Abstract
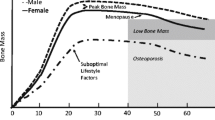
Bone mass is a key determinant of osteoporosis and fragility fractures. Epidemiologic studies have shown that a 10% increase in peak bone mass (PBM) at the population level reduces the risk of fracture later in life by 50%. Low PBM is possibly due to the bone loss caused by various conditions or processes that occur during adolescence and young adulthood. Race, gender, and family history (genetics) are responsible for the majority of PBM, but other factors, such as physical activity, calcium and vitamin D intake, weight, smoking and alcohol consumption, socioeconomic status, age at menarche, and other secondary causes (diseases and medications), play important roles in PBM gain during childhood and adolescence. Hence, the optimization of lifestyle factors that affect PBM and bone strength is an important strategy to maximize PBM among adolescents and young people, and thus to reduce the low bone mass or osteoporosis risk in later life. This review aims to summarize the available evidence for the common but important factors that influence bone mass gain during growth and development and discuss the advances of developing high PBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrari SL, Rizzoli R. Gene variants for osteoporosis and their pleiotropic effects in aging. Mol Aspects Med 2005; 26(3): 145–167
Pisani P, Renna MD, Conversano F, Casciaro E, Di Paola M, Quarta E, Muratore M, Casciaro S. Major osteoporotic fragility fractures: risk factor updates and societal impact. World J Orthop 2016; 7(3): 171–181
Liu ZH, Zhao YL, Ding GZ, Zhou Y. Epidemiology of primary osteoporosis in China. Osteoporos Int 1997; 7(Suppl 3): 84–87
Si L, Winzenberg TM, Jiang Q, Chen M, Palmer AJ. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010–2050. Osteoporos Int 2015; 26(7): 1929–1937
Rizzoli R, Bianchi ML, Garabédian M, McKay HA, Moreno LA. Maximizing bone mineral mass gain during growth for the prevention of fractures in the adolescents and the elderly. Bone 2010; 46(2): 294–305
Hernandez CJ, Beaupré GS, Carter DR. A theoretical analysis of the relative influences of peak BMD, age-related bone loss and menopause on the development of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 2003; 14(10): 843–847
Boreham CA, McKay HA. Physical activity in childhood and bone health. Br J Sports Med 2011; 45(11): 877–879
Forlino A, Marini JC. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 2016; 387 (10028): 1657–1671
Jha S, Chapman M, Roszko K. When low bone mineral density and fractures is not osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2019; 17(5): 324–332
Writing Group for the ISCD Position Development Conference. Indications and reporting for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Clin Densitom 2004; 7(1): 37–44
Gordon CM, Bachrach LK, Carpenter TO, Crabtree N, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Kutilek S, Lorenc RS, Tosi LL, Ward KA, Ward LM, Kalkwarf HJ. Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry interpretation and reporting in children and adolescents: the 2007 ISCD Pediatric Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 2008; 11(1): 43–58
Kyriakou A, Shepherd S, Mason A, Faisal Ahmed S. A critical appraisal of vertebral fracture assessment in paediatrics. Bone 2015; 81: 255–259
Adiotomre E, Summers L, Allison A, Walters SJ, Digby M, Broadley P, Lang I, Morrison G, Bishop N, Arundel P, Offiah AC. Diagnostic accuracy of DXA compared to conventional spine radiographs for the detection of vertebral fractures in children. Eur Radiol 2017; 27(5): 2188–2199
