Abstract
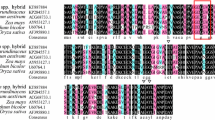
A full-length cDNA, SmPR10-1, encoding a pathogenesis-related class 10 protein, was isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza, a well-known Chinese herbal plant. From the coding region of nucleotide sequence, the amino acid sequence can be predicted which contained conserved domain (K–A–X–E–X–Y) in the C-terminal helix found in most members of the PR10 protein family. Phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that the SmPR10-1 protein showed a sequence similarity which was much higher to dicot proteins than to other PR10 proteins. Prokaryotic expression of SmPR10-1 protein in fusion with a His-tag produced a 22 kDa protein in E. coli BL21 (DE3), which exhibited ribonuclease activity in vitro. The purified protein was used to assay antifungal activity and the results showed SmPR10-1 only inhibited the growth of Phytophthora infestans. The RT-PCR results showed that the SmPR10-1 was expressed in high transcript level in leaves, stalks and low levels in roots. This protein seems to involve in the plant active defense response through activation of the methyl jasmonate signaling pathway rather than salicylic acid or abscisic acid pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adie BAT, Perez-Perez J, Perez-Perez MM et al (2007) ABA is an essential signal for plant resistance to pathogens affecting JA biosynthesis and the activation of defenses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:1665–1681
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Bari R, Jones J (2009) Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol Biol 69:473–488
Barratt DHP, Clark JA (1991) Proteins arising during the late stages of embryogenesis in Pisum sativum L. Planta 184:14–23
Breiteneder H, Pettenburger K, Bito A et al (1989) The gene coding for the major birch pollen allergen Betv1, is highly homologous to a pea disease resistance response gene. EMBO J 8:1935–1938
Bufe A, Spangfort MD, Kahlert H et al (1996) The major birch pollen allergen, Bet v 1, shows ribonuclease activity. Planta 199:413–415
Chadha P, Das RH (2006) A pathogenesis related protein, AhPR10 from peanut: an insight of its mode of antifungal activity. Planta 225:213–222
Cheng TO (2006) Danshen: a popular Chinese cardiac herbal drug. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:1499–1500
Crowell DN, John ME, Russell D, Amasino RM (1992) Characterization of a stress-induced, developmentally regulated gene family from soybean. Plant Mol Biol 18:459–466
Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nature Protocol 2:953–971
Fernandes H, Michalska K, Sikorski M, Jaskolski M (2013) Structural and functional aspects of PR-10 proteins. FEBS J 280:1169–1199
Flores T, Alape-Giron A, Flores-Diaz M, Flores HE (2002) Ocatin. A novel tuber storage protein from the andean tuber crop oca with antibacterial and antifungal activities. Plant Physiol 128:1291–1302
Gajhede M, Osmark P, Poulsen FM et al (1996) X-ray and NMR structure of Bet v 1, the origin of birch pollen allergy. Nat Struct Biol 3:1040–1045
Gao ZS, van de Weg WE, Schaart JG et al (2005) Genomic cloning and linkage mapping of the Mal d 1 (PR-10) gene family in apple (Malus domestica). Theor Appl Genet 111:171–183
Gao W, Hillwig ML, Huang L et al (2009) A functional genomics approach to tanshinone biosynthesis provides stereochemical insights. Org Lett 11:5170–5173
Ge XC, Wu JY (2005) Tanshinone production and isoprenoid pathways in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots induced by Ag+ and yeast elicitor. Plant Sci 168:487–491
Gómez-Gómez L, Rubio-Moraga A, Ahrazem O (2011) Molecular cloning and characterisation of a pathogenesis-related protein CsPR10 from Crocus sativus. Plant Biol 13:297–303
Guo J et al (2013) CYP76AH1 catalyzes turnover of miltiradiene in tanshinones biosynthesis and enables heterologous production of ferruginol in yeasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:12108–12113
Hashimoto M, Kisseleva L, Sawa S et al (2004) A novel rice PR10 protein, RSOsPR10, specifically induced in roots by biotic and abiotic stresses, possibly via the jasmonic acid signaling pathway. Plant Cell Physiol 45:550–559
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, Berkeley, pp 30–32
Hoffmann-Sommergruber K, Vanek-Krebitz M, Radauer C et al (1997) Genomic characterization of members of the Bet v 1 family: genes coding for allergens and pathogenesis-related proteins share intron positions. Gene 197:91–100
