Abstract
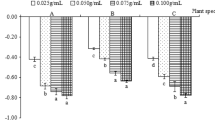
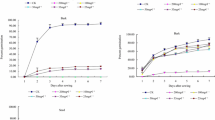
The allelopathic influence of aqueous extracts of Thymus kotschyanus on Bromus tomentellus and Trifolium repens germination (%), germination speed, and seedling growth (length, fresh and dry weight) was examined. It was noted that aqueous extracts had a considerable inhibitory effect on target plant germination, and the effect at 50%, 75%, and 100% concentration was found to be significantly higher than that at lower concentrations (5% and 25%) and control treatment (distilled water). Seedling length in addition to fresh and dry weights was also reduced significantly over control. The inhibitory effect was increased as the extract concentration was increased. B. tomentellus showed a higher sensitivity against T. kotschyanus in allelopathic effects compared to T. repens, which indicates that B. tomentellus planted in rangelands with leaf litter of T. kotschyanus will be adversely affected in terms of its germination, growth, and ultimately low forage production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avers C J, Goodwin R H (1956). Studies on roots IV. Effects of coumarin and scopoletin on the standard root growth pattern of Phleum pratens. Am J Bot, 43(8): 612–620
Bewley J D, Black M (1978). Physiology and Biochemistry of Seeds in Relation to Germination. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1:128–130
Bhawmik P C, Doll J D (1982). Corn and soybean response to allelopathic effects of weed and crop residues. Agron J, 74: 601–606
Black M (1989). Seed research-past, present and future. In: Taylorson R B, ed. Recent Advances in the Development and Germination of Seeds. New York: Plenum, 1–6
Chon S U, Nelson C J, Coutts J H, (2004). Osmotic and autotoxic effects of leaf extracts on germination and seedling growth of alfalfa. Agron J, 96: 1673–1679
Chon S U, Jang H G, Kim D K, Kim Y M, Boo H O, Kim Y J (2005). Allelopathic potential in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) plants. J Scie Hort, 106(3): 309–317
Escudero A, Albert M J, Pita J M, Pérez-García F (2000). Inhibitory effects of Artemisia herba-alba on the germination of the gypsophyte Helianthemum squamatum. Plant Ecol, 148(1): 71–80
Friedman J (1995). Allelopathy, autotoxicity, and germination. In: Kigel J, Galili G, eds. Seed Development and Germination. New York: Marcel Dekker. Inc, 599–628
Kpoviessi D S, Gdaguid F, Gbenou J D, Accrombessi J D, Haddad M, Moudachiou M, Quetin-leclerrco J (2006). Allelopathic effects on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp) plant and cytotoxic activities of sterols and triterpene isolated from Justicia anselliana (NEES) T. Anders. J Nat Subs, 1: 12–19
Maguire J D (1962). Speed of germination—Aid in selection and evaluation for seedling emergence and vigor. Crop Sci, 2: 176–177
Molisch H (1937). Der Einfluss einer Pflanze auf die andere-Allelopathie, Fischer. Jena, Germany (in German)
Putnam A R, Weston L A (1986). Adverse impacts of allelopathy in agricultural system. In: Putnam, A R, Tang S C, eds. The Science of Allelopathy. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc, 235–239
Rezaei M, Khajeddin S J (2008). Allelopathic effects of Onobrychis on Scariola orientalis and Agropyron elongatum. Iranian J Rangeland, 4: 386–400
Rice E L (1984). Allelopathy. 2nd ed. New York: Academic Press
Roa V S (2000). Principles of Weed Science. Enfield, NH: Science Publisher, Inc
Rustaiyan A, Lajevardi T, Rabbani M, Yari M, Masoudi S (1999). Chemical constituents of the essential oil of Thymus kotschyanus Boiss & Hohen from Iran. J Daru, 7(4): 27–28
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Safari, H., Tavili, A. & Saberi, M. Allelopathic effects of Thymus kotschyanus on seed germination and initial growth of Bromus tomentellus and Trifolium repens . Front. Agric. China 4, 475–480 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-010-1030-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-010-1030-x