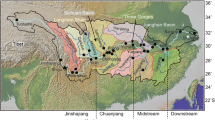
Abstract
New Nd and Sr isotope data are presented in this paper for sediments from the Yellow and Yangtze River drainage basins. The average 143Nd/144Nd isotope compositions of fine-grained sediments from two drainage basins seem similar. The T NdDM ages of sediments from the two drainage basins are relatively uniform but exhibit subtle differences. This reflects the different underlying bedrocks, in association with the unique tectonic terranes that comprise central and southeastern China, including the North China Block, the Yangtze Block, the South China Block, the Tibet Plateau and the Qinling-Dabie Orogenic Belt. In contrast, there is an obvious difference in the 87Sr/86Sr ratios between fine-grained sediments of the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, which actually reflects an increase in chemical weathering intensity from northwestern to southeastern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg G, Jacks G, Hamilton P J (1989). Weathering rates and 87Sr/86Sr ratios: An isotopic approach. J Hydrology, 109: 65–78
Asahara Y (1999). 87Sr/86Sr variation in north Pacific sediments: a record of the Milankovitch cycle in the past 3 million years. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 171: 453–464
Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al (1995). Asian continental nature of 87Sr/86Sr ratios in north Central Pacific sediments. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 133: 105–116
Asahara Y, Tanaka T, Kamioka H, et al (1999). Provenance of the north Pacific sediments and process of source material transport as derived from Rb-Sr isotopic systematics. Chem Geol, 158: 271–291
Blum J D, Erel Y, Brown K (1994). 87Sr/86Sr ratios of Nevada stream waters: implications for relative mineral weathering rates. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 58: 5019–5025
Brass G W (1975). The effect of weathering on the distribution of strontium isotopes in weathering profile. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 39: 1647–1653
Chen N S, Han Y J, You Z D, et al (1991). Rb-Sr isotopic and zircon 207Pb-206Pb constraints on the age of formation of bulk complex in the core of eastern Qinling Belt, western Henan province and its implications for crustal evolution. Geochimica, 20: 219–227 (in Chinese)
Chen S H (1991). Emplacement ages and evolution of several ultrabasic rock belts on the northern margin of the North China Platform. Geochimica, 20: 128–133 (in Chinese)
Faure G (1986). Principles of Isotope Geology. New York: Wiley, 141–153
Goldstein S J, Jacobsen S B (1987). The Nd and Sr isotopic systematics of river-water dissolved material: Implications for the sources of Nd and Sr in seawater. Chem Geol, 66: 245–272
Goldstein S J, Jacobsen S B (1988). Nd and Sr isotopic systematics of river water suspended material: implications for crustal evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 87: 249–265
Goldstein S L, O’Nions R K, Hamilton P, et al (1984). A Sm-Nd isotopic study of atmospheric dusts and particulates from major river systems. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 70: 221–236
Graustein W C, Armstrong R L (1983). The use of Strontium-87/Strontium-86 ratios to measure atomospheric transport into forested watersheds. Science, 219: 289–292
Hodell D A, Mead G A, Mueller P A (1990). Variation in the strontium isotopic compositions of sea water (8 Ma to present): Implications for chemical weathering rates and dissolved fluxes to the oceans. Chem Geol, 80: 291–307
Huang X (1989). Study of sources of Paleozoic granitoids and the basement of South China by means of Nd-Sr isotope. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1: 28–36 (in Chinese)
Krishnaswami S, Trivedi J R, Sarin M M, et al (1992). Strontium isotopes and rubidium in the Ganga-brahmaputra river system: Weathering in the Himalaya, fluxes to the Bay of Bengal and contributions to the evolution of oceanic 87Sr/86Sr. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 109: 243–253
Li S G, Ge N J, Liu D L, et al (1989). Sm-Nd isotopic model ages of C-type eclogite collected from Dabie group, northern Dabie Mountain and their tectonic significances. Chinese Sci Bull, 34: 522–525 (in Chinese)
Li S G, Hart S R, Zheng S G, et al (1989). Time of collision between North China Block and South China Block: Evidences of Sm-Nd isotopic age. Science in China (B), 19: 312–319 (in Chinese)
Li X H, Zhao Z H, Gui X T, et al (1991). Sm-Nd isotopic and zircon U-Pb constraints on the age of formation of the Precambrian crust in Southeast China. Geochimica, 20: 255–262 (in Chinese)
Liu C Q, Masuda A, Okada A, et al (1993). A geochemical study of loess and desert sand in northern China: Implications for continental crust weathering and composition. Chem Geol, 106: 359–374
Liu C Q, Masuda A, Okada A, et al (1994). Isotope geochemistry of Quaternary deposits from the arid lands in northern China. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 127: 25–38
Liu D Y, Nutman A P, Compston W, et al (1992). Remants of ⩾ 3800 Ma crust in the Chinese part of the Sino-Korean craton. Geology, 20: 339–342
Liu D Y, Shen Q H, Zhang Z Q, et al (1990). Archean crustal evolution in China: U-Pb geochronology of Qianxi Complex. Precambrian Res, 48: 223–244
Mao J W, Zhang Z Q, Dong B L (1990). A new Sm-Nd isotopic chronology of Sibao Group in Southern margin of Yangtze massif. Geol Review, 36: 264–268 (in Chinese)
Ottesen R T, Bogen J, Bolviken B, et al (1989). Overbank sediment: a representative sample medium for regional geochemical mapping. J Geochem Explor, 32: 257–277
Palmer M R, Edmond J M (1992). Controls over the strontium isotope composition of river water. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 56: 2099–2111
Wadleigh M A, Veizer J, Brooks C (1985). Strontium and its istopes in Canadian rivers: Fluxes and Global implication. Geochim Cosomochim Acta, 49: 1727–1736
Wang W X (1993). Study of affecting factors on acidity of rainfall in China. Environmental Science in China, 13: 404–407 (in Chinese)
Xie X J, Yin B C (1993). Geochemical patterns from local to global. J Geochem Explor, 47: 109–129
Yang S Y, Jiang S Y, Ling H F, et al (2007). Sr and Nd isotopic compositions of sediments from the rivers of Changjiang drainage area and their implication for tracing sources of marine sediments. Science in China (D), 37(5): 682–690
Zhang Z Q, Liu D Y, Fu GM(1994). Isotope Chronology of Meta-Stratum in Northern Qinling. Beijing: Geology Press, 55–65
Zhang Z Q, Ye X J (1987). Mass-spectrometric isotope dilution analysis of REE and precise measurement of 143Nd/144Nd ratios. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 8: 108–126
Zhu J C, Shen W Z, Liu C S, et al (1990). Nd-Sr isotopic characteristics and genetic discussion of Mesozoic granitoids of syntexis series in South China. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 9: 97–105 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Liu, Y., Shi, X. et al. Nd and Sr isotopic compositions of sediments from the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers: Implications for partitioning tectonic terranes and crust weathering of the Central and Southeast China. Front. Earth Sci. China 2, 418–426 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-008-0054-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-008-0054-5