Jwa NS, Kumar Agrawal G, Rakwal R et al (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel Jasmonate inducible pathogenesis-related class 10 protein gene, JIOsPR10, from rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedling leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:973–983
Kim ST, Yu S, Kang YH et al (2008) The rice pathogen-related protein 10 (JIOsPR10) is induced by abiotic and biotic stresses and exhibits ribonuclease activity. Plant Cell Rep 27:593–603
Lee EJ, Facchini P (2010) Norcoclaurine synthase is a member of the pathogenesis-related 10/Bet v1 protein family. Plant Cell 22:3489–3503
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AK (2006) The family 10 of plant pathogenesis-related proteins: their structure, regulation, and function in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 68:3–13
Liu JJ, Ekramoddoullah AKM, Yu XS (2003) Differential expression of multiple PR10 proteins in western white pine following wounding, fungal infection and cold-hardening. Physiol Plant 119:544–553
Liu X, Huang B, Lin J et al (2006) A novel pathogenesis-related protein (SsPR10) from Solanum surattense with ribonucleolytic and antimicrobial activity is stress- and pathogen-inducible. J Plant Physiol 163:546–556
Ma Y, Yuan L, Wu B et al (2012) Genome-wide identification and characterization of novel genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Exp Bot 63:2809–2823
Markovic-Housley Z, Degano M, Lamba D et al (2003) Crystal structure of a hypoallergenic isoform of the major birch pollen allergen Bet v 1 and its likely biological function as a plant steroid carrier. J Mol Biol 325:123–133
Matton DP, Brisson N (1989) Cloning, expression, and sequence conservation of pathogenesis-related gene transcripts of potato. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 2:325–331
Midoh N, Iwata M (1996) Cloning and characterization of a probenazole-inducible gene for an intracellular pathogenesis-related protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 37:9–18
Park CJ, Kim KJ, Shin R et al (2004) Pathogenesis-related protein 10 isolated from hot pepper functions as a ribonuclease in an antiviral pathway. Plant J 37:186–198
Rost B, Yachdav G, Liu J (2004) The PredictProtein server. Nucl Acid Res 32:W321–W326
Schwede T, Kopp J, Guex N, Peitsch MC (2003) SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucl Acid Res 31:3381–3385
Sels J, Mathys J, De Coninck BM et al (2008) Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: a focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:941–950
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CM (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Walter MH, Liu JW, Wunn J, Hess D (1996) Bean ribonuclease-like pathogenesis-related protein genes (Ypr10) display complex patterns of developmental, dark-induced and exogenous-stimulus-dependent expression. Eur J Biochem 239:281–293
Warner SAJ, Scott R, Draper J (1992) Characterisation of a wound-induced transcript from the monocot asparagus that shares similarity with a class of intracellular pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins. Plant Mol Biol 19:555–561
Wenping H, Yuan Z, Jie S, Lijun Z, Zhezhi W (2011) De novo transcriptome sequencing in Salvia miltiorrhiza to identify genes involved in the biosynthesis of active ingredients. Genomics 98:272–279
Wilson CM (1975) Plant nucleases. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 26:187–208
Xie YR, Chen ZY, Brown RL, Bhatnagar D (2010) Expression and functional characterization of two pathogenesis-related protein 10 genes from Zea mays. J Plant Physiol 167:121–130
Yan Q, Shi M, Ng J, Wu HY (2006) Elicitor-induced rosmarinic acid accumulation and secondary metabolism enzyme activities in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Plant Sci 170:853–858
Zhou XJ, Lu S, Xu YH et al (2002) A cotton cDNA (GaPR-10) encoding a pathogenesis-related 10 protein with in vitro ribonuclease activity. Plant Sci 162:629–636
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81173490, 81130070) and Doctoral Research Fund of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. BSJJ2011-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by S. Abe.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Ma, Lg., Wang, Zs. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a pathogenesis-related protein SmPR10-1 from Salvia miltiorrhiza . Acta Physiol Plant 37, 205 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1959-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-015-1959-8