Abstract
Background
Until recently, there was limited documented data on both dietary and serum selenium deficiency in bariatric surgery. We performed an evaluation of selenium intake and both serum selenium and glutathione peroxidase (GTP; as a functional measurement of selenium) before and after roux-en-Y (RNY) gastric bypass and gastric banding surgery.
Methods
The endpoints obtained from the subjects included dietary intake of selenium and vitamins E and C, as well as serum levels of selenium, GTP and vitamins E. These were analyzed at pre-surgery (baseline) and 3 and 12 months post surgery.
Results
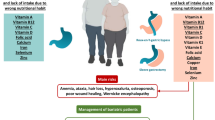
Dietary deficiencies in selenium intake (38.2 % recommended daily allowance) were noted at 3 months, but not baseline or 12 months, in the gastric bypass group. No dietary deficiencies were noted in the lap band group. For both surgeries, there was a significant reduction from baseline to 3 months in both serum selenium and GTP levels (p = 0.033 and 0.0033 respectively). The serum selenium levels and GTP levels both trended back toward baseline values by 12 months without concomitant selenium supplementation. Mean GTP levels were below normal at all three time points while mean serum selenium levels were all at or above normal.
Conclusions
This study shows that RNY gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding procedures, and accompanying dietary restrictions, increases the risk for disturbances of selenium and GTP homeostasis. Consideration for selenium supplementation at higher levels than the current RDA of 55 mcg daily during the first 3 months and perhaps longer should be studied further.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloomberg R. Nutritional deficiencies following bariatric surgery: what have we learned? Obes Surg. 2005;15:145–54.
Gjorup I, et al. Serum selenium and zinc concentrations in morbid obesity. Comparison of controls and patients with jejunoileal bypass. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1988;23(10):1250–2.
Rannem T, et al. Selenium status in patients with Crohn’s disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1992;56(5):933–7.
Ghayour-Mobarhan, et al. Serum selenium and glutathione peroxidase in patients with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Pak J Nutr. 2008;7(1):112–7.
Alasfar F, et al. Selenium is significantly depleted among morbidly obese female patients seeking bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2011;21:1710–3.
Kimmons JE, et al. Associations between body mass index and the prevalence of low micronutrient levels among US adults. Med Gen Med. 2006;8(4):59.
Kushner R. Managing micronutrient deficiency in bariatric surgical patients: treatment of obesity patient. 2007; 2:379–94.
SAGES Guidelines Committee. SAGES guideline for clinical application of laparoscopic bariatric surgery. Surg Endosc. 2008;22:2281–300.
Neve J, et al. New approaches to assess selenium status and requirement. Nutr Rev. 2000;58(12):363–9.
Monson ER, et al. Dietary intakes for antioxidant nutrients: vitamin C, vitamin E, selenium and carotenoids. J Am Diet Assoc. 2000;100(6):637–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The source of financial and material support comes from E. Donnall Thomas Resident Research Grant, Bassett Research Institute, 1 Atwell Road Cooperstown, NY 13326.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freeth, A., Prajuabpansri, P., Victory, J.M. et al. Assessment of Selenium in Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Gastric Banding Surgery. OBES SURG 22, 1660–1665 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0680-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0680-6