Abstract
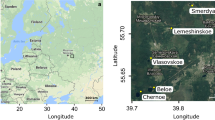
The middle Yangtze Reach is one of the most developed regions of China. As a result, most lakes in this area have suffered from eutrophication and serious environmental pollution during recent decades. The aquatic biodiversity in the lakes of the area is thus currently under significant threat from continuous human activities. Testate amoebae (TA) are benthic (rarely planktonic) microorganisms characterized by an agglutinated or autogenous shell. Owing to their high abundance, preservation potential in lacustrine sediments, and distinct response to environmental stress, they are increasingly used as indicators for monitoring water quality and reconstructing palaeoenvironmental changes. However this approach has not yet been developed in China. This study presents an initial assessment of benthic TA assemblages in eight lakes of Lake Donghu in the region of Wuhan, China. Testate amoeba community structure was most strongly correlated to water pH. In more alkaline conditions, communities were dominated by Centropyxis aculeata, Difflugia oblonga, Pontigulasia compressa, Pon. elisa and Lesquereusia modesta. These results are consistent with previous studies and show that TA could be useful for reconstructing past water pH fluctuations in China. To achieve this, the next step will be to expand the database and build transfer function models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bobrov A, Mazei Y, Chernyshov V, Gong Y, Feng W (2012). Testate amoebae communities from some freshwater and soil habitats in China (Hubei and Shandong Provinces). Front Earth Sci, 6(1): 1–9
Bobrov A A, Charman D J, Warner B G (1999). Ecology of testate amoebae (Protozoa: Rhizopoda) on peatlands in western Russia with special attention to niche separation in closely related taxa. Protist, 150(2): 125–136
Dalby A P, Kumar A, Moore J M, Patterson R T (2000). Preliminary survey of arcellaceans (Thecamoebians) as limnological indicators in tropical lake Sentani, Irian Java, Indonesia. J Foraminiferal Res, 30(2): 135–142
Escobar J, Brenner M, Whitmore T J, Kenney W F, Curtis J H (2008). Ecology of testate amoebae (thecamoebians) in subtropical Florida lakes. J Paleolimnol, 40(2): 715–731
Gu Y, Li X, Qiu H, Huang J, Xie S, Ruan X, Zhou X (2008). Sediments records of eutrophication history in the Donghu Lake, Wuhan, over the past 100 years. Ecol Environ, 17: 35–40 (in Chinese)
Gu Y, Wang H, Huang X, Peng H, Huang J (2012). Phytolith records of the climate change since the past 15000 years in the middle reach of the Yangtze River in China. Front Earth Sci, 6(1): 10–17
Hu Y, Qi S, Wu C, Ke Y, Chen J, Chen W, Gong X (2012). Preliminary assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments from Honghu Lake, East Central China. Front Earth Sci, 6(1): 39–47
Jiang J G, Wu S G, Shen Y F (2007). Effects of seasonal succession and water pollution on the protozoan community structure in an eutrophic lake. Chemosphere, 66(3): 523–532
Kowalewska G (2005). Algal pigments in sediments as a measure of eutrophication in the Baltic environment. Quat Int, 130(1): 141–151
Kumar A, Patterson R T (2000). Arcellaceans (thecamoebians): new tools for monitoring long- and short-term changes in lake bottom acidity. Environ Geolo, 39(6): 689–697
Legendre P, Gallagher E D (2001). Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia, 129(2): 271–280
Liu Z, Liu Q, Du Y, Wang Z (2006). Characteristics of heavy elements in sediments of Lake Donghu (Wuhan) and relations to urban pollution. J Lake Sci, 18: 79–85 (in Chinese)
Margalef R (1972). Homage to Evelyn Hutchinson, or why is there an upper limit to diversity. Trans Conn Acad Arts Sci, 44: 211–235
Mazei Yu, Tsyganov A (2006). Freshwater Testate Amoebae. Moscow: KMK Science Press (in Russia)
Medioli F S, Scott D B (1988). Lacustrine thecamoebians (mainly Arcellaceans) as potential tools for paleolimnological interpretations. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 62(1–4): 361–386
Meisterfeld R (2002). Order Arcellinida Kent, 1880. In: Lee J J, Leedale G F, Bradbury P, eds. An Illustrated Guide to the Protozoa. Lawrence Kansas: Allen Press
Meng C, Zhao B (2008). Vertical distributions of species of nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediments of Donghu Lake. Environ Sci, 29: 1831–1837
