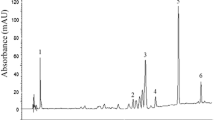
Abstract
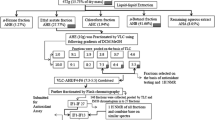
Research on natural anti-oxidant agents increased due to their wide range of applications on various diseases. HPTLC-DPPH is the novel technique where anti-oxidant potential of complex herbal extract can be detected on TLC plate. In thin-layer chromatography, silica gel plates (60 F-254) were used as a stationary phase along with THF/Toluene/Acetic Acid/Water [16:8:2:1 (v/v)] as a mobile phase. Cytochrome P-450 inhibitors were predicted by in-silico method as anti-oxidant agent. HPTLC method development and validation were performed on CAMAG HPTLC system along with quantitative estimation of epigallocatechin in hydroalcoholic extract of Acacia suma. HPTLC method had ensured no change in RF value (0.944) at wavelength 269 nm and revealed presence of epigallocatechin in Acacia suma is 404.2 mg/g. Yellow coloured bands on TLC plate were observed with DPPH reagent to confirm radical scavenging property. The in vitro DPPH radical scavenging assay, hydrogen peroxide assay, nitric oxide assay, total anti-oxidant assay and lipid peroxidation assay were performed, and IC50 values are 81.46 ± 2.72, 61.39 ± 1.85, 21.30 ± 2.26, 55.13 ± 2.86 and 77.03 ± 2.47 µg/ml, respectively. Additionally, in-silico data predicted ‘Diinsininol’ as cytochrome P450 inhibitor with docking score -13.51 kcal/mol. The study findings evident that hydroalcoholic extract of Acacia suma had significant anti-oxidant potential which was confirmed by in vitro assays, molecular docking study and HPTLC-DPPH anti-oxidant approaches.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alegaon SG, Alagawadi Kumar KavalapureRanadeJalalpure UVKRDRSSDSS (2021) Synthesis, molecular docking and adme studies of thiazole-thiazolidinedione hybrids as antimicrobial agents. J Biomol Struct Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2021.1880479
Anouhe JB, Niamké FB, Faustin M, Virieux D, Pirat JL, Adima AA, Kati-Coulibaly S, Amusant N (2018) The role of extractives in the natural durability of the heartwood of dicorynia guianensis amsh: new insights in antioxydant and antifungal properties. Ann for Sci 75(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13595-018-0691-0
Ayurvedic Pharmacopoeia of India. New Delhi, Government of India Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Department of AYUSH; 5:89–91
Baranowska M, Suliborska K, Todorovic V, Kusznierewicz B, Chrzanowski W, Sobajic S, Bartoszek A (2020) Interactions between bioactive components determine anti-oxidant, cytotoxic and nutrigenomic activity of cocoa powder extract. Free Radic Biol Med 154:48–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.04.022
Barteková M, Adameová A, Görbe A, Ferenczyová K, Pecháňová O, Lazou A, Dhalla NS et al (2021) Natural and synthetic anti-oxidants targeting cardiac oxidative stress and redox signaling in cardiometabolic diseases. Free Radic Biol Med 169:446–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.045
Bhole RP, Shinde SS, Chitlange SS, Wankhede SB (2015) A High-performance thin layer chromatography (hptlc) method for simultaneous determination of diphenhydramine hydrochloride and naproxen sodium in tablets. Chem. Insights, Anal. https://doi.org/10.4137/ACI.S31506
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset CL (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate anti-oxidant activity. Lwt-Food Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0023-6438(95)80008-5
Cadenas E, Davies KJ (2000) Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic Biol Med 29(3–4):222–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00317-8
Chang ST, Wu JH, Wang SY, Kang PL, Yang NS, Shyur LF (2001) Anti-oxidant activity of extracts from acacia confusa bark and heartwood. J Agric Food Chem 49(7):3420–3424. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0100907
Cieśla Ł, Staszek D, Kowalska T, Waksmundzka-Hajnos M (2013) The use of TLC-DPPH• test with image processing to study direct anti-oxidant activity of phenolic acid fractions of selected lamiaceae family species. J AOAC Int 96(6):1228–1232. https://doi.org/10.5740/jaoacint.sgeciesla
