013) Silver as antibacterial agent: ion, nanoparticle, and metal. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:1636–1653
De Biasi MG, Astolfi S, Acampora A, Zuchi S, Fonzo V, Satangelo E, Caccia R, Badiani M, Soressi GP (2003) A H2O2-forming peroxidase rather than a NAD(P) H-dependent O2− synthase may be the major player in cell death responses controlled by the pto-Fen complex following fenthion treatment. Funct Plant Biol 30:409–417
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Dudjak J, Lachman J, Miholová D, Kolihová D, Pivec V (2004) Effect of cadmium on polyphenol content in young barley plants (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Soil Environ 50:471–477
Fabrega J, Luoma SN, Tyler CR, Galloway TS, Lead JR (2011) Silver nanoparticles: behaviour and effects in the aquatic environment. Environ Int 37:517–553
Farkas J, Peter H, Christian P, Urrea JAG, Hassellöv M, Tuoriniemi J, Gustafsson S, Olsson E, Hylland K, Thomas KV (2011) Characterization of the effluent from a nanosilver producing washing machine. Environ Int 37:1057–1062
Fuhrer J (1982) Early effects of excess cadmium uptake in Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Cell Environ 5:263–270
Gaiser BK, Biswas A, Rosenkranz P, Jepson MA, Lead JR, Stone V, Tyler CR, Fernandes TF (2011) Effects of silver and cerium dioxide micro- and nano-sized particles on Daphnia magna. J Environ Monit 13:1227–1235
Griffitt RJ, Luo J, Gao J, Bonzongo J-C, Barber DS (2008) Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1972–1978
Gubbins EJ, Batty LC, Lead JR (2011) Phytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to Lemna minor L. Environ Poll 159:1551–1559
Harris AT, Bali R (2008) On the formation and extent of uptake of silver nanoparticles by live plants. J Nanopart Res 10:691–695
Hegedus A, Erdei S, Horváth G (2001) Comparative studies of H2O2 detoxifying enzymes in green and greening barley seedlings under cadmium stress. Plant Sci 160:1085–1093
Jyothsna Y, Usha Rani P (2013) Environmental effects of nanosilver: impact on castor seed germination, seedling growth, and plant physiology. Environ Sci Poll Res 20(12):8636–8648
Kennedy AJ, Hull MS, Bednar AJ, Goss JD, Gunter JC, Bouldin JL, Vikesland PJ, Steevens JA (2010) Fractionating nanosilver: importance for determining toxicity to aquatic test organisms. Environ Sci Technol 44:9571–9577
Kim E, Kim SH, Kim H, Lee SG, Lee SJ, Jeong SW (2011) Growth inhibition of aquatic plant caused by silver and titanium oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 3(1):1–6
Krishnaraj C, Jagan EG, Ramachandran R, Abirami SM, Mohan N, Kalaichelvan PT (2012) Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on Bacopa monnieri (Linn) plant growth metabolism. Process Biochem 47:651–658
Lee WM, An YJ, Yoon H, Kweon HS (2008) Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Nanomat Environ 27:1915–1921
Lee CW, Mahendra S, Zodrow K, Li D, Tsai YC, Braam J, Alvarez PJJ (2010) Developmental phytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ Toxicol Chem 29:669–675
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Meth Enzymol 148:350–382
Lin S, Reppert J, Hu Q, Hudson JS, Reid ML, Ratnikova TA, Rao AM, Luo H, Ke PC (2009) Uptake, translocation, and transmission of carbon nanomaterials in rice plants. Small 5:1128–1132
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Luoma SN (2008) Silver nanotechnologies and the environment: old problems and new challenges?. Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars or The PEW Charitable Trusts, Washington DC
Ma X, Geiser-Lee J, Deng Y, Kolmakov A (2010) Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake and accumulation. Sci Total Environ 408:3053–3061
Mahamadi C, Nharingo T (2010a) Utilization of water hyacinth weed (Eichhornia crassipes) for the removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) from aquatic environments: an adsorption isotherm study. Environ Technol 31(11):1221–1228
Mahamadi C, Nharingo T (2010b) Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) ions onto Eichhornia Crassipes in Binary and Ternary systems. Bioresour Technol 101(3):859–864
Mahmood T, Malik SA, Hussain ST (2010) Biosorption and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth) ash. BioResources 5(2):1244–1256
Malik A (2007) Environmental challenge vis a vis opportunity: the case of water hyacinth. Environ Int 33:122–138
Mane PC, Bhosle AB, Kulkarni PA (2011) Biosorption and biochemical study on water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) with reference to selenium. Arch Appl Sci Res 3(1):222–229
Matsumura T, Tabayashi N, Kamagata Y, Souma C, Saruyama H (2002) Wheat catalase expressed in transgenic rice can improve tolerance against low temperature stress. Physiol Plant 116:317–327
Miralles P, Church TL, Harris AT (2012) Toxicity, uptake, and translocation of engineered nanomaterials in vascular plants. Environ Sci Technol 46(17):9224–9239
