Background
Some lines of evidence suggest that endotoxin may induce non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in a background of fatty liver. However, a clear association between increased endotoxemia and development of steatohepatitis in obese patients has not been confirmed. We aim to assess the endotoxemic state of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its relationship with the liver expression of TNF-α and the presence of NASH.
Methods
Prospective study comprising 40 patients with morbid obesity who were diagnosed with NAFLD. Blood samples and liver biopsies were collected. Endotoxemia was assessed by the evaluation of circulating level of LPS-binding protein (LBP). Plasma levels of LBP and TNF-α were assessed by ELISA. The expression of TNF-α in liver tissue was evaluated by real-time PCR. Histological examination was performed to evaluate the presence of steatosis or NASH.
Results
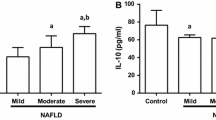
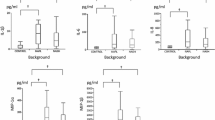
Levels of LBP were increased in obese patients with NAFLD. In addition, plasma level of LBP was increased in patients with steatohepatitis (14.2 ±3.9 μg/mL) when compared with patients with simple steatosis (11.5 ±3.2 μg/mL), P=0.041.The TNF-α mRNA expression in liver tissue was significantly higher in patients with NASH.This increment correlated with the rise in plasma levels of LBP (r=0.412, P=0.036).
Conclusion
NAFLD patients have elevated plasma levels of LBP and they are further increased in patients with NASH. This increase is related to a rise in TNF-α gene expression in the hepatic tissue which supports a role for endotoxemia in the development of steatohepatitis in obese patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thurman RG. II. Alcoholic liver injury involves activation of Kupffer cells by endotoxin. Am J Physiol 1998; 275 (4 Pt 1): G605–G611.
Bode C, Bode JC. Activation of the innate immune system and alcoholic liver disease: effects of ethanol per se or enhanced intestinal translocation of bacterial toxins induced by ethanol? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2005; 29 (Suppl 11): 166S–171S.
Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Lane MD et al. Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: implications for the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 2557–62.
Li Z, Yang S, Lin H et al. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003; 37: 343–50.
Wigg AJ, Roberts-Thomson IC, Dymock RB et al. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumour necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2001; 48: 206–11.
Sax HC, Talamini MA, Brackett K et al. Hepatic steatosis in total parenteral nutrition: failure of fatty infiltration to correlate with abnormal serum hepatic enzyme levels. Surgery 1986; 100: 697–704.
Loguercio C, De Simone T, D’Auria MV et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a multicentre clinical study by the Italian Association for the Study of the Liver. Dig Liver Dis 2004; 36: 398–405.
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Interactions of bacterial lipopolysaccharides with serum proteins. Prog Clin Biol Res 1988; 272: 309–18.
Anker SD, Egerer KR, Volk HD et al. Elevated soluble CD14 receptors and altered cytokines in chronic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 1997; 79: 1426–30.
Lequier LL, Nikaidoh H, Leonard SR et al. Preoperative and postoperative endotoxemia in children with congenital heart disease. Chest 2000; 117: 1706–12.
Albillos A, de la Hera A, Gonzalez M et al. Increased lipopolysaccharide binding protein in cirrhotic patients with marked immune and hemodynamic derangement. Hepatology 2003; 37: 208–17.
Tobias PS, Soldau K, Ulevitch RJ. Isolation of a lipopolysaccharide-binding acute phase reactant from rabbit serum. J Exp Med 1986; 164: 777–93.
Geller DA, Kispert PH, Su GL et al. Induction of hepatocyte lipopolysaccharide binding protein in models of sepsis and the acute-phase response. Arch Surg 1993; 128: 22–7.
Calvano SE, Thompson WA, Marra MN et al. Changes in polymorphonuclear leukocyte surface and plasma bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein and plasma lipopolysaccharide binding protein during endotoxemia or sepsis. Arch Surg 1994; 129: 220–6.