Cota D, Mishra S, Shengule S (2019) Terminalia Arjuna hydroalcoholic extract ameliorates trinitrobenzenes ulphonic acid induced colitis mediated through inhibition of inflammation, oxidative stress and improvement in structure of gut microbiota. J Ethnopharmacol 230:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.10.020
Dadoriya P, Dey Y, Sharma D, Yadav M, Wanjari MM, Gaidhani SN, Subhose V (2020) In-vitro anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activity of an ayurvedic formulation–Trayodashang guggulu. J Herb Med 23:100366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100366
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42717
Fernández-Sánchez A, Madrigal-Santillán E, Bautista M, Esquivel-Soto J, Morales-González A, Esquivel-Chirino C et al (2011) Inflammation, oxidative stress, and obesity. Int J Mol Sci 12(5):3117–3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12053117
Flensted-Jensen M, Gram M, Dela F, Helge JW, Larsen S (2021) Six weeks of high intensity cycle training reduces h2o2 emission and increases anti-oxidant protein levels in obese adults with risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Free Radic Biol Med 173:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.07.020
Grace SC (2005) Phenolics as anti-oxidants. Anti-Oxid React Oxyg Species Plants. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470988565
Gülçin İ, Huyut Z, Elmastaş M, Aboul-Enein HY (2010) Radical scavenging and anti-oxidant activity of tannic acid. Arab J Chem 3(1):43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2009.12.008
Habu JB, Ibeh BO (2015) In vitro anti-oxidant capacity and free radical scavenging evaluation of active metabolite constituents of newbouldia laevis ethanolic leaf extract. Biol Res 48(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0007-x
Halliwell B, Aeschbach R, L¨oliger J, Aruoma OI (1995) The characterization of anti-oxidants. FTC 33(7):601–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(95)00024-v
Hema NS, Shivamurthy MV, Karunakar P (2021) Novel simultaneous identification of capsaicin and it’s quantification in transferosome formulation By HP-TLC technique. Curr Pharm Anal 17(1):172–183. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573412916666200128121032
Hurkadale PJ, Nandanwadkar SM, Bidikar CM, Patil RN, Hegde HV (2021) High-performance thin-layer chromatographic method development and determination of bio-enhancer from piper trichostachyon: an ethnomedicinal plant. JPC-J Planar Chrom 34(4):329–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00764-021-00113-9
Islam MK, Sostaric T, Lim LY, Hammer K, Locher C (2021) Anti-oxidant HPTLC-DPPH fingerprinting of honeys and tracking of anti-oxidant constituents upon thermal exposure. Foods 10(2):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020357
Kanbarkar N, Mishra S, Khanal P (2020) Beneficial effect of phospholipase a2 group iia inhibitors from acacia suma in obesity: an in silico and in vitro study. Adv Tradit Med 20(4):599–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00456-4
Kanbarkar N, Mishra S (2021) Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors identified from camellia sinensis for COVID-19 prophylaxis: an in silico approach. Adv Tradit Med 21(1):173–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-020-00508-9
Kanbarkar N, Mishra S, Dodmani S, Kurangi B (2022) Simultaneous estimation of epigallocatechin, fisetin, and quercetin in acacia suma and its potential against postprandial hyperglycemia. Int J Ayurvedic Med 13(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.47552/ijam.v13i1.2361
Khanal P, Patil BM (2020) In vitro and in silico anti-oxidant, cytotoxicity and biological activities of ficus benghalensis and duranta repens. Chin Herb Med 12(4):406–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chmed.2020.02.004
Marseglia L, Manti S, D’Angelo G, Nicotera A, Parisi E, Di Rosa G, Gitto E, Arrigo T (2015) Oxidative stress in obesity: a critical component in human diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):378–400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010378
Moon HS, Lee HG, Choi YJ, Kim TG, Cho CS (2007) Proposed mechanisms of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate for anti-obesity. Chem Biol Interact 167(2):85–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2007.02.008
Muthukumaran P, Saraswathy N, Aswitha V, Balan R, Gokhul VB, Indumathi P, Yuvapriya S (2016) Assessment of total phenolic, flavonoid, tannin content and phytochemical screening of leaf and flower extracts from peltophorum pterocarpum (DC.) backer ex K.heyne: a comparative study. Pharmacogn J 8(2):140–143. https://doi.org/10.5530/pj.2016.2
Nandanwadkar SM, Hurkadale PJ, Bidikar CM, Godbole MM (2021) Multielemental analysis and in vitro evaluation of free radical scavenging activity of natural phytopigments by ICP-OES and HPTLC. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.620996
Olatidoye OP (2019) Total anti-oxidant potential of some selected beverages consumed in lagos state, Nigeria. ECNU 14:261–272
Pandian BA, Sathishraj R, Djanaguiraman M, Prasad PV, Jugulam M (2020) Role of cytochrome p450 enzymes in plant stress response. Anti-Oxidants 9(5):454. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9050454
Ruch RJ, Cheng SJ, Klaunig JE (1989) Prevention of cytotoxicity and inhibition of intercellular communication by anti-oxidant catechins isolated from chinese green tea. Carcinogenesis 10(6):1003–1008. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/10.6.1003
Saeed N, Khan MR, Shabbir M (2012) Anti-oxidant activity, total phenolic and total flavonoid contents of whole plant extracts torilis leptophylla L. BMC Complement Altern Med 12(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-12-221
Schieber M, Chandel NS (2014) ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol 24(10):R453–R462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.03.034
Selenski C, Pettus TR (2006) (±)-Diinsininone: made nature’s way. Tetrahedron 62:5298–5307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2006.01.109
Sowndhararajan K, Joseph J M, Manian S (2013) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of indian acacias acacia. Int J Food Prope 16(8):1717–1729. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2011.604895
Stohs SJ, Bagchi D (2015) Anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and chemoprotective properties of acacia catechu heartwood extracts. Phytother Res 29(6):818–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5335
Upadhyay R, Chaurasia JK, Tiwari KN, Singh K (2013) Comparative anti-oxidant study of stem and stem induced callus of phyllanthus fraternus webster—an important antiviral and hepatoprotective plant. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 171(8):2153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0487-5
Upadhyay R, Chaurasia JK, Tiwari KN, Singh K (2014) Anti-oxidant property of aerial parts and root of phyllanthus fraternus webster, an important medicinal plant. World J, Sci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/692392
Vaidyaratnam PS, Varier’s, (1994) Indian medicinal plants arya vaidhya sala. Kottakkal 1:30–31
Wang J, Yue YD, Tang F, Sun J (2012) TLC screening for anti-oxidant activity of extracts from fifteen bamboo species and identification of anti-oxidant flavone glycosides from leaves of bambusa textilis McClure. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171012297
Yıldırım A, Mavi A, Oktay M, Kara AA, Algur ÖF, Bilaloǧlu V (2000) Comparison of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of tilia (tilia argentea desf ex Dc), sage (salvia triloba L.),and black tea (camellia sinensis) extracts. J Agric Food Chem 48(10):5030–5034. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf000590k
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Late Dr. Sanjay Mishra for his suggestions in refining this draft. Authors are also thankful to the director of Analytical laboratory at KAHER’s BSRC, Belagavi 590010, Karnataka, India for providing facilities to complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NK, SM, SN contributed to conceptualization. NK contributed to writing. SM, SN, SA contributed to review. NK, SN contributed to data analysis. NK, SM contributed to additional works. All authors agreed position and publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanbarkar, N., Mishra, S., Nandanwadkar, S. et al. Assessment of anti-oxidant activity and quantification of epigallocatechin in Acacia suma heartwood by HPTLC-DPPH fingerprinting method. Chem. Pap. 76, 5865–5878 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02295-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02295-w