Abstract
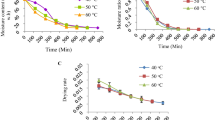
Improving the accessibility of bioactive compounds enriched ripen graviola fruit (Annona muricata) by the application of post-harvest processing technology would overcome their climatic barriers and be used as a folk medicine. Therefore, hot air drying technique was applied at various temperatures (40 °C, 50 °C and 60 °C) to evaluate the nutritional efficiency of the medicinal fruit. Drying characteristics of the ripen graviola fruit were determined, and predictive capability of artificial neural network and eight semiempirical models was evaluated. The Weibull model gave satisfactory results over the other models. Levenberg–Marquardt’s algorithm along with LOGSIGMIOD transfer function, predicted the moisture content and moisture ratio with better accuracy. Interestingly, the R2 value of ANN was 0.9999, which was significantly more than that of the semiempirical model. Moisture diffusivity and mass transfer coefficient increased to 4.73 × 10−6m2/s and 2.386 × 10−6 m/s, respectively, as the temperature rose. Activation energy proved the conservative requirement of energy and was obtained as 24.659 kJ/mol. Radical scavenging activity (IC 50), polyphenol and flavonoid content were found to be maximum at 60 °C, and the values were 933.975 µg/ml, 7.088 mg GAE/g, 18.42 mg QE/g, respectively. Fruits dried at 60 °C showed lower moisture content (8% d.b), lower drying time, higher drying rate, better physico-chemical properties and sustainable colour value. Therefore, drying at 60 °C was recommended for commercialization in various nutraceutical applications and biotechnology aspects.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apriyanto DR, Aoki-Utsubo C, Hartati S, Dewi BE, Hotta H (2018) Potential of Indonesian plants (Annona muricata, Garcinia latissima, and Garcinia celebica) against hepatitis C virus. Adv Sci Lett 24:6807–6810. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2018.12850
Ashtiani SHM, Rafiee M, Morad MM, Khojastehpour M, Khani M, Rohani A, Martynenko A (2020) Impact of gliding arc plasma pretreatment on drying efficiency and physicochemical properties of grape. Innov Food Sci & Emerg Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2020.102381
Ashtiani SM, Salarikia A, Golzarian MR (2017) Analyzing drying characteristics and modeling of thin layers of peppermint leaves under hot-air and infrared treatments. Inf Process Agric 4(2):128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2017.03.001
Bi Y-X, Zielinska S, Ni J-B, Li X-X, Xue X-F, Tian W-L, Peng W-J, Fang X-M (2022) Effect of hot air drying temperature on drying characteristics and color deterioration of rape bee pollen. Food Chem 16:100464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100464
Chikpah SK, Korese JK, Sturam B, Hensel O (2022) Colour change kinetics of pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) slices during convective air drying and bioactive compounds of the dried products. J Agric Food Res 10:100409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100409
Coria-Tellez AV, Montalvo-Gonzalez E, Yahia EM, Obledo-vazquez EN (2018) Annona muricata : a comprehensive review on its traditional medicinal uses, phytochemicals and pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action and toxicity. Arebian J Chem 11(5):662–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.01.004
Crank J (1975) The mathematics of diffusion. Clarendon press, Oxford, UK
Darvishi H, Farhudi Z, Behroozi-Khazaei N (2016) Mass transfer parameters and modeling of hot air drying kinetics of dill leaves. Chem Prod Process Model 21(2):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1515/cppm-2015-0079
Darvishi H, Mohammadi P, Azadbakht M, Farhudi Z (2018) Effect of different drying conditions on the mass transfer characteristics of kiwi slices. J Agric Sci Technol 20:249–264
De Medeiros FGM, Machado IP, Dantas TNP, Dantas SCM, de Alsina OLS, de Medeiros MFD (2021) Spouted bed drying of fruit pulps: a case study on drying of graviola (Annona muricata) pulp. In: Delgado J, Barbosa de Lima A (eds) Transport processes and separation technologies. Advanced structured materials, vol 133. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-47856-8_5
Dincer I (1998) Moisture transfer analysis during drying of slabwoods. Heat Mass Transf 34(4):317–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002310050265
Dincer I, Hussain MM (2004) Development of new biot number and log factor correlation for drying applications. Int J Heat Mass Transf 47:653–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2003.08.006
Donne ML, Lentini M, Alibrandi A, Salimbeni V, Giuffre G, Mazzeo F (2017) Antiviral activity of ellagic acid and Annona muricata in cervical HPV related pre-neoplastic lesions: a randomized trial. J Funct Foods 35:549–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2017.06.006
Doymaz I (2007) The kinetics of forced convective air drying of pumpkin slices. J Food Eng 79:243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.01.049
Doymaz I (2017) Drying kinetics, rehydration and colour characteristics of convective hot—air drying of carrot slices. Heat Mass Transf 53:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-016-1791-8
Erbay Z, Icier I (2010) A review of thin layer drying of foods: theory, modeling, and experimental results. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 50:441–464. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390802437063
