Abstract
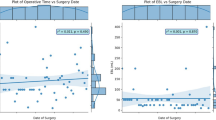
The Intuitive Surgical DaVinci SP (“Single Port”) robotic platform was approved in 2014, but, recently, there has been a dissemination of the technology with multiple urological procedures successfully adapted to this robot. There are some important differences from prior models. We aimed to share our early outcomes and lessons learned for performing successful single-port robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy (SP-RAPN). This study is a retrospective review of sequential SP-RAPN cases between 7/2019 and 3/2020. We extracted patient characteristics and early surgical outcomes. Surgical tips and tricks were recorded during these cases and compiled. SP-RAPN was successfully completed in 12 patients. Patients mean age was 57.8 ± 11.0 years and median ASA score was 2. Mean tumor size was 3.1 ± 2.2 cm. The average OR Time was 172 ± 41 min and EBL was 68 ± 75 mL. All cases had warm ischemia time < 25 min. Tumor pathology included 8 RCC (6 pT1a, 1 pT1b, 1 pT2a), 2 AML, and 2 oncocytoma. There were no complications. Our top surgical tips involved: (1) patient positioning, (2) port placement, (3) insufflation, (4) air docking, (5) assistant port placement, (6) dynamic arm control, (7) hilar clamping, (8) camera relocation, (9) tumor excision, and (10) extraction and port closure. SP-RAPN is safe and feasible in this series. There are advantages and disadvantages to this platform. As the technology matures and techniques evolve, SP-RAPN may become more appealing. Future studies should focus on long-term outcomes and cost-effectiveness of the SP system.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parekh DJ, Reis IM, Castle EP, Gonzalgo ML, Woods ME, Svatek RS, Weizer AZ, Konety BR, Tollefson M, Krupski TL, Smith ND, Shabsigh A, Barocas DA, Quek ML, Dash A, Kibel AS, Shemanski L, Pruthi RS, Montgomery JS, Weight CJ, Sharp DS, Chang SS, Cookson MS, Gupta GN, Gorbonos A, Uchio EM, Skinner E, Venkatramani V, Soodana-Prakash N, Kendrick K, Smith JA Jr, Thompson IM (2018) Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 391(10139):2525–2536. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30996-6
Peyronnet B, Seisen T, Oger E, Vaessen C, Grassano Y, Benoit T, Carrouget J, Pradère B, Khene Z, Giwerc A, Mathieu R, Beauval JB, Nouhaud FX, Bigot P, Doumerc N, Bernhard JC, Mejean A, Patard JJ, Shariat S, Roupret M, Bensalah K (2016) Comparison of 1800 robotic and open partial nephrectomies for renal tumors. Ann Surg Oncol 23(13):4277–4283. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5411-0
Kaouk JH, Haber GP, Goel RK, Desai MM, Aron M, Rackley RR, Moore C, Gill IS (2008) Single-port laparoscopic surgery in urology: initial experience. Urology 71(1):3–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.11.034
Spana G, Rane A, Kaouk JH (2011) Is robotics the future of laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS)? BJU Int 108(6b):1018–1023. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10513.x
Administration FaD (2018) 510(k) Summary: SP1098 da Vinci SP Surgical System, pp 1–13
Kaouk J, Garisto J, Eltemamy M, Bertolo R (2019) Pure single-site robot-assisted partial nephrectomy using the SP surgical system: initial clinical experience. Urology 124:282–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.11.024
Kaouk J, Bertolo R, Eltemamy M, Garisto J (2019) Single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: first clinical experience using the SP surgical system. Urology 124:309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2018.10.025
Dobbs RW, Halgrimson WR, Madueke I, Vigneswaran HT, Wilson JO, Crivellaro S (2019) Single-port robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: initial experience and technique with the da Vinci(®) SP platform. BJU Int 124(6):1022–1027. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.14864
Kutikov A, Uzzo RG (2009) The R.E.N.A.L. nephrometry score: a comprehensive standardized system for quantitating renal tumor size, location and depth. J Urol 182(3):844–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.05.035
Maurice MJ, Ramirez D, Kaouk JH (2017) Robotic laparoendoscopic single-site retroperitioneal renal surgery: initial investigation of a purpose-built single-port surgical system. Eur Urol 71(4):643–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.005
Fang AM, Saidian A, Magi-Galluzzi C, Nix JW, Rais-Bahrami S (2020) Single-port robotic partial and radical nephrectomies for renal cortical tumors: initial clinical experience. J Robot Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01053-y
Funding
This study was not funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by DS and AS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DS and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Devki Shukla, Alexander Small, Reza Mehrazin, and Michael Palese declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted retrospectively from data obtained for clinical purposes. We consulted with the IRB of Mount Sinai who determined our study did not need ethical approval. An IRB official waiver of ethical approval was granted from the Mount Sinai Institutional Review Board. This study was performed in its entirety at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai with no outside support.
Consent to participate
Consent to participate given the retrospective design of this article and reporting of de-identified data, this study was approved for consent exemption under IRB approval
Consent for publication
Consent for publication given the retrospective design of this article and reporting of de-identified data, this study was approved for consent exemption under IRB approval
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, D., Small, A., Mehrazin, R. et al. Single-port robotic-assisted partial nephrectomy: initial clinical experience and lessons learned for successful outcomes. J Robotic Surg 15, 293–298 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01106-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-020-01106-2