Mitchell E A D, Charman D J, Warner B G (2008). Testate amoebae analysis in ecological and paleoecological studies of wetlands: past, present and future. Biodivers Conserv, 17(9): 2115–2137
Ogden C G (1983). Observations on the systematics of the genus Difflugia in Britain (Rhizopoda, Protozoa). Bull Br Mus Nat Hist (Zool), 44: 1–73
Ogden C G, Hedley R H (1980). An Atlas of Freshwater Testate Amoebae. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Olson D M, Dinerstein E (1998). The global 200: a representation approach to conserving the Earth’s most biologically valuable ecoregions. Conserv Biol, 12(3): 502–515
Patterson R T, Dalby A, Kumar A, Henderson L A, Boudreau R E A (2002). Arcellaceans (thecamoebians) as indicators of land-use change: settlement history of the Swan Lake area, Ontario as a case study. J Paleolimnol, 28(3): 297–316
Patterson R T, Kumar A (2000). Assessment of arcellacea (thecamoebian) assemblages, species and strains as contaminant indicators in variably contaminated James Lake, north eastern Ontario. J Foraminiferal Res, 30: 310–320
Payne R, Mitchell E A D (2009). How many is enough? Determining optimal count totals for ecological and palaeoecological studies of testate amoebae. J Paleolimnol, 42(4): 483–495
Qin Y, Booth R K, Gu Y, Wang Y, Xie S (2009). Testate amoebae as indicators of 20th century environmental change in Lake Zhangdu, China. Fundam Appl Limnol, 175(1): 29–38
Qin Y, Payne R, Gu Y, Huang X, Wang H (2012). Ecology of testate amoebae in Dajiuhu peatland of Shennongjia Mountains, China, in relation to hydrology. Front Earth Sci, 6(1): 57–65
Qin Y, Xie S, Smith H G, Swindles G T, Gu Y (2011). Diversity, distribution and biogeography of testate amoebae in China: implications for ecological studies in Asia. Eur J Protistol, 47(1): 1–9
Qin Y, Xie S, Swindles G T, Gu Y S, Zhou X G (2008a). Pentagonia zhangduensis nov. spec. (Lobosea, Arcellinida), a new freshwater species from China. Eur J Protistol, 44(4): 287–290
Qin Z, Fan T, Wu Q, Zhou X (2008b). Analysis of “Red Tide” in East Lake and trend of development. Environ Sci Technol, 31: 93–95 (in Chinese)
R Development Core Team (2010). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria
Reinhardt E G, Dalby A P, Kumar A, Patterson R T (1998). Arcellaceans as pollution indicators in mine tailing contaminated lakes near Cobalt, Ontario, Canada. Micropaleontol, 44(2): 131–148
Roe H M, Patterson R T (2006). Distribution of thecamoebians (testate amoebae) in small lakes and ponds, Barbados, West Indies. J Foraminiferal Res, 36(2): 116–134
Roe H M, Patterson R T, Swindles G T (2010). Controls on the contemporary distribution of lake thecamoebians (testate amoebae) within the Greater Toronto Area and their potential as water quality indicators. J Paleolimnol, 43(4): 955–975
Scott D B, Medioli F S (1983). Agglutinated Rhizopods in Lake Erie: modern distribution and stratigraphic implications. J Paleontol, 57: 809–820
Shannon C E, Weaver W (1949). The Mathematical Theory of Communication. Urbana: University of Illinois Press
Wall A, Gilbert D, Magny M, Mitchell E A D (2010). Testate amoeba analysis of lake sediments: impact of filter size and total count on estimates of density, species richness and assemblage structure. J Paleolimnol, 43: 689–704
Wang Q, Wang H, Cui Y (2010). Community characteristics of the macrozoobenthos and bioassessment of water quality in Lake Donghu Distinct, Wuhan. Acta Hydrobiol Sin, 34(4): 739–746 (in Chinese)
Xie P, Huang X F, Takamura N (2000). Changes of Leptodora kindti. abundance (1957–1996) in a planktivorous fishes dominated subtropical Chinese lake (Lake Donghu). Arch Hydrobiol, 147: 351–372
Xu M, Cao H, Xie P, Deng D, Feng W, Xu J (2005). Use of PFU protozoan community structural and functional characteristics in assessment of water quality in a large, highly polluted freshwater lake in China. J Environ Monit, 7(7): 670–674
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Fournier, B., Lara, E. et al. Relationships between testate amoeba communities and water quality in Lake Donghu, a large alkaline lake in Wuhan, China. Front. Earth Sci. 7, 182–190 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0352-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-013-0352-4