Abstract
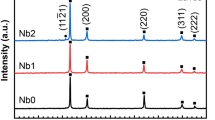
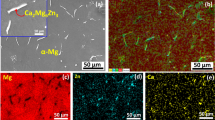
The samples made of a Mg-2.5wt.%Zn-0.5wt.%Zr alloy were immersed in the 20% hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution at room temperature for different time, with the aim of improving the properties of magnesium (Mg) alloy in applications as biomaterials. The corrosion resistance and in vitro biocompatibility of untreated and fluoride-coated samples were investigated. The results show that the optimum process is to immerse Mg alloys in the 20% HF solution for 6 h. After the immersion, a dense magnesium fluoride (MgF2) coating of 0.5 μm was synthesized on the surface of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy. Polarization tests recorded a reduction in the corrosion current density from 2.10 to 0.05 μA/cm2 due to the MgF2 protective coating. Immersion tests in the simulated body fluid (SBF) also reveal a much milder corrosion on the fluoride-coated samples, and its corrosion rate was calculated to be 0.05 mm/yr. Hemolysis test suggests that the conversion coated Mg alloy has no obvious hemolysis reaction. The hemolysis ratio (HR) of the samples decreases from 11.34% to 1.86% with the HF treatment, which meets the requirements of biomaterials (HR < 5%). The coculture of 3T3 fibroblasts with Mg alloy results in the adhesion and proliferation of cells on the surface of fluoride-coated samples. All the results show that the MgF2 conversion coating would markedly improve the corrosion resistance and in vitro biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li L C, Gao J C, Wang Y. Corrosion behaviors and surface modification of magnesium alloys for biomaterial applications. Materials Review, 2003, 17(10): 29–32
Song G L. Control of biodegradation of biocompatible magnesium alloys. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(4): 1696–1701
Gurrappa I. Corrosion and its importance in selection of materials for biomedical applications. Corrosion Prevention Control, 2001, 48(1): 23–27
El-Rahman S S A. Neuropathology of aluminum toxicity in rats (glutamate and GABA impairment). Pharmacological Research, 2003, 47(3): 189–194
Zhang Y, Tao H R, He Y H, et al. Cytotoxicity and hemolytic properties of biodegradable Mg-Zn alloy. Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2008, 12(41): 8162–8166
Hawkeq D, Albright D L. Phosphate permanganate conversion coating for magnesium. Metal Finishing, 1995, 93(10): 4–9
Li L C, Gao J C, Wang Y. Evaluation of cyto-toxicity and corrosion behavior of alkali-heat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2004, 185(1): 92–98
Chiu K Y, Wong M H, Cheng F T, et al. Characterization and corrosion studies of fluoride conversion coating on degradable Mg implants. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2007, 202(3): 590–598
Kokubo T, Takadama H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials, 2006, 27(15): 2907–2915
Yang X F, Xi T F. Progress in the studies on the evaluation of biocompatibility of biomaterials. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2001, 18(1): 123–128 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, XY., Chen, MF., You, C. et al. The influence of HF treatment on corrosion resistance and in vitro biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy. Front. Mater. Sci. China 4, 132–138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-010-0025-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11706-010-0025-0