Abstract
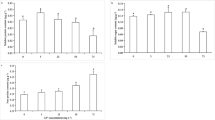
Pteris vittata is known as an arsenic hyperaccumulator, but there is little information about its tolerance to cadmium and on its ability to accumulate this heavy metal. Our aim was to analyse the accumulation capacity, oxidative stress and antioxidant response of this fern after cadmium treatments. Cadmium content, main markers of oxidative stress and antioxidant response were detected in leaves of plants grown in hydroponics for both short- (5 days) and long- (15 days) term exposure to 0 (control) 60 and 100 μM CdCl2. In leaves, the concentration of cadmium and oxidative stress were parallel with the increase of cadmium exposure. In the short-term exposure, antioxidant response was sufficient to contrast cadmium phytotoxicity only in 60 μM cadmium-treated plants. In the long-term exposure all treated plants, in spite of the increase in activity of some peroxide-scavenging enzymes, showed a significant increase in oxidative damage. As in the long-term stress markers were comparable in all treated plants, with no clear correlation with hydrogen peroxide content, at least part of cadmium-induced oxidative injury seems not mediated by H2O2. Based on our studies, P. vittata, able to uptake relatively high concentrations of cadmium, is only partially tolerant to this heavy metal.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Method Enzymol 105:121–125
Aghaz M, Bandehagh A, Aghazade E, Toorchi M, Ghassemi-Gholezani K (2013) Effects of cadmium stress on some growth and physiological characteristics in dill (Anethum graveolens) ecotypes. Int J Agric Res Rev 3:409–413
Arezki O, Boxus P, Kevrs C, Gaspar T (2001) Changes in peroxidase activity and level compounds during light-induced plantlet regeneration from Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn. nodes in vitro. Plant Growth Regul 33:215–219
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of proline for water stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Benavides MP, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2005) Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:21–34
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chaoui A, Mazhoudi S, Ghorbal MH, Ferjani EE (1997) Cadmium and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effect on antioxidant enzyme activities in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 127:139–147
Chen J, Shiyab S, Han FX, Monts DL, Waggoner CA, Yang Z, Su Y (2009) Bioaccumulation and physiological effects of mercury in Pteris vittata and Nephrolepis exaltata. Ecotoxicol 18:110–121
Dandekar AM, Uratsu SL (1988) A single base pair change in proline biosynthesis genes causes osmotic stress tolerance. J Bacteriol 170:5943–5945
De Vos CHR, Vooijs R, Schat H, Ernst WHO (1989) Copper-induced damage to the permeability barrier in roots of Silene cucubalus. J Plant Physiol 135:165–169
Drava G, Roccotiello E, Minganti V, Manfredi A, Cornara L (2012) Effects of cadmium and arsenic on Pteris vittata under hydroponic conditions. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:1375–1380
Ederli L, Reale L, Ferranti F, Pasqualini S (2004) Responces induced by high concentration of cadmium in Phragmites australis roots. Physiol Plant 121:66–74
Fayiga AO, Ma LQ, Cao X, Rathinasabapathi B (2004) Effects of heavy metals on growth and arsenic accumulation in the arsenic hyperaccumulator Pteris vittata L. Environ Pollut 132:289–296
Gallego SM, Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Iannone MF, Rosales EP, Zawoznik MS, Groppa MD, Benavides MP (2012) Unravelling cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: insight into regulatory mechanisms. Environ Exp Bot 83:33–46
Gossett DR, Millhollon EP, Lucas MC (1994) Antioxidant response to NaCl stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive cultivars of cotton. Crop Sci 34:706–714
Gupta M, Devi S (1994) Chronic toxicity of cadmium in Pteris vittata, a roadside fern. Ecotoxicol 3:235–247
Gupta M, Tripathi RD, Rai UN, Chandra P (1998) Role of glutathione and phytochelatin in Hydrilla verticillata (I.f.) Royle and Valusneria spiralis L. under mercury stress. Chemosphere 37:785–800
Gupta M, Cuypers A, Vangronsveld H, Clijsters H (1999) Copper affects the enzymes of the ascorbate-glutathione cycle and its related metabolites in the roots of Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol Plant 106:262–267
Hartley-Whitaker J, Ainsworth G, Vooijs R, Bookum WT, Schat H, Merag AA (2001) Phytochelatins are involved in differential arsenate tolerance in Holcus lanatus. Plant Physiol 126:299–306
Hassanzadeh M, Ebadi A, Panahyan-e-Kivi M, Eshghi AG, Jamaati-e-Somarin Sh, Saeidi M, Zabihi-e-Mahmoodabad R (2009) Evaluation of drought stress on relative water content and chlorophyll content of Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) genotypes at early flowering stage. Res J Environ Sci 3:345–350
Hossain MA, Hassanuzzaman M, Fujita M (2010) Up-regulation of antioxidant and glyoxalase systems by exogenous glycinebetaine and proline in mung bean confer tolerance to cadmium stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:259–272
Jana S, Choudhuri MA (1982) Glycolate metabolism of three submerged aquatic angiosperm during aging. Aquat Bot 12:345–354
Jócsák I, Villányi V, Rabnecz G, Droppa M (2008) Investigation of nickel stress induction in terms of metal accumulation and antioxidative enzyme activity in barley seedlings. Acta Biol Szeg 52:167–171
