Abstract
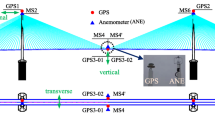
This paper addresses the problem of condition assessment of bridge expansion joints using long-term measurement data under changing environmental conditions. The effects of temperature, traffic loading and wind on the expansion joint displacements are analyzed and interpreted, which reveal that measured displacements are observed to increase with an increase in temperature and to decrease with increased traffic loading, while the correlation between displacement and wind speed is very weak. Two regression models are developed to simulate the varying displacements under the changes in temperature and traffic loadings. Based on these models, the effects of the environmental conditions are removed to obtain the normalized displacement. Statistical process control using mean value control charts is further used to detect damage to the bridge expansion joints. The results reveal that the proposed method had a good capability for detecting the damage-induced 1.0% variances of the annual changes in the expansion joint displacements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doebling S W, Farrar C R, Prime M B. A summary review of vibration-based damage identification methods. Shock and Vibration Digest, 1998, 30(2): 91–105
Ko J M, Ni Y Q. Technology developments in structural health monitoring of large-scale bridges. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(12): 1715–1725
Ni Y Q, Hua X G, Fan K Q, Ko J M. Correlating modal properties with temperature using long-term monitoring data and support vector machine technique. Engineering Structures, 2005, 27(12): 1762–1773
Ding Y L, Li A Q, Liu T. Environmental variability study on the measured responses of Runyang Cable-stayed Bridge using wavelet packet analysis. Science in China Series E: Technological Sciences, 2008, 51(5): 517–528
Abdel Wahab M, De Roeck G. Effect of temperature on dynamic system parameters of a highway bridge. Structural Engineering International, 1997, 7(4): 266–270
Cornwell P, Farrar C R, Doebling S W, Sohn H. Environmental variability of modal properties. Experimental Techniques, 1999, 23(6): 45–48
Sohn H, Dzwonczyk M, Straser E G, Kiremidjian A S, Law K H, Meng T. An experimental study of temperature effect on modal parameters of the Alamos Canyon Bridge. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 1999, 28(8): 879–897
Hua X G, Ni Y Q, Ko J M, Wong K Y. Modeling of temperaturefrequency correlation using combined principal component analysis and support vector regression technique. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2007, 21(2): 122–135
Ni Y Q, Hua X G, Wong K Y, Ko J M. Assessment of bridge expansion joints using long-term displacement and temperature measurement. Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities, 2007, 21(2): 143–151
Chen J, Xu Y L, Zhang R C. Modal parameters identification of Tsing Ma Suspension Bridge Under Typhoon Victor: EMD-HT method. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2004, 92(10): 805–827
Zhang Q W, Fan L C, Yuan W C. Traffic-induced variability in dynamic properties of cable-stayed bridge. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2002, 31(11): 2015–2021
Fuqate M L, Sohn H, Farrar C R. Vibration-based damage detection using statistical process control. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2001, 15(4): 707–721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y., Li, A. Assessment of bridge expansion joints using long-term displacement measurement under changing environmental conditions. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 5, 374–380 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-011-0122-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-011-0122-x