Adams JE. Quantitative computed tomography. Eur J Radiol 2009; 71(3): 415–424
Hunter DJ, de Lange M, Andrew T, Snieder H, MacGregor AJ, Spector TD. Genetic variation in bone mineral density and calcaneal ultrasound: a study of the influence of menopause using female twins. Osteoporos Int 2001; 12(5): 406–411
Faulkner RA, Bailey DA. Osteoporosis: a pediatric concern? Med Sport Sci 2007; 51: 1–12
Bachrach LK, Hastie T, Wang MC, Narasimhan B, Marcus R. Bone mineral acquisition in healthy Asian, Hispanic, black, and Caucasian youth: a longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999; 84(12): 4702–4712
Berger C, Goltzman D, Langsetmo L, Joseph L, Jackson S, Kreiger N, Tenenhouse A, Davison KS, Josse RG, Prior JC, Hanley DA; CaMos Research Group. Peak bone mass from longitudinal data: implications for the prevalence, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 2010; 25(9): 1948–1957
Bonjour JP, Chevalley T. Pubertal timing, bone acquisition, and risk of fracture throughout life. Endocr Rev 2014; 35(5): 820–847
Recker RR, Davies KM, Hinders SM, Heaney RP, Stegman MR, Kimmel DB. Bone gain in young adult women. JAMA 1992; 268 (17): 2403–2408
Teegarden D, Proulx WR, Martin BR, Zhao J, McCabe GP, Lyle RM, Peacock M, Slemenda C, Johnston CC, Weaver CM. Peak bone mass in young women. J Bone Miner Res 1995; 10(5): 711–715
Bishop N, Arundel P, Clark E, Dimitri P, Farr J, Jones G, Makitie O, Munns CF, Shaw N; International Society of Clinical Densitometry. Fracture prediction and the definition of osteoporosis in children and adolescents: the ISCD 2013 Pediatric Official Positions. J Clin Densitom 2014; 17(2): 275–280
Mäyränpää MK, Mäkitie O, Kallio PE. Decreasing incidence and changing pattern of childhood fractures: a population-based study. J Bone Miner Res 2010; 25(12): 2752–2759
Gordon CM, Zemel BS, Wren TA, Leonard MB, Bachrach LK, Rauch F, Gilsanz V, Rosen CJ, Winer KK. The determinants of peak bone mass. J Pediatr 2017; 180: 261–269
Clark EM, Ness AR, Bishop NJ, Tobias JH. Association between bone mass and fractures in children: a prospective cohort study. J Bone Miner Res 2006; 21(9): 1489–1495
Kalkwarf HJ, Laor T, Bean JA. Fracture risk in children with a forearm injury is associated with volumetric bone density and cortical area (by peripheral QCT) and areal bone density (by DXA). Osteoporos Int 2011; 22(2): 607–616
Cooper C, Westlake S, Harvey N, Javaid K, Dennison E, Hanson M. Review: developmental origins of osteoporotic fracture. Osteoporos Int 2006; 17(3): 337–347
Nilsson M, Ohlsson C, Mellström D, Lorentzon M. Previous sport activity during childhood and adolescence is associated with increased cortical bone size in young adult men. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24(1): 125–133
Rudäng R, Darelid A, Nilsson M, Nilsson S, Mellström D, Ohlsson C, Lorentzon M. Smoking is associated with impaired bone mass development in young adult men: a 5-year longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(10): 2189–2197
Bachrach LK. Acquisition of optimal bone mass in childhood and adolescence. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2001; 12(1): 22–28
Heaney RP, Abrams S, Dawson-Hughes B, Looker A, Marcus R, Matkovic V, Weaver C. Peak bone mass. Osteoporos Int 2000; 11 (12): 985–1009
Ralston SH. Genetic determinants of osteoporosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2005; 17(4): 475–479
Zhai G, Andrew T, Kato BS, Blake GM, Spector TD. Genetic and environmental determinants on bone loss in postmenopausal Caucasian women: a 14-year longitudinal twin study. Osteoporos Int 2009; 20(6): 949–953