Kampfenkel K, Montagu MV, Inzé D (1995) Extraction and determination of ascorbate and dehydroascorbate from plant tissue. Anal Biochem 225:165–167
Kováčik J (2013) Hyperaccumulation of cadmium in Matricaria chamomilla: a never-ending story? Acta Physiol Plant 35:1721–1725
Lenher A, Bailly C, Flechel B, Poels P, Côme D, Corbineau F (2006) Changes in wheat seed germination ability, soluble carbohydrate and antioxidant enzymes activities in the embryo during the desiccation phase of maturation. J Cereal Sci 43:175–182
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Method Enzymol 148:350–382
Lux A, Martinka M, Vaculik M, White PJ (2011) Root responses to cadmium in the rhizosphere: a review. J Exp Bot 62:21–37
Ma LQ, Komar KM, Tu C, Zhang WH, Cai Y, Kenneley ED (2001) A fern that hyperaccumulates arsenic: a hardy versatile, fast growing plant helps to remove arsenic from contaminated soils. Nature 409:579
Mittler R (2002) Oxidative stress, antioxidants and stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 7:405–410
Munne-Bosch S, Alegre L (2000) Changes in carotenoids, toco-pherols and diterpenes during drought and recovery, and the biological significance of chlorophyll loss in Rosmarinus officinalis plants. Planta 210:925–931
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Navari-Izzo F, Meneguzzo S, Loggini B, Vazzana C, Sgherri CLM (1997) The role of the glutathione system during dehydration of Boea hygroscopica. Physiol Plant 99:23–30
Pál M, Horváth E, Janda T, Páldi E, Szalai G (2006) Physiological changes and defense mechanisms induced by cadmium stress in maize. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 169:239–246
Pickering IJ, Prince RC, George MJ, Smith RD, George GN, Salt DE (2000) Reduction and coordination of arsenic in Indian mustard. Plant Physiol 122:1171–1177
Rao MV, Beverley AH, Ormrod DP (1995) Amelioration of ozone-induced oxidative damage in wheat plants grown under high carbon dioxide. Role of antioxidant enzymes. Plant Physiol 109:421–432
Romero-Puertas MC, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Corpas FJ, Gómez M, del Rio LA, Sandalio LM (2004) Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2 − and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ 27:1122–1134
Rout NP, Shaw BP (2001) Salt tolerance in aquatic macrophytes: possible involvement of the antioxidative enzymes. Plant Sci 160:415–423
Sanità di Toppi L, Gabbrielli R (1999) Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ Exp Bot 41:105–130
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Smeets K, Cuypers A, Lambrechts A, Semane B, Hoet P, Van Laere A, Vangronsveld J (2005) Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidative mechanisms in Phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol Biochem 43:437–444
Smeets K, Opdenakker K, Remans T, Van Sanden S, Van Belleghem F, Semane B, Horemans N, Guisez Y, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2009) Oxidative stress-related responses at transcriptional and enzymatic levels after exposure to Cd or Cu in a multipollution context. J Plant Physiol 166:1982–1992
Somashenkaraiah BV, Padmaja K, Prasad ARK (1992) Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germination seedling of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorophyll degradation. Physiol Plant 85:85–89
Spanò C, Crosatti C, Pacchini R, Meletti P, Grilli I (2002) Ribonucleases during cold acclimation in winter and spring wheats. Plant Sci 162:809–815
Spanò C, Buselli R, Ruffini Castiglione M, Bottega S, Grilli I (2007) RNases and nucleases in embryos and endosperms from naturally aged wheat seeds stored in different conditions. J Plant Physiol 164:487–495
Spanò C, Bruno M, Bottega S (2013) Calystegia soldanella: dune versus laboratory plants to highlight key adaptive physiological traits. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1329–1336
Su Y, Han FX, Sridhar BBM, Monts DL (2005) Phytotoxicity and phytoaccumulation of trivalent and hexavalent chromium in brake fern. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2019–2026
Szabados L, Savouré A (2009) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
Turner NC (1981) Techniques and experimental approaches for the measurement of plant water status. Plant Soil 58:339–366
Wang Z, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Huang L (2008) Antioxidative response of metal-accumulator and non-accumulator plants under cadmium stress. Plant Soil 310:137–149
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080
Xiao X, Chen T, An Z, Lei M, Huang Z, Liao X, Liu Y (2008) Potential of Pteris vittata L. for phytoremediation of sites co-contaminated with cadmium and arsenic: the tolerance and accumulation. J Environ Sci 20:62–67
Yu L, Gao R, Shi Q, Wang X, Wei M, Yang F (2013) Exogenous application of sodium nitroprusside alleviated cadmium induced chlorosis, photosynthesis inhibition and oxidative stress in cucumber. Pak J Bot 45:813–819
Zhu YL, Pilon-Smits EAH, Tarun AS, Weber SU, Jouanin L, Terry N (1999) Cadmium tolerance and accumulation in Indian mustard is enhanced by overexpressing γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Plant Physiol 121:1169–1177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Kovacik.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balestri, M., Bottega, S. & Spanò, C. Response of Pteris vittata to different cadmium treatments. Acta Physiol Plant 36, 767–775 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1454-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-013-1454-z