Abstract
Objective
To observe the clinical effect and syndrome scores improvements of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion (HPM) and ginger-partitioned moxibustion (GPM) in treating ulcerative colitis (UC).
Methods
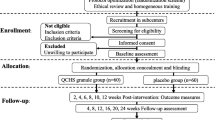
A total of 65 eligible cases were randomly divided into a HPM group (n=32) and a GPM group (n=33) according to their visiting order. Bilateral Tianshu (ST 25) and Dachangshu (BL 25) were selected for the HPM or the GPM treatment once daily, 12 d as a treatment course with a 3-day interval, 6 courses in all. The clinical effect, syndrome scale and Mayo scale were evaluated and compared between the two groups.
Results
Of the 65 cases enrolled, 2 cases dropped out in the HPM group and 3 cases dropped out in the GPM group, 30 cases of each group finished the treatment courses. The total effective rate is 93.3% in HPM group and 86.7% in the GPM group, there was no statistically significant difference in the total effective rate between the two groups (P>0.05); there were statistically significant differences between the two groups in score evaluation of lasting time of abdominal pain and frequency of diarrhea, HPM is prior to GPM (P=0.032, P=0.044). There are no statistical significant differences between the two groups in scores evaluation of general symptom, three main symptoms, quality of life (QOL), frequency and severity of abdominal pain, times, and pattern of diarrhea (all P>0.05). There was a statistical significant difference in the improvement of Mayo score between the two groups, and HPM was superior to GPM (P=0.048).
Conclusion
HPM and GPM are both promising ways to treat UC, and the total effect is quite similar. HPM is superior to GPM in the improvement of lasting time of abdominal pain and frequency of diarrhea, and also the Mayo score.
摘要
目的
观察隔药饼灸和隔姜灸治疗溃疡性结肠炎(ulcerative colitis, UC)的临床疗效和症状评分改善情况。
方法
将65 例慢性UC 患者随机分为隔药饼灸组(n=32)和隔姜灸组(n=33)。两组取相同穴位, 即双侧天枢和大肠俞, 分别采用隔药饼灸和隔姜灸治疗, 每天治疗1 次, 12 次为1 疗程, 疗程间休息3 d, 共治疗6 个疗程。观察并比较两组临床疗效、症状评分以及Mayo 评分改善状况。
结果
治疗过程中, 隔药饼灸组脱落2 例,隔姜灸组脱落3 例, 最终每组30 例纳入统计。治疗后, 隔药饼灸组总有效率为93.3%, 隔姜灸组总有效率为86.7%, 两组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。隔药饼灸组腹痛时间和腹泻频度改善情况均优于隔姜灸组(P=0.032, P=0.044)。治疗后, 总体症状评分, 主要症状评分, 生活质量改善, 腹痛频度、程度评分以及腹泻次数、性状评分比较, 组间差异均无统计学意义(均P>0.05)。隔药饼灸组患者Mayo 评分改善情况优于隔姜灸组(P=0.048)。
结论
隔药饼灸和隔姜灸均是治疗慢性UC 的有效方法, 两者总体疗效相当; 隔药饼灸在改善腹痛时间评分、腹泻频度评分和Mayo 评分方面优于隔姜灸组。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Branch of Gastroenterology of Chinese Medical Association. To standardize the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in China consensus opinion. Gastroenterology, 2007, 12(8): 488–495.
Ye Y, Pang Z, Chen WC, Ju SW, Zhou CL. The epidemiology and risk factors of inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(12): 22529–22542.
Zhang Q, Sha S, Xu B, Liang S, Wu K. Prevalence of colorectal cancer in patients with ulcerative colitis: A retrospective, multicenter study in China. J Cancer Res Ther, 2015, 11(4): 899–903.
Ashwin N. Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel diseases: a review. Dig Dis Sci, 2015, 60(2): 290–298.