Koay MA, Tobias JH, Leary SD, Steer CD, Vilariño-Güell C, Brown MA. The effect of LRP5 polymorphisms on bone mineral density is apparent in childhood. Calcif Tissue Int 2007; 81(1): 1–9
Tobias JH, Steer CD, Vilarino-Güell C, Brown MA. Estrogen receptor alpha regulates area-adjusted bone mineral content in late pubertal girls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(2): 641–647
Timpson NJ, Tobias JH, Richards JB, Soranzo N, Duncan EL, Sims AM, Whittaker P, Kumanduri V, Zhai G, Glaser B, Eisman J, Jones G, Nicholson G, Prince R, Seeman E, Spector TD, Brown MA, Peltonen L, Smith GD, Deloukas P, Evans DM. Common variants in the region around Osterix are associated with bone mineral density and growth in childhood. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18(8): 1510–1517
Medina-Gomez C, Kemp JP, Estrada K, Eriksson J, Liu J, Reppe S, Evans DM, Heppe D, van den Put L, Herrera L, Ring SM, Kruithof C, Timpson NJ, Zillikens MC, Olstad OK, St Pourcain B, Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Smith GD, Lorentzon M, Gautvik KM, Uitterlinden AG, Brommage R, Ohlsson C, Tobias JH, Rivadeneira F. Meta-analysis of genome-wide scans for total body BMD in children and adults reveals allelic heterogeneity, pleiotropy and age-specific effects at the WNT16 locus. Bone 2012; 50: S33
Chesi A, Mitchell JA, Kalkwarf HJ, Bradfield JP, Lappe JM, McCormack SE, Gilsanz V, Oberfield SE, Hakonarson H, Shepherd JA, Kelly A, Zemel BS, Grant SFA. A trans-ethnic genome-wide association study identifies gender-specific loci influencing pediatric aBMD and BMC at the distal radius. Hum Mol Genet 2015; 24(17): 5053–5059
Paternoster L, Lorentzon M, Vandenput L, Karlsson MK, Ljunggren Ö, Kindmark A, Mellstrom D, Kemp JP, Jarett CE, Holly JMP, Sayers A, St Pourcain B, Timpson NJ, Deloukas P, Davey Smith G, Ring SM, Evans DM, Tobias JH, Ohlsson C. Genome-wide association meta-analysis of cortical bone mineral density unravels allelic heterogeneity at the RANKL locus and potential pleiotropic effects on bone. PLoS Genet 2010; 6(11): e1001217
Koller DL, Ichikawa S, Lai D, Padgett LR, Doheny KF, Pugh E, Paschall J, Hui SL, Edenberg HJ, Xuei X, Peacock M, Econs MJ, Foroud T. Genome-wide association study of bone mineral density in premenopausal European-American women and replication in African-American women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(4): 1802–1809
Koller DL, Zheng HF, Karasik D, Yerges-Armstrong L, Liu CT, McGuigan F, Kemp JP, Giroux S, Lai D, Edenberg HJ, Peacock M, Czerwinski SA, Choh AC, McMahon G, St Pourcain B, Timpson NJ, Lawlor DA, Evans DM, Towne B, Blangero J, Carless MA, Kammerer C, Goltzman D, Kovacs CS, Prior JC, Spector TD, Rousseau F, Tobias JH, Akesson K, Econs MJ, Mitchell BD, Richards JB, Kiel DP, Foroud T. Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies identifies WNT16 and ESR1 SNPs associated with bone mineral density in premenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 2013; 28(3): 547–558
Paternoster L, Ohlsson C, Sayers A, Vandenput L, Lorentzon M, Evans DM, Tobias JH. OPG and RANK polymorphisms are both associated with cortical bone mineral density: findings from a metaanalysis of the Avon longitudinal study of parents and children and gothenburg osteoporosis and obesity determinants cohorts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95(8): 3940–3948