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Navarro E, Piccapietra F, Wagner B, Marconi F, Kaegi R, Odzak N, Sigg L, Behra R (2008) Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Environ Sci Technol 42:8959–8964
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311:622–627
Noctor G, Foyer CH (1998) Ascorbate and glutathione: keeping active oxygen under control. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:249–279
Nowack B, Krug HF, Height M (2011) 120 years of nanosilver history: implications for policy makers. Environ Sci Tech 45(4):1177–1183
Odjegba VJ, Fasidi IO (2007) Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities in Eichhornia crassipes (Pontederiaceae) and Pistia stratiotes (Araceae) under heavy metal stress. Rev Biol Trop 55(3–4):815–823
Oukarroum A, Barhoumi L, Pirastru L, Dewez D (2013) Silver nanoparticle toxicity effect on growth and cellular viability of the aquatic plant Lemna gibba. Environ Toxicol Chem 32:902–907
Ouzounidou G (1994) Root growth and pigment composition in relationship to element up take in Silene compacta plants treated with copper. J Plant Nutr 17:933–943
Pal S, Tak YK, Song JM (2007) Does the antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles depend on the shape of the nanoparticle? A study of the gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(6):1712–1720
Qian JH, Zayed A, Zhu YL, Yu M, Terry N (1999) Phytoaccumulation of trace elements by wetland plants: III. Uptake and accumulation of ten trace elements by twelve plant species. J Environ Qual 28:1448–1455
Rajasekharreddy P, Usha Rani P, Sreedhar B (2010) Qualitative assessment of silver and gold nanoparticle synthesis in various plants: a photobiological approach. J Nanopar Res 12(5):1711–1721
Ratte HT (1999) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:89–108
Rico CM, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agric Food Chem 59(8):3485–3498
Silver S (2003) Bacterial silver resistance: molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:341–353
Singh Y, Malik CP (2011) Phenols and their antioxidant activity in Brassica juncea seedlings growing under HgCl2 stress. J Microbiol Biotech Res 1(4):124–130
Singh S, Eapen S, Souza SFD (2006) Cadmium accumulation and its influence on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative system in an aquatic plant, Bacopa monnieri L. Chemosphere 62:233–246
Song JY, Kim B (2008) Rapid biological synthesis of silver nanoparticles using plant leaf extracts. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 32:79–84
Sytar O, Cai Z, Brestic M, Kumar A, Prasad MNV, Taran N, Smetanska I (2013) Foliar applied nickel on buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) induced phenolic compounds as potential antioxidants. CLEAN Soil Air Water 41:1129–1137
Thwala M, Musee N, Sikhwivhilud L, Wepener V (2013) The oxidative toxicity of Ag and ZnO nanoparticles towards the aquatic plant Spirodela punctuta and the role of testing media parameters. Environ Sci Processes Impacts 15:1830
Tolaymat TM, El Badawy AM, Genaidy A, Scheckel KG, Luxton TP, Suidan M (2010) An evidence-based environmental perspective of manufactured silver nanoparticle in syntheses and applications: a systematic review and critical appraisal of peer reviewed scientific papers. Sci Total Environ 408(5):999–1006
Unrine JM, Colman BP, Bone AJ, Gondikas AP, Matson CW (2012) Biotic and abiotic interactions in aquatic microcosms determine fate and toxicity of Ag nanoparticles. Part 1. Aggregation and dissolution. Environ Sci Technol 46(13):6915–6924
Usha Rani P, Rajasekharreddy P (2011) Green synthesis of silver-protein (core–shell) nanoparticles using Piper betle L. leaf extract and its ecotoxicological studies on Daphnia magna. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 389(1):188–194
Yin LY, Cheng YW, Espinasse B, Colman BP, Auffan M, Wiesner M, Rose J, Liu J, Bernhardt ES (2011) More than the ions: the effects of silver nanoparticles on Lolium multiflorum. Environ Sci Technol 45:2360–2367
Yin L, Colman BP, McGill BM, Wright JP, Bernhardt ES (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on germination and early growth of eleven wetland plants. PLoS One 7(10):e47674
Zhao CM, Wang WX (2012) Size-dependent uptake of silver nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ Sci Technol 46(20):11345–11351
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. S. Chandrasekhar, Director, CSIR- Indian Institute of Chemical Technology, Hyderabad, India, for providing the facilities and Ministry of Environment and Forests, New Delhi for research grant to carry out the present research. One of the authors JY thanks CSIR, New Delhi, for Senior Research Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A Krolicka.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rani, P.U., Yasur, J., Loke, K.S. et al. Effect of synthetic and biosynthesized silver nanoparticles on growth, physiology and oxidative stress of water hyacinth: Eichhornia crassipes (Mart) Solms . Acta Physiol Plant 38, 58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2074-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-016-2074-1