Hua XG, Pan YY, Wu HG, Zhang LS, Zhang P. Observation on the effect of chronic nonspecific colitis by herbpartitioned moxibusiton. Modern Rehabilitation, 2000, 4(8): 1250–1251.
Wu HG, Gao ZW, Zhang L. Clinical and experimental research on the effect of chronic nonspecific colitis by herb-partitioned moxibusiton. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 1992, 12(1): 28–31.
Wu HG, Wang JH, Chen HP, Zhang LD, Shi Z. Effect of herb-partitioned moxibustion in treating chronic ulcerative colitis and research on the colonic mucosal immunology. JCAM, 1995, 11(8): 20–23.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Branch of Gastroenterology of Chinese Medical Association. To standardize the diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in China consensus opinion. Zhonghua Xiaohua Zazhi, 2007, 27(8): 545–550.
The spleen and stomach disease branch of Chinese Medical Association. Consensus of TCM diagnosis and treatment of ulcerative colitis. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi, 2010, 25(6): 891–895.
State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of Diagnosis and Therapeutic Effects of Diseases and Syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 132–134.
Schroeder KM, Tremaine WJ, Ilstrup DM. Coated oral 5-aminosalicylic acid therapy for mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis: a randomized study. N Eng J Med, 1987, 317(26): 1625–1629.
Zhou L, Lu XH. Health-related quality of life of inflammatory bowel disease. Zhonghua Neike Zazhi, 2004, 43(5): 392–394.
Wu HG. Moxibustion. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2016: 200.
Wu HG, Shi Z, Zhu Y, Ma XP, Yao Y, Cui YH, Zhao TP, Liu HR. Clinical research on the effect of chronic nonspecific colitis by herb-partitioned moxibusiton. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2007, 26(4): 3–4.
Shi Z, Wu HG, Wang JH, Chen HP, Zhang LS. Effect of moxibustion in treating chronic ulcerative colitis and research on the colonic mucosal immunology. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi, 2000, 8(21): 90–92.
Wu HG, Tan WL, Chen HP, Shi Z, Hua XG. Effect of moxibustion in treating chronic ulcerative colitis and research on the influence of the intestinal epithelial cells HLA-DR antigen. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 1999, 24(1): 12–16.
Sun TA, Ji J, Wu HG, Weng ZJ, Wu LY, Wang LD, Liu HR. Meta analysis for the treatment of ulcerative colitis by ginger-partitioned moxibusiton. 2014 Annual Conference of Clinical Chapter of China Association for Acupuncture and Moxibustion and the 21st National Acupuncture Clinical Academic Symposium Proceedings, 2014: 215–218.
Wei JZ, Shen XY, Ding GH, Zhao L. Analysis on the pathways and mechanism on warming regulation effect of material-partitioned moxibusiton. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2007, 27(5): 391–393.
Yang HY, Xiao YC. Determination on the radiation characteristics of the near infrared spectrum of material-partitioned moxibusiton. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2003, 22(9): 15–17.
Hong WX, Cai JH, Jing J. Research on the thermal radiation spectrum features of moxibustion. Yingyong Guangxue, 2004, 25(4): 1–3.
Zhao TP, Zhou S, Qin XD. Regulation on colonic mucosa sticky protein of UC rats of different moxibustion. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2010, 28(8): 1590–1594.
Zhang M, Liu ZZ, Yang JM. The research status of moxibustion. Zhongyiyao Xuebao, 2015, 43(1): 73–77.
Xu YQ, Shang XK. The 11 years of clinical and experimental researches on material-partitioned moxibustion. Liaoning Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2014, 11(3): 228–230.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhao, Jm., Guan, X. et al. Observation on the effects of different partitioned moxibustion in treating ulcerative colitis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 14, 231–241 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0931-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-016-0931-5
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Indirect Moxibustion
- Colitis
- Ulcerative
- Diarrhea
- Point
- Tianshu (ST 25)
- Point
- Dachangshu (BL 25)