Kemp JP, Medina-Gomez C, Estrada K, St Pourcain B, Heppe DHM, Warrington NM, Oei L, Ring SM, Kruithof CJ, Timpson NJ, Wolber LE, Reppe S, Gautvik K, Grundberg E, Ge B, van der Eerden B, van de Peppel J, Hibbs MA, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Choi K, Koller DL, Econs MJ, Williams FMK, Foroud T, Zillikens MC, Ohlsson C, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Davey Smith G, Jaddoe VWV, Tobias JH, Rivadeneira F, Evans DM. Phenotypic dissection of bone mineral density reveals skeletal site specificity and facilitates the identification of novel loci in the genetic regulation of bone mass attainment. PLoS Genet 2014; 10(6): e1004423
Zheng HF, Forgetta V, Hsu YH, Estrada K, Rosello-Diez A, Leo PJ, Dahia CL, Park-Min KH, Tobias JH, Kooperberg C, Kleinman A, Styrkarsdottir U, Liu CT, Uggla C, Evans DS, Nielson CM, Walter K, Pettersson-Kymmer U, McCarthy S, Eriksson J, Kwan T, Jhamai M, Trajanoska K, Memari Y, Min J, Huang J, Danecek P, Wilmot B, Li R, Chou WC, Mokry LE, Moayyeri A, Claussnitzer M, Cheng CH, Cheung W, Medina-Gómez C, Ge B, Chen SH, Choi K, Oei L, Fraser J, Kraaij R, Hibbs MA, Gregson CL, Paquette D, Hofman A, Wibom C, Tranah GJ, Marshall M, Gardiner BB, Cremin K, Auer P, Hsu L, Ring S, Tung JY, Thorleifsson G, Enneman AW, van Schoor NM, de Groot LCPGM, van der Velde N, Melin B, Kemp JP, Christiansen C, Sayers A, Zhou Y, Calderari S, van Rooij J, Carlson C, Peters U, Berlivet S, Dostie J, Uitterlinden AG, Williams SR, Farber C, Grinberg D, LaCroix AZ, Haessler J, Chasman DI, Giulianini F, Rose LM, Ridker PM, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV, Center JR, Nogues X, Garcia-Giralt N, Launer LL, Gudnason V, Mellström D, Vandenput L, Amin N, van Duijn CM, Karlsson MK, Ljunggren Ö, Svensson O, Hallmans G, Rousseau F, Giroux S, Bussière J, Arp PP, Koromani F, Prince RL, Lewis JR, Langdahl BL, Hermann AP, Jensen JEB, Kaptoge S, Khaw KT, Reeve J, Formosa MM, Xuereb-Anastasi A, Åkesson K, McGuigan FE, Garg G, Olmos JM, Zarrabeitia MT, Riancho JA, Ralston SH, Alonso N, Jiang X, Goltzman D, Pastinen T, Grundberg E, Gauguier D, Orwoll ES, Karasik D, Davey-Smith G; AOGC Consortium, Smith AV, Siggeirsdottir K, Harris TB, Zillikens MC, van Meurs JBJ, Thorsteinsdottir U, Maurano MT, Timpson NJ, Soranzo N, Durbin R, Wilson SG, Ntzani EE, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Hinds DA, Spector T, Cupples LA, Ohlsson C, Greenwood CMT; UK10K Consortium, Jackson RD, Rowe DW, Loomis CA, Evans DM, Ackert-Bicknell CL, Joyner AL, Duncan EL, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F, Richards JB. Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature 2015; 526(7571): 112–117
Mitchell JA, Chesi A, McCormack SE, Roy SM, Cousminer DL, Kalkwarf HJ, Lappe JM, Gilsanz V, Oberfield SE, Shepherd JA, Kelly A, Zemel BS, Grant SFA. Rare EN1 variants and pediatric bone mass. J Bone Miner Res 2016; 31(8): 1513–1517
Zheng HF, Tobias JH, Duncan E, Evans DM, Eriksson J, Paternoster L, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Lehtimäki T, Bergström U, Kähönen M, Leo PJ, Raitakari O, Laaksonen M, Nicholson GC, Viikari J, Ladouceur M, Lyytikäinen LP, Medina-Gomez C, Rivadeneira F, Prince RL, Sievanen H, Leslie WD, Mellström D, Eisman JA, Movérare-Skrtic S, Goltzman D, Hanley DA, Jones G, St Pourcain B, Xiao Y, Timpson NJ, Smith GD, Reid IR, Ring SM, Sambrook PN, Karlsson M, Dennison EM, Kemp JP, Danoy P, Sayers A, Wilson SG, Nethander M, McCloskey E, Vandenput L, Eastell R, Liu J, Spector T, Mitchell BD, Streeten EA, Brommage R, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Brown MA, Ohlsson C, Richards JB, Lorentzon M. WNT16 influences bone mineral density, cortical bone thickness, bone strength, and osteoporotic fracture risk. PLoS Genet 2012; 8(7): e1002745
