Abstract
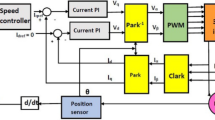
This paper investigates a Luenberger flux observer with speed adaptation for a direct field oriented control of an induction motor. An improved method of speed estimation that operates on the principle of speed adaptive flux and current observer has been proposed. An observer is basically an estimator that uses a plant model and a feedback loop with measured stator voltage and current. Simulation results show that the proposed direct field oriented control with the proposed observer provides good performance dynamic characteristics. The induction motor is fed by an indirect power electronics converter. This indirect converter is controlled by a sliding mode technique that enables minimization of harmonics introduced by the line converter, as well as the control of the power factor and DC-link voltage. The robustness of the overall system is studied using simulation for different operating modes and varied parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barut M, Bogosyan O S, Gokasan M. An extended Kalman filter based sensorless direct vector control of induction motors. In: IECON’03. 29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Roanoke, USA, 2003, 318–322
Sturtzer G, Smigiel E. Modeling and control of three phase motors: vector control of synchronous motors, numeric control by DSP controllers. Paris: Ellipses, 2000
Ouhrouche M, Lefebre A, Do X D. Application of an extended Kalman filter to rotor speed and resistance estimation in induction motor vector control. In: 1998 IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering. Waterloo, Canada, 1998, 297–300
Benchouia M T, Zouzou S E. A. Golea A, Ghamri A. Modeling and simulation of variable speed system with adaptive fuzzy controller application to PMSM. In: IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology ICIT, Hammamet, Tunisia, 2004, 683–687
Capolino G A, Goléa A, Hénao H. Modeling and simulation of variable speed control with sliding mode. In: Proceedings of International Conference on electromechanical regulation, Metz, France, 1992
Grabowski P Z, Kazmierkowski M P, Bose B K, Blaabjerg F. A simple direct-torque neuro-fuzzy control of PWM-inverterfedinduction motor drive. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2000, 47(4): 863–870
Benchabnae F, Titaouine A. Sensorless control strategy for permanent magnet synchronous motor fed by AC/DC/AC converter, In: IEEE International Conference on Electrical Machines ICEM. Rome, Italy, 2010, 1–6
Lin B R. High power factor AC/DC/AC converter with random PWM. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1999, 35(3): 935–943
Jezernik K. VSS control of unity power factor. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1999, 46(2): 325–332
He Y Y, Jiang W. A new variable structure controller for direct torque controlled interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drive, In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics. Jinan, China, 2007, 2349–2354
Benchabane F, Titaouine A, Bennis O. Systematic fuzzy sliding mode approach combined with extended Kalman filter for permanent magnet synchronous motor control. Mediterranean Journal of Measurement and Control, 2011, 7(1): 183–189
Zelechowski M, Kazmierkowski M P, Blaabjerg F. Controller design for direct torque controlled space vector modulated (DTCSVM) induction motor drives. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics. Dubrovnik, Croatia, 2005, 951–956
Oscar B, Altour G J, Maseda F J. A robust field oriented control of induction motor with flux observer and speed adaptation. In: Proceedings of ETFA 2003 IEEE Conference. Lisbon, Portugal, 2003, 245–252
Montanari M, Peresada S M, Rossi C, Tilli A. Speed sensorless control of induction motors based on reduced-order adaptive observer. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2007, 15(6): 1049–1064
Yahia K, Zouzou S E, Benchabane F. Indirect vector control of induction motor with on line rotor resistance identification. Asian Journal of Information Technology, 2006, 5(12): 1410–1415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benchabane, F., Titaouine, A., Bennis, O. et al. Direct field oriented control scheme for space vector modulated AC/DC/AC converter fed induction motor. Front. Energy 6, 129–137 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-012-0183-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-012-0183-0