Abstract
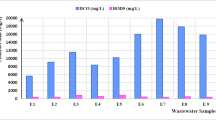
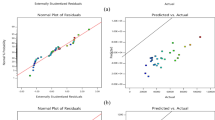
The effectiveness of using complex salt–Luffa cylindrica seed extract (CS-LCSE) in a coagulation/flocculation (CF) method for the treatment of textile wastewater was investigated. Jar test procedure was used at different pH (2–10), dosage (1000–1800 mg/L) and stirring time (10–30 min). The optimum condition for the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) and color/total suspended solids (CTSS) from textile wastewater was determined. Response surface methodology (RSM), artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) models were used to predict COD and CTSS removal efficiencies from textile wastewater under different conditions. The adequacy and predictive relevance of the three optimization methods were assessed using regression coefficient (R2), and mean square error (MSE). ANFIS (R2 0.9997, MSE 0.0002643), ANN (R2 0.9955, MSE 0.0845014) and RSM (R2 0.9474, MSE 1.049412) are the model indicators for CTSS removal, while for COD removal, the indicators are: ANFIS (R2 0.9996, MSE 0.0038472), ANN (R2 0.9885, MSE 0.0160658) and RSM (R2 0.9731, MSE 0.9083140). The suitability of ANFIS models over ANN and RSM in predicting COD and CTSS removal efficiency is demonstrated by the results obtained.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Adj R 2 :
-
Adjusted coefficient of determination
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- ANFIS:
-
Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system
- BBD:
-
Box–Behnken design
- BOD:
-
Biochemical oxygen demand
- CF:
-
Coagulation/flocculation
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- CS:
-
Complex salt
- CTSS:
-
Color/total suspended solids
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- LCS:
-
Luffa cylindrica seed
- LCSE:
-
Luffa cylindrica seed extract
- MSE:
-
Mean square error
- R 2 :
-
Coefficient of determination
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TSK:
-
Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy
- TW:
-
Textile wastewater
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Adegbite AJ, Afolabi O, Ogunji JM (2017) Effect of two extractants on the chemical composition of the defatted seed of Luffa cylindrica. Int J Innov Sci Eng Technol 4(7):356–368
Abitogun AS, Ashogbon AO, Polytechnic RG, State O (2010) Nutritional assessment and chemical composition of raw and defatted Luffa cylindrica seed flour. Ethnobot Leaflets 14:225–235
Adesina OA, Abdulkareem F, Yusuff AS, Lala M, Okewale A (2019) Response surface methodology approach to optimization of process parameter for coagulation process of surface water using Moringa oleifera seed. S Afr J Chem Eng 28:46–51
Adewuyi A, Vargas F (2017) Underutilized Luffa cylindrica sponge: a local bio-adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) pollutant from water system. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci 6(2):118–126
Ahmad R, Haseeb S (2015) Competitive adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ on Luffa acutangula modified Tetraethoxysilane (LAP-TS) from the aqueous solution: thermodynamic and isotherm studies. Groundw Sustain Dev 1(1–2):146–154
Al-sameraiy M (2017) A new approach using coagulation rate constant for evaluation of turbidity removal. Appl Water Sci 7(3):1439–1448
Anadebe VC, Onukwuli OD, Abeng FE, Okafor NA, Ezeugo JO, Okoye CC (2020) Electrochemical-kinetics, MD-simulation and multi-input single-output (MISO) modeling using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) prediction for dexamethasone drug as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in 2 M HCl electrolyte. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 115:251–265
Anastopoulos I, Pashalidis I (2020) Environmental applications of Luffa cylindrica-based adsorbents. J Mol Liq 319:114127
Ani JU, Nnaji NJN, Onukwuli OD, Okoye COB (2012) Nephelometric and functional parameters response of coagulation for the purification of industrial wastewater using Detarium microcarpum. J Hazard Mater 243:59–66
Aniagor CO, Menkiti MC (2018) Kinetics and mechanistic description of adsorptive uptake of crystal violet dye by lignified elephant grass complexed isolate. J Environ Chem Eng 6(2):2105–2118
AOAC (2005) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemist, Gaitherburg
AWWA, APHA, WEF (2012) Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater, 22 edn, New York
Badawi AK, Zaher K (2021) Hybrid treatment system for real textile wastewater remediation based on coagulation/flocculation, adsorption and filtration processes: performance and economic evaluation. J Water Process Eng 40:101963
Baharlouei A, Jalilnejad E, Sirousazar M (2018) Fixed-bed column performance of methylene blue biosorption by Luffa cylindrica: statistical and mathematical modeling. Chem Eng Commun 205(11):1537–1554
Betiku E, Ishola NB (2020) Optimization of sorrel oil biodiesel production by base heterogeneous catalyst from kola nut pod husk: neural intelligence-genetic algorithm versus neuro-fuzzy-genetic algorithm. Environ Prog Sustain Energy. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13393
Bruno P, Campo R, Giustra MG, De Marchis M, Di Bella G (2020) Bench scale continuous coagulation-flocculation of saline industrial wastewater contaminated by hydrocarbons. J Water Process Eng 34:101156
Chamoli S (2015) ANN and RSM approach for modeling and optimization of designing parameters for a V down perforated baffle roughened rectangular channel. Alex Eng J 54(3):429–446