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OM, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, González-Macías J, Kähönen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren Ö, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellström D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, Slagboom PE, Tang NL, Urreizti R, van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gómez C, Palsson ST, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JB, Verlaan D, Williams FM, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimäki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HA, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AW, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JP, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet 2012; 44(5): 491–501
Rivadeneira F, Styrkársdottir U, Estrada K, Halldórsson BV, Hsu YH, Richards JB, Zillikens MC, Kavvoura FK, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Cupples LA, Deloukas P, Demissie S, Grundberg E, Hofman A, Kong A, Karasik D, van Meurs JB, Oostra B, Pastinen T, Pols HA, Sigurdsson G, Soranzo N, Thorleifsson G, Thorsteinsdottir U, Williams FM, Wilson SG, Zhou Y, Ralston SH, van Duijn CM, Spector T, Kiel DP, Stefansson K, Ioannidis JP, Uitterlinden AG; Genetic Factors for Osteoporosis (GEFOS) Consortium. Twenty bone-mineral-density loci identified by large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 2009; 41(11): 1199–1206
Mitchell JA, Chesi A, Elci O, McCormack SE, Kalkwarf HJ, Lappe JM, Gilsanz V, Oberfield SE, Shepherd JA, Kelly A, Zemel BS, Grant SF. Genetics of bone mass in childhood and adolescence: effects of sex and maturation interactions. J Bone Miner Res 2015; 30(9): 1676–1683
Chesi A, Mitchell JA, Kalkwarf HJ, Bradfield JP, Lappe JM, Cousminer DL, Roy SM, McCormack SE, Gilsanz V, Oberfield SE, Hakonarson H, Shepherd JA, Kelly A, Zemel BS, Grant SFA. A genomewide association study identifies two sex-specific loci, at SPTB and IZUMO3, influencing pediatric bone mineral density at multiple skeletal sites. J Bone Miner Res 2017; 32(6): 1274–1281
Paternoster L, Lorentzon M, Lehtimäki T, Eriksson J, Kähönen M, Raitakari O, Laaksonen M, Sievänen H, Viikari J, Lyytikäinen LP, Mellström D, Karlsson M, Ljunggren O, Grundberg E, Kemp JP, Sayers A, Nethander M, Evans DM, Vandenput L, Tobias JH, Ohlsson C. Genetic determinants of trabecular and cortical volumetric bone mineral densities and bone microstructure. PLoS Genet 2013; 9(2): e1003247
Dimitri P. The impact of childhood obesity on skeletal health and development. J Obes Metab Syndr 2019; 28(1): 4–17
van Leeuwen J, Koes BW, Paulis WD, van Middelkoop M. Differences in bone mineral density between normal-weight children and children with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 2017; 18(5): 526–546
Clark EM, Ness AR, Tobias JH. Adipose tissue stimulates bone growth in prepubertal children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91 (7): 2534–2541
Wey HE, Binkley TL, Beare TM, Wey CL, Specker BL. Cross-sectional versus longitudinal associations of lean and fat mass with pQCT bone outcomes in children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011; 96(1): 106–114
Burrows M, Baxter-Jones A, Mirwald R, Macdonald H, McKay H. Bone mineral accrual across growth in a mixed-ethnic group of children: are Asian children disadvantaged from an early age? Calcif Tissue Int 2009; 84(5): 366–378
Petit MA, Beck TJ, Hughes JM, Lin HM, Bentley C, Lloyd T. Proximal femur mechanical adaptation to weight gain in late adolescence: a six-year longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23(2): 180–188
