Abstract
Introduction
The usage of bougie devices in guiding the extent of sleeve gastrectomies has been associated with several laryngeal and pharyngeal complications. Despite these being distressing for patients, they draw little attention in current literature.
Objectives
To study the role of preoperative nebulized dexamethasone in relieving the symptoms related to bougie insertion during laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy postoperatively.
Materials and Methods
A prospective interventional study that included 80 patients. The patients were assigned to two groups, 40 patients in each group: the dexamethasone group (D) which received nebulized dexamethasone 8 mg 1 h before surgery and the control group (S) which received saline nebulizer instead. Assessment of postoperative sore throat, nausea and vomiting, odynophagia, and change of voice was used as an outcome comparative tool.
Results
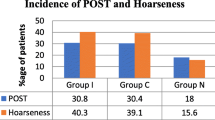
The patient’s age ranged from 17 to 61 years, and the mean age of patients was 34.51 (± 9.5) years. Patients were composed of 13 (16.3%) males and 67 (83.8%) females. The study found a significant preference of outcome values in the dexamethasone group. Sore throat mean and medians were less at all-time intervals: 0 h (p < 0.001), 1 h (p < 0.001), 6 h (p < 0.004), and 24 h (p < 0.001). Nineteen patients of the saline group suffered from a change of voice (p < 0.001), compared to only 4 patients in the dexamethasone group. On the contrary, no significant differences are noted in the incidences of PONV and odynophagia.
Conclusion
Preoperative nebulized dexamethasone was found to be an effective measure in reducing bougie insertion complications in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Theodorou D, Doulami G, Larentzakis A, et al. Bougie insertion: a common practice with underestimated dangers. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2012;3(2):74–7.
Hung KC. To assess the changes of tracheal cuff pressure after a calibrating orogastric tube insertion. J Anesth. 2014;28(1):128–31.
Ashwini H, Seema Kumari K, Lavanya R. Comparative study of dexamethasone nebulisation with magnesium sulphate nebulisation in preventing post operative sore throat following endotracheal intubation. Indian Journal of Clinical Anaesthesia. 2018;5(3):341–7.
Ozayar E, Kurtay A, Gulec H, et al. The effect of bougie size on the incidence of postoperative sore throat in bariatric surgery. Bariatr Surg Pract Patient Care. 2016;11(1):11–4.
Welbourn R, Small P, Finlay I, et al, on behalf of The United Kingdom National Bariatric Surgery Registry (NBSR). Second Registry Report 2014. http://www.bomss.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/Extract_from_the_NBSR_2014_Report.pdf (accessed 11 May 2018).
English WJ, DeMaria EJ, Brethauer SA, et al. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery estimation of metabolic and bariatric procedures performed in the United States in 2016. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2018;14(3):259–63.
Robinson MK. Surgical treatment of obesity--weighing the facts. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(5):520–1.
Segal-Lieberman G, Segal P, Dicker D. Revisiting the role of BMI in the guidelines for bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(Suppl 2):S268–73.
Signorini FJ, Verónica G, Marcos M, et al. Iatrogenic injury of the intrathoracic oesophagus with bougie during sleeve gastrectomy. J Minim Access Surg. 2018;14(1):79–82.
Salama AK, El-badawy AM. Does nebulized dexamethasone decrease the incidence of postextubation sore throat? A randomized controlled study. Ain-Shams J Anaesthesiol. 2016;9:104–7.
Kochkodan J, Telem DA, Ghaferi AA. Physiologic and psychological gender differences in bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2018;32(3):1382–8.
Gagner M, Huang RY. Comparison between orogastric tube/bougie and a suction calibration system for effects on operative duration, staple-line corkscrewing, and esophageal perforation during laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(4):1648–55.
Medhat H. Bougie size 32 versus 40 french in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Egypt J Surg. 2018;37(2):200–8.
Figueredo E, Vivar-Diago M, Muñoz-Blanco F. Laryngo-pharyngeal complaints after use of the laryngeal mask airway. Can J Anaesth. 1999;46(3):220–5.
McHardy FE, Chung F. Postoperative sore throat: cause, prevention and treatment. Anaesthesia. 1999;54(5):444–53.
Beirne OR. Evaluation dexamethasone for reduction of postsurgical sequele of third molar removal. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992;50:1182–3.
Nauck M, Karakiulakis G, Perruchoud AP, et al. Corticosteroids inhibit the expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;341:309–15.
Widar F, Kashani H, Alsén B, et al. The effects of steroids in preventing facial oedema, pain, and neurosensory disturbances after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: a randomized controlled trial. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:252–8.
Edelman JL, Lutz D, Castro MR. Corticosteroids inhibit VEGF-induced vascular leakage in a rabbit model of blood retinal and blood aqueous barrier breakdown. Exp Eye Res. 2005;80:249–58.
Koedam JA, Smink JJ, Van Buul-offers SC. Glucocorticoids inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor expression in growth plate chondrocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002;197:35–44.
Har A, Biswas A, Chatterjee S, et al. Preoperative dexamethasone reduce postoperative pain and analgesic consumption in patient undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Glob Anesth Perioper Med. 2015;1(2):55–7.
Mensah-Nyagan AG, Meyer L, Schaeffer V, et al. Evidence for a key role of steroids in the modulation of pain. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009;34(Suppl 1):S169–77.
Ho CM, Wu HL, Ho ST, et al. Dexamethasone prevents postoperative nausea and vomiting : benefit versus risk. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2011;49(3):100–4.
Groene P, Eisenlohr J, Zeuzem C, et al. Postoperative nausea and vomiting in bariatric surgery in comparison to non-bariatric gastric surgery. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2019;14(1):90–5.
Parthasarathy P, Babu K, Raghavendra Rao RS, et al. The effect of single-dose intravenous dexamethasone on postoperative pain and postoperativenausea and vomiting in patients undergoing surgery under spinal anesthesia: a double-blind randomized clinical study. Anesth Essays Res. 2018;12(2):313–7.
Bülbüller N, Oner OZ. Esophageal calibration with soft orogastric tube during laparoscopic Nissen Fundoplication may reduce reduce postoperative transient dysphagia. Indian J Surg. 2015;77(Suppl 3):759–63.
Acknowledgments
The study was conducted in a tertiary referral hospital. It was financed by the team of the study. The study met all the requirements of the IRB committee. The team of the study has no financial benefits from any dexamethasone based products.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights/Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was obtained from the university hospital research ethics committee (REF 67/299/1176).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almustafa, M., Obeidat, F., Mismar, A. et al. Role of Preoperative Dexamethasone Nebulization in Reducing Bougie Complications Encountered After Sleeve Gastrectomy: a Prospective Double-Blind Control Interventional Study. OBES SURG 30, 501–506 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-019-04202-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-019-04202-x