Dal Magro Follmann HV, Souza E, Aguiar Battistelli A, Rubens Lapolli F, Lobo-Recio MÁ (2020) Determination of the optimal electrocoagulation operational conditions for pollutant removal and filterability improvement during the treatment of municipal wastewater. J Water Process Eng 36:101295
Dalvand A, Gholibegloo E, Ganjali MR, Golchinpoor N, Khazaei M, Kamani H, Hosseini SS, Mahvi AH (2016) Comparison of Moringa stenopetala seed extract as a clean coagulant with Alum and Moringa stenopetala-Alum hybrid coagulant to remove direct dye from Textile Wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16396–16405
de Souza MTF, de Almeida CA, Ambrosio E, Santos LB, de Souza Freitas TKF, Manholer DD, de Carvalho GM, Garcia LB (2016) Extraction and use of Cereus peruvianus cactus mucilage in the treatment of textile effluents. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 67:174–183
Desai KM, Survase SA, Saudagar PS, Lele SS, Singhal RS (2008) Comparison of artificial neural network (ANN) and response surface methodology (RSM) in fermentation media optimization: case study of fermentative production of scleroglucan. Biochem Eng J 41(3):266–273
Elsayed K, Lacor C (2011) Modeling, analysis and optimization of aircyclones using artificial neural network, response surface methodology and CFD simulation approaches. Powder Technol 212(1):115–133
Ezemagu IG, Ejimofor MI, Menkiti MC, Nwobi-Okoye CC (2021) Modeling and optimization of turbidity removal from produced water using response surface methodology and artificial neural network. S Afr J Chem Eng 35:78–88
Ezemagu IG, Menkiti MC, Ugonabo VI, Aneke MC (2016) Adsorptive approach on nepholometric study of paint effluent using Tympanotonos fuscatus extract. Bull Chem Soc Ethiop 30(3):377–390
Gupta KN, Kumar R (2020) Fixed bed utilization for the isolation of xylene vapor: kinetics and optimization using response surface methodology and artificial neural network. Environ Eng Res 26(2):200105
Hadi SM, Al-Mashhadani MKH, Eisa MY (2019) Optimization of dye adsorption process for Albizia lebbeck pods as a biomass using central composite rotatable design model. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 25(1):39–46
Hammoudi A, Moussaceb K, Belebchouche C, Dahmoune F (2019) Comparison of artificial neural network (ANN) and response surface methodology (RSM) prediction in compressive strength of recycled concrete aggregates. Constr Build Mater 209:425–436
Igwegbe CA, Oba SN, Aniagor CO, Adeniyi AG, Ighalo JO (2021) Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from water: a comprehensive review. J Ind Eng Chem 93:57–77
Imen F, Lamia K, Asma T, Neacute ji G, Radhouane G (2013) Optimization of coagulation-flocculation process for printing ink industrial wastewater treatment using response surface methodology. Afr J Biotechnol 12(30):4819–4826
Joshi S, Bajpai S, Jana S (2020) Application of ANN and RSM on fluoride removal using chemically activated D. sissoo sawdust. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(15):17717–17729
Karam A, Bakhoum ES, Zaher K (2020) Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: experimental and numerical perspectives. Int J Sustain Eng 14(5):983–995
Khayet M, Zahrim AY, Hilal N (2011) Modelling and optimization of coagulation of highly concentrated industrial grade leather dye by response surface methodology. Chem Eng J 167(1):77–83
Kim SC (2016) Application of response surface method as an experimental design to optimize coagulation–flocculation process for pre-treating paper wastewater. J Ind Eng Chem 38:93–102
Maroneze MM, Zepka LQ, Vieira JG, Queiroz MI, Jacob-Lopes E (2014) A tecnologia de remoção de fósforo: Gerenciamento do elemento em resíduos industriais. Revista Ambiente e Agua 9(3):445–458
Mdlovu NV, Lin KS, Chen ZW, Liu YJ, Mdlovu NB (2020) Treatment of simulated chromium-contaminated wastewater using polyethylenimine-modified zero-valent iron nanoparticles. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 108:92–101
Menkiti MC, Okoani AO, Ejimofor MI (2018) Adsorptive study of coagulation treatment of paint wastewater using novel Brachystegia eurycoma extract. Appl Water Sci 8(6):1–15
Menkiti M, Ezemagu I, Okolo B (2016) Perikinetics and sludge study for the decontamination of petroleum produced water (PW) using novel mucuna seed extract Collision factor for Brownian transport. Pet Sci 13(2):328–339
Mohamad Yusof MS, Othman MHD, Abdul Wahab R, Abu Samah R, Kurniawan TA, Mustafa A, Rahman MA, Jaafar J, Ismail AF (2020) Effects of pre and post-ozonation on POFA hollow fibre ceramic adsorptive membrane for arsenic removal in water. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 110:100–111
Naghibi SA, Salehi E, Khajavian M, Vatanpour V, Sillanpää M (2021) Multivariate data-based optimization of membrane adsorption process for wastewater treatment: multi-layer perceptron adaptive neural network versus adaptive neural fuzzy inference system. Chemosphere 267:129268
Nnaji P, Anadebe C, Onukwuli OD (2020a) Application of experimental design methodology to optimize dye removal by mucuna sloanei induced coagulation of dye-based wastewater. Desalin Water Treat 198:396–406
Nnaji PC, Okolo BI, Onukwuli OD (2020b) Luffa cylindrica seed: Biomass for wastewater treament, sludge generation study at optimum conditions. Chem Ind Chem Eng Q 26(4):349–358
Oboh I, Aluyor E, Audu T (2015) Kinetic modelling for zinc(II) ions biosorption onto Luffa cylindrica. In: AIP Conference Proceedings, 1653 (Ii).