Wetzsteon RJ, Petit MA, Macdonald HM, Hughes JM, Beck TJ, McKay HA. Bone structure and volumetric BMD in overweight children: a longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23(12): 1946–1953
Hoy CL, Macdonald HM, McKay HA. How does bone quality differ between healthy-weight and overweight adolescents and young adults? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2013; 471(4): 1214–1225
Dimitri P, Jacques RM, Paggiosi M, King D, Walsh J, Taylor ZA, Frangi AF, Bishop N, Eastell R. Leptin may play a role in bone microstructural alterations in obese children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100(2): 594–602
Farr JN, Amin S, LeBrasseur NK, Atkinson EJ, Achenbach SJ, McCready LK, Joseph Melton L 3rd, Khosla S. Body composition during childhood and adolescence: relations to bone strength and microstructure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014; 99(12): 4641–4648
Chen XX, Yang T. Roles of leptin in bone metabolism and bone diseases. J Bone Miner Metab 2015; 33(5): 474–485
Thomas T, Burguera B. Is leptin the link between fat and bone mass? J Bone Miner Res 2002; 17(9): 1563–1569
Upadhyay J, Farr OM, Mantzoros CS. The role of leptin in regulating bone metabolism. Metabolism 2015; 64(1): 105–113
Bailey CA, Brooke-Wavell K. Exercise for optimising peak bone mass in women. Proc Nutr Soc 2008; 67(1): 9–18
Wanner M, Richard A, Martin B, Linseisen J, Rohrmann S. Associations between objective and self-reported physical activity and vitamin D serum levels in the US population. Cancer Causes Control 2015; 26(6): 881–891
Zhang P, Hamamura K, Yokota H. A brief review of bone adaptation to unloading. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics 2008; 6(1): 4–7
Baxter-Jones AD, Kontulainen SA, Faulkner RA, Bailey DA. A longitudinal study of the relationship of physical activity to bone mineral accrual from adolescence to young adulthood. Bone 2008; 43(6): 1101–1107
Löfgren B, Dencker M, Nilsson JA, Karlsson MK. A 4-year exercise program in children increases bone mass without increasing fracture risk. Pediatrics 2012; 129(6): e1468–e1476
Meyer U, Ernst D, Zahner L, Schindler C, Puder JJ, Kraenzlin M, Rizzoli R, Kriemler S. 3-Year follow-up results of bone mineral content and density after a school-based physical activity randomized intervention trial. Bone 2013; 55(1): 16–22
Warden SJ, Mantila Roosa SM, Kersh ME, Hurd AL, Fleisig GS, Pandy MG, Fuchs RK. Physical activity when young provides lifelong benefits to cortical bone size and strength in men. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111(14): 5337–5342
Janz KF, Letuchy EM, Burns TL, Eichenberger Gilmore JM, Torner JC, Levy SM. Objectively measured physical activity trajectories predict adolescent bone strength: Iowa Bone Development Study. Br J Sports Med 2014; 48(13): 1032–1036
Fuchs RK, Bauer JJ, Snow CM. Jumping improves hip and lumbar spine bone mass in prepubescent children: a randomized controlled trial. J Bone Miner Res 2001; 16(1): 148–156
Hind K, Burrows M. Weight-bearing exercise and bone mineral accrual in children and adolescents: a review of controlled trials. Bone 2007; 40(1): 14–27
Gunter K, Baxter-Jones AD, Mirwald RL, Almstedt H, Fuchs RK, Durski S, Snow C. Impact exercise increases BMC during growth: an 8-year longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23(7): 986–993
Weeks BK, Young CM, Beck BR. Eight months of regular in-school jumping improves indices of bone strength in adolescent boys and girls: the POWER PE study. J Bone Miner Res 2008; 23 (7): 1002–1011
Crandall CJ, Merkin SS, Seeman TE, Greendale GA, Binkley N, Karlamangla AS. Socioeconomic status over the life-course and adