Abstract
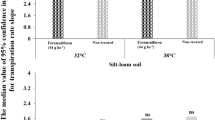
The practices with low clippings production to save time, money, or landfill space, were favored by turf managers. Understanding the responses of Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) to Trinexapac-ethyl (TE) would facilitate recommendations regarding its safe and effective use in Northern China. The objectives of this study are (1) to investigate the effects of TE on vertical growth, clipping yield, leaf width, and chlorophyll content of Kentucky bluegrass, and (2) to compare the seasonal application impacts of TE. Both spring and autumn experiment results demonstrated that Trinexapac-ethyl applied to Kentucky bluegrass, suppressed the vertical grass growth and significantly reduced the Kentucky bluegrass clippings production within a few weeks after initial treatment. Applied trinexapac-ethyl enhanced Kentucky bluegrass leaf width in both spring and autumn experimental periods. Discoloration on leaf tips was observed and lasted for four weeks when the same TE rate of 0.191 mL$m-2 was applied in early autumn. Darker leaves with higher chlorophyll content compared with non-TE-treatments appeared after the initial four weeks of the treatment in autumn and the treatment for the entire spring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R, Kerber E, Pfister K, Weiler E W (1992). Studies on the action of the new growth retardant CGA 163’935 (Primo). In: Karssen C M, Van Loon L C, Vreugdenhil D, eds. Progress in Plant Growth Regulation. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 818–827
Burpee L L, Green D E, Stephens S L (1996). Interactive effects of plant growth regulators and fungicides on epidemics of dollar spot in creeping bentgrass. Plant Dis, 80(11): 1245–1250
Daniels RW, Sugden S K (1996). Opportunities for growth regulation of amenity grass. Pestic Sci, 47: 363–369
Ervin E H, Koski A J (1998). Growth responses of Lolium perenne L. to trinexapac-ethyl. Hort Sci, 33: 1200–1202
Fagerness M J, Yelverton F H (2000). Tissue production and quality of Tifway bermudagrass as affected by seasonal application patterns of trinexapac-ethyl. Crop Sci, 40: 493–497
Goatley JMJr, Maddox V L, Watkins RM (1996). Growth regulation of bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum Fluegge) with imazaquin and AC 263, 222. Hort Sci, 31: 396–399
Johnson B J (1993). Response of tall fescue to plant growth regulators and mowing frequencies. J Environ Hortic, 11(4): 163–167
Li G Y (2006). Study on influence of applying plant growth retardants on growth of turfgrass. Dissertation for the Master Degree. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 50–51 (in Chinese)
Li S Q, Lei T W, Yan W H, Qu L Q, Xiao J (2006). Effects of mowed heights on the water consumption of turf grasses in Beijing. Agricultural Engineering, 22(11): 74–78 (in Chinese)
Qian Y L, Engelke M C, Foster M J V, Reynolds S (1998). Trinexapacethyl restricts shoot growth and improves quality of ‘Diamond’ zoysiagrass under shade. Hort Sci, 33: 1019–1022
Watschke T L, Di Paola J M (1995). Plant growth regulators. Golf Course Manage, 63: 59–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, G., Bian, X., Li, H. et al. Growth responses of Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis L.) to trinexapac-ethyl applied in spring and autumn. Front. Agric. China 3, 186–189 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0038-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11703-009-0038-6