Okolo BI, Nnaji PC, Onukwuli OD (2016) Nephelometric approach to study coagulation-flocculation of brewery effluent medium using Detarium microcarpum seed powder by response surface methodology. J Environ Chem Eng 4(1):992–1001
Onu CE, Nwabanne JT, Ohale PC, Asadu CO (2020) Preparation and characterization of clay ANN and ANFIS models; critical comparative analysis of the three models; evaluation of mechanistic modeling of the adsorption process; optimization using genetic algorithm. S Afr J Chem Eng 36:24–42
Onukwuli OD, Nnaji PC, Menkiti MC, Anadebe VC, Oke EO, Ude CN, Okafor NA (2021) Dual-purpose optimization of dye-polluted wastewater decontamination using bio-coagulants from multiple processing techniques via neural intelligence algorithm and response surface methodology. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 125:372–386
Salem RH (2017) Functional characterization of luffa (Luffa cylindrica) seeds powder and their utilization to improve stabilized emulsions. Middle East J Appl Sci 7:613–625
Samsami S, Mohamadi M, Sarrafzadeh MH, Rene ER, Firoozbahr M (2020) Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: overview and perspectives. Process Saf Environ Prot 143:138–163
Sangal VK, Kumar V, Mishra IM (2012) Optimization of structural and operational variables for the energy efficiency of a divided wall distillation column. Comput Chem Eng 40:33–40
Sarkar S, Chowdhury R, Das R, Chakraborty S, Choi H, Bhattacharjee C (2014) Application of ANFIS model to optimise the photocatalytic degradation of chlorhexidine digluconate. RSC Adv 4(40):21141–21150
Singh B, Kumar P (2020) Pre-treatment of petroleum refinery wastewater by coagulation and flocculation using mixed coagulant: optimization of process parameters using response surface methodology (RSM). J Water Process Eng 36:101317
Thirunavukkarasu A, Nithya R (2020) Adsorption of acid orange 7 using green synthesized CaO/CeO2 composite: an insight into kinetics, equilibrium, thermodynamics, mass transfer and statistical models. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 111:44–62
Wang J, Chen Y, Wang Y, Yuan S, Yu H (2011) Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process for pulp mill wastewater treatment using a combination of uniform design and response surface methodology. Water Res 45(17):5633–5640
Youssefi S, Emam-Djomeh Z, Mousavi SM (2009) Comparison of artificial neural network (ANN) and response surface methodology (RSM) in the prediction of quality parameters of spray-dried pomegranate juice. Drying Technol 27(7):910–917
Zhang W, Wei Q, Xiao J, Liu Y, Yan C, Liu J, Sand W, Chow CWK (2020) The key factors and removal mechanisms of sulfadimethoxazole and oxytetracycline by coagulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(14):16167–16176
Zhao B, Xiao W, Shang Y, Zhu H, Han R (2017) Adsorption of light green anionic dye using cationic surfactant-modified peanut husk in batch mode. Arab J Chem 10:S3595–S3602
Zhao Z, Sun W, Ray MB, Ray AK, Huang T, Chen J (2019) Optimization and modeling of coagulation-flocculation to remove algae and organic matter from surface water by response surface methodology. Front Environ Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-019-1159-7
Zin KM, Effendi Halmi MI, Abd Gani SS, Zaidan UH, Samsuri AW, Abd Shukor MY (2020) Microbial decolorization of Triazo Dye, Direct Blue 71: an optimization approach using Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Biomed Res Int 2020:1–16
Acknowledgements
V.C. Anadebe is grateful to CSIR, India, and TWAS, Italy, for the Postgraduate Fellowship (Award No. 22/FF/CSIR-TWAS/2019) to purse research program in CSIR-CECRI, India. In addition, Alex Ekwueme Federal University Ndufu-Alike Ebonyi State, Nigeria, is acknowledged for the Research Leave to visit CECRI, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all other authors, I declare that there is no conflict of interest whatsoever. All authors read and agreed with the author order.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nnaji, P.C., Anadebe, V.C., Onukwuli, O.D. et al. Multifactor optimization for treatment of textile wastewater using complex salt–Luffa cylindrica seed extract (CS-LCSE) as coagulant: response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial intelligence algorithm (ANN–ANFIS). Chem. Pap. 76, 2125–2144 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01971-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01971-7