Abstract
Background
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) in patients with severe and morbid obesity is one of the current challenges in prosthetic knee surgery. The body mass index (BMI) is used to identify patients who may present difficulties during surgery and postoperative complications. We carried out a prospective study with an initial hypothesis that BMI is not associated with tourniquet time in obese patients undergoing TKA and that some anthropometric parameters may be useful in predicting tourniquet time in severely and morbidly obese patients.
Methods
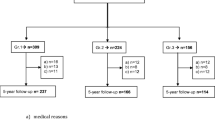
One hundred consecutive patients diagnosed with knee osteoarthritis with BMI ≥35 kg/m2 scheduled for TKA were prospectively studied. Suprapatellar, infrapatellar, and supra/infrapatellar anthropometric indexes were calculated before surgery. The tourniquet time was determined.
Results
The mean BMI was 39.81 kg/m2 (SD ± 3.75). A total of 58% of patients were classified as class III obesity (BMI 35–39.99) and 42% as class IV (BMI ≥ 40) Mean tourniquet time was 41.67 min (SD ± 9.26). There was no association between the BMI and tourniquet time. The suprapatellar index was negatively associated with tourniquet time (p < 0.038).
Discussion
The BMI is not the only parameter that should be considered in order to identify severely and morbidly obese patients who may have more surgical difficulties during TKA. Preoperative determination of the suprapatellar index helped us to classify these patients according to the morphology of the knee and predicted a longer tourniquet time and, therefore, greater surgical difficulty, in patients with a suprapatellar ratio below 1.6 in this study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stickles B, Philips L, Brox WT, et al. Defining the relationship between obesity and total joint arthroplasty. Obes Res. 2001;9:219–23.
Bourne R, Mukhi S, Zhu N, et al. Role of obesity on the risk for total hip or knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop. 2007;465:185–8.
Guss D, Bhattacharyya T. Perioperative management of the obese orthopaedic patient. J AAOS. 2006;14:425–32.
Naik G. Surgeons weighty dilemma. The Wall Street Journal. 2006;28.
Fehring Th, Odum S, Griffin WL, et al. The obesity epidemic. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22 Supl 2:71–6.
Gilliespi GN, Proteus AJ. Obesity and knee arthroplasty. The Knee. 2007;14:81–6.
Winarsky R, Barth P, Lotke P. Total Knee Arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 1998;80A:1770–4.
Booth RE Jr. Total Knee arthroplasty in the obese patient: tips and quips. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17 Suppl 1:69–70.
Rottman SJ, Dvorkin M, Gold D. Extramedullary versus intramedullary tibial alignment guides for total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2005;28:1445–8.
Krushell R, Fingeroth R. Primary total knee arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. A 5-to-14-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22 Suppl 1:77–80.
Amin AK, Patton JT, Cook RE. Does obesity influence the clinical outcome at five years following total knee replacement for osteoarthritis? J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88B:335–40.
Miric A, Moe LimKahn B, et al. Perioperative morbidity following total knee arthroplasty among obese patients. J Knee Surg. 2002;15:77–83.
Patel VP, Walsh M, Shegal B, et al. Factors associated with prolonged wound drainage after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007;89A:33–8.
Foran JRH, Mont MA, Gracia E, et al. The outcome of total knee arthroplasty in obese patients. J Bone Joint Surg. 2004;86A:1609–15.
Foran JRH, Mont MA, Rajadhyaksha AD, et al. Total Knee arthroplasty in obese Group. J Arthroplasty. 2004;19:817–24.
Namba RS, Paxton L, Fithian D. Obesity and perioperative morbidity in total hip and total knee arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20 Suppl 3:46–50.
Deshmukh RG, Hayes JH, Pinder IM. Does body weight influence outcome after total knee arthroplasty? A 1-Year Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:315–9.
Spicer P, Schaper B, et al. Body mass index as a predictor of outcome in total knee replacement. Int Orthop. 2001;25:246–9.
Núñez M, Núñez E, del Val JL, et al. Health-related quality of life in patients with osteoarthritis after total knee replacement: factors influencing outcomes at 36 months of follow-up. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2007;15:1001–7.
Chen L, Peeters A, Magliano DJ, et al. Anthropometric measures and absolute cardiovascular risk estimates in the Australian Diabetes, Obesity and Lifestyle (AusDiab) Stydy. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2007;14:740–5.
Rama R, Apsingi S, Poovali S, et al. Timing of tourniquet release in knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2007;89A:605–99.
Stürmer T, Günther KP, Brenner H. Obesity, overweight and patterns of osteoarthritis: the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53:307–13.
Powell A, Teichtahl AJ, Wluka AE, et al. Obesity a preventable risk factor for large joint osteoarthritis which may act through biomechanical factors. Br J Sports Med. 2005;39:4–5.
Messier SO, Gutekunst DJ, Davis C, et al. Weight loss reduces knee-joint loads in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Reum. 2005;52:2026–32.
Focht BC, Rejeski WJ, Ambrosius WT, et al. Exercise, Self-efficacy, and mobility performance in overweight and obese older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Reum. 2005;53:659–65.
Nevitt MC. Obesity outcomes in disease management: clinical outcomes for osteoarthritis. Obes Res. 2002:10 Suppl 1:33–7.
Liu B, Balkwill E, Cooper C, et al. Relationship of height, weight and body mass index to the risk of hip and knee replacements in middle-aged women. Rheumatology. 2007;46:861–7.
Abbate LM, Stevens J, Schwartz TA, et al. Anthropometric measures, body composition, body fat distribution, and knee osteoarthritis in women. Obesity. 2006;14:1274–81.
Ding Ch, Cicuttini F, Scott F, et al. Knee structural alteration and BMI: a cross-sectional Study. Obes Res. 2005;13:350–61.
Wang Y, Wluka A, English D, et al. Body composition and knee cartilage properties in healthy, community-based adults. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66:1244–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lozano, L.M., Núñez, M., Segur, J.M. et al. Relationship Between Knee Anthropometry and Surgical Time in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Severely and Morbidly Obese Patients: A New Prognostic Index of Surgical Difficulty. OBES SURG 18, 1149–1153 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-008-9481-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-008-9481-3