Schumann RR. Mechanisms of transcriptional activation of lipopolysaccharide binding protein (LBP). Prog Clin Biol Res 1995; 392: 297–304.
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94: 2467–74.
Brunt EM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Oliver D et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: histologic features and clinical correlations with 30 blinded biopsy specimens. Hum Pathol 2004; 35: 1070–82.
Roslansky PF, Novitsky TJ. Sensitivity of Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) to LAL-reactive glucans. J Clin Microbiol 1991; 29: 2477–83.
Hurley JC. Endotoxemia: methods of detection and clinical correlates. Clin Microbiol Rev 1995; 8: 268–92.
Novitsky TJ. Limitations of the Limulus amebocyte lysate test in demonstrating circulating lipopolysac-charides. Ann NY Acad Sci 1998; 851: 416–21.
Munford RS. Detoxifying endotoxin: time, place and person. J Endotoxin Res 2005; 11: 69–84.
Schumann RR, Leong SR, Flaggs GW et al. Structure and function of lipopolysaccharide binding protein. Science 1990; 249 (4975): 1429–31.
Zweigner J, Schumann RR, Weber JR. The role of lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in modulating the innate immune response. Microbes Infect 2006; 8: 946–52.
Hiki N, Berger D, Mimura Y et al. Release of endotoxin-binding proteins during major elective surgery: role of soluble CD14 in phagocytic activation. World J Surg 2000; 24: 499–506.
Wiezer MJ, Meijer C, Sietses C et al. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein preserves leukocyte functions after major liver resection. Ann Surg 2000; 232: 208–15.
Brun P, Castagliuolo I, Leo VD et al. Increased intestinal permeability in obese mice: new evidences in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2006; 292: G518–25.
Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits” Gastroenterology 1998; 114: 842–5.
Chitturi S, Farrell GC. Etiopathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Semin Liver Dis 2001; 21: 27–41.
Kugelmas M, Hill DB, Vivian B et al. Cytokines and NASH: a pilot study of the effects of lifestyle modification and vitamin E. Hepatology 2003; 38: 413–9.
Crespo J, Cayon A, Fernandez-Gil P et al. Gene expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha and TNFreceptors, p55 and p75, in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatology 2001; 34: 1158–63.
Katsuki A, Sumida Y, Murashima S et al. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha are increased in obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998; 83: 859–62.
Tsigos C, Kyrou I, Chala E et al. Circulating tumor necrosis factor alpha concentrations are higher in abdominal versus peripheral obesity. Metabolism 1999; 48: 1332–5.
Wright SD, Tobias PS, Ulevitch RJ et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding protein opsonizes LPS-bearing particles for recognition by a novel receptor on macrophages. J Exp Med 1989; 170: 1231–41.
Viriyakosol S, Tobias PS, Kitchens RL et al. MD-2 binds to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 38044–51.
Thomas CJ, Kapoor M, Sharma S et al. Evidence of a trimolecular complex involving LPS, LPS binding protein and soluble CD14 as an effector of LPS response. FEBS Lett 2002; 531: 184–8.
Fenton MJ, Golenbock DT. LPS-binding proteins and receptors. J Leukoc Biol 1998; 64: 25–32.
Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS. Receptor-dependent mechanisms of cell stimulation by bacterial endotoxin. Annu Rev Immunol 1995; 13: 437–57.
Gioannini TL, Teghanemt A, Zarember KA et al. Regulation of interactions of endotoxin with host cells. J Endotoxin Res 2003; 9: 401–8.
Weiss J. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (BPI) and lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP): structure, function and regulation in host defence against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochem Soc Trans 2003; 31 (Pt 4): 785–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerra Ruiz, A., Casafont, F., Crespo, J. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein Plasma Levels and Liver TNF-Alpha Gene Expression in Obese Patients: Evidence for the Potential Role of Endotoxin in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. OBES SURG 17, 1374–1380 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9243-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-007-9243-7