Esparza-Martínez FJ, Miranda-López R, Mata-Sánchez SM, Guzmán-Maldonado SH (2016) Extractable and non-extractable phenolics and antioxidant capacity of mandarin waste dried at different temperatures. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 71(3):294–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-016-0559-0
Falade KO, Shogaolu OT (2010) Effect of pretreatment on air- drying pattern and color of dried pumpkin (Cucurbita maxima) slices. J Food Process Eng 33:1129–1147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-4530.2008.00330.x
Gavamukulya Y, Wamunyokoli F, El-Shemy HA (2017) Annona muricata: is the natural therapy to most disease conditions including cancer growing in our backyard? A systematic review of its research history and future prospects. Asian Pac J Trop Med 10:835–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtm.2017.08.009
Guclu SF, Oncu Z, Koyuncu F (2020) Pollen performance modeling with an artificial neural network on commercial stone fruit. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 61(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00208-7
Guine RPF, Barroca MJ, Goncalves FJ, Alves M, Oliveira S, Mendes M (2015) Artificial neural network modeling of the antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of bananas submitted to different drying treatments. Food Chem 168:454–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.094
Jafari AM, Ganje M, Dehnad D, Ghanbari V (2016) Mathematical, fuzzy logic and artificial neural network modeling techniques to predict drying kinetics of onion. J Food Process Preserv 40(2):329–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.12610
Kipcak AS (2017) Microwave drying kinetics of mussels (Mytilus edulis). Res Chem Intermed 43(3):1429–1445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-016-2707-4
Koraqi H, Petkoska AT, Khalid W, Sehrish A, Ambreen S, Lorenzo JM (2023) Optimization of the extraction conditions of antioxidant phenolic compounds from strawberry fruits (Fragaria x ananassan Duch.) using response surface methodology. Food Anal Methods. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-023-02469-6
Kosasih EA, Zikri A, Dzaky MI (2020) Effects of drying temperature, airflow, and cut segment on drying rate and activation energy of elephant cassava. Case Stud Therm Eng 19:100633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2020.100633
Kumar D, Tarafdar A, Kumar Y, Badgujar PC (2019) Intelligent modeling and detailed analysis of drying, hydration, thermal, and spectral characteristics for convective drying of chicken breast slices. J Food Process Eng 42(5):e13087. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13087
Kuttigounder D, Limgamallu JR, Bhattacharya S (2011) Turmeric powder and starch: selected physical, physicochemical and microstructural properties. J Food Sci 76:C1284–C1291. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02403.x
Lopes AP, Galuch MB, Petenuci ME, Oliveira JH, Canesin EA, Schneider VVA, Visentainer JV (2020) Quantification of phenolic compounds in ripe and unripe bitter melons (Momordica charantia) and evaluation of the distribution of phenolic compounds in different parts of the fruit by UPLC–MS/MS. Chem Pap 74:2613–2625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01094-5
Marquez CJ, Villacorta V, Yepes D, Ciro H, Cartagena J (2012) Physiological and physic-chemical characterization of the soursop. Journal Revistafacultadnacional De Agronomiamedellin 65:6477–6486
Maskan A, Kaya S, Maskan M (2002) Hot air and sun drying of grape leather (pestil). J Food Eng 54:81–88. https://doi.org/10.12691/jfnr-4-11-4
Miraei Ashtiani SH, Rohani A, Aghkhani MH (2020) Soft computing-based method for estimation of almond kernel mass from its shell features. Scientia Hortic 262:109071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.109071
Movagharnejad K, Nikzad M (2007) Modeling of tomato drying using artificial neural network. Comput Electron Agric 59:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2007.05.003
Ndukwu MC, Dirioha C, Abam FI, Ihediwa VE (2017) Heat and mass transfer parameters in the drying of cocoyamslice. Case Studies Therm Eng 9:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2016.12.003
Neta MTSL, De Jesus MS, Da Silva JLA, Araujo HCS, Sandes RDD, Shanmugam S, Narain N (2018) Effect of spray drying on bioactive and volatile compounds in soursop (Annona muricata) fruit pulp. Food Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.09.039
Ni JB, Zhang JS, Bhandari B, Xiao HW, Ding CJ, Peng WJ, Fang XM (2022) Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) plasma on the drying kinetics, color, phenolic compounds, energy consumption and microstructure of lotus pollen. Dry Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2022.2048306
Nugraha AS, Damayanti YD, Wangchuk P, Keller PA (2019) Anti infective and anti cancer properties of the annona species: their ethnomedicinal uses, alkaloid diversity and pharmacological activities. Molecules 24(23):4419. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24234419
Onwude DI, Hashim N, Janius RB, Nawi NM, Abdan K (2016) Modeling the thin layer drying of fruits and vegetables: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 15:599–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12196
Radhai M, Arivuchudar R (2020) Confirmation and nutritional evaluation of gummy candy complemented with Annona muricata. Biosci Biotech Res Comm 13(2):616–619. https://doi.org/10.21786/bbrc/13.2/38
Rahman A, Harunsani MH, Tan AL, Ahmed N, Khan MM (2021) Antioxidant and antibacterial studies of phytogenic fabricated ZnO using aqueous leaf extract of Ziziphus mauritiana Lam. Chem Pap 75:3295–3308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01553-7
Rodriguez J, Clemente G, Sanjuaan N, Bon J (2014) Modeling drying kinetics of thyme (Thymus vulgaris L): theoretical and empirical models and neural networks. Food Sci Technol Int 20:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1082013212469614
Sergio G, Irigoyen RMT, Cicuttin S, Fiorentini C (2010) The variable nature of biot numbers in food drying. J Food Eng 101:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.07.005
Siddiqui Y, Munusamy U, Naidu Y, Ahmad K (2020) Integrated effect of plant growth-promoting compost and npk fertilizer on nutrient uptake, phenolic content, and antioxidant properties of Orthosiphon stamineus and Cosmos caudatus. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 61:1051–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-020-00277-z
Steel RGD, Torrie JH (1960) Principles and procedures of statistics. McGraw-Hill, New York. https://doi.org/10.1002/bimj.19620040313
Tarafdar A, Jothi N, Kaur BP (2021) Mathematical and artificial neural network modeling for vacuum dying kinetics of Moringa olifera leaves followed by determination of energy consumption and mass transfer parameters. J Appl Res Med Aromat Plants 24:100306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jarmap.2021.100306
Tiencheu B, Claudia Egbe A, Achidi AU, Ngongang EFT, Tenyang N, Tonfack Djikeng F, Tatsinkou Fossi B (2021) Effect of oven and sun drying on the chemical properties, lipid profile of soursop (Annona muricata) seed oil, and the functional properties of the defatted flour. Food Sci Nutr 9(8):4156–4168. https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2380
Tran NYT, Nhan NPT, Thanh VT, Nguyen DV, Thinh PV, Vy TA, Truc TT (2020). Effects of drying conditions on total phenolic content and other parameters of soursop jelly (Annona muricata L.).In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering. vol 736(2), p 022064. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/736/2/022064
Van de Venter M, Pruissen M, Koekemoer T, Sowemimo A, Govender S (2014) In vitro anti-HIV and-TB activities of Annona muricata and Artemisia afra extracts. Planta Med 80(16):P1L29. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1394687
Vega-Galvez A, Lemus-Mondaca R, Billbao-Sainz C, Fito A, Andres P (2008) Effect of air drying temperature on the quality of rehydrated dried red bell pepper (var.Lamuyo). J Food Eng 85:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.06.032
Vu ND, Tran NTY, Le TD, Phan NTM, Doan PLA, Huynh LB, Dao PT (2022) Kinetic model of moisture loss and polyphenol degradation during heat pump drying of soursop fruit (Annona muricata L). Processes 10:2082. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10102082
Wang CT, Cao JC, Jiang WB (2016) Effect of the drying method on browning of flesh, antioxidant compounds and antioxidant capacity of Chinese jujube (Zizyphus jujube Mill.) fruit. Curr Top Nutraceut R 14(2):161–170
Wang Z, Sun J, Liao X, Chen F, Zhao G, Wu J, Hu X (2006) Mathematical modeling on hot air drying of thin layer apple pomace. Food Res Int 40:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2006.07.017
Winardiantika V, Lee YH, Park NI, Yeoung YR (2015) Effect of cultivar and harvest time on the contents of antioxidant phytochemicals in strawberry fruits. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 56(6):732–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-015-0052-y
Xiao HW, Pang CL, Wang LH, Bai JW, Yang WX, Gao ZJ (2010) Drying kinetics and quality of Monukka seedless grapes dried in an air-impingement jet dryer. Biosys Eng 105(2):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.11.001
Zhou B, Jin Z, Schwarz PB, Li Y (2021) Effect of grinding and extraction conditions on the determination of antioxidant activity and phenolic acids in barley. Food Meas 15:3823–3836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-00964-0
Zhu A, Shen X (2014) The model and mass transfer characteristics of convection drying of peach slices. Int J Heat Mass Transf 72:45–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.01.001
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the Bannari Amman Institute of Technology for providing laboratory facilities and raw material availability for the research experiment and also thankful to Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Research, Training and Human Development Institute, Pune, India, for fellowship to the first author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JSM had done experimental work, data analysis and manuscript writing; KR given experimental design idea; RB supervised the work and manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mahesh, J.S., Ramalakshmi, K. & Balakrishnaraja, R. Investigation of mass transfer parameters, phytochemical analysis of dried ripen graviola fruit (Annona muricata) and its comparative approach by using statistical tools: ANN and mathematical modelling. Chem. Pap. 77, 7085–7098 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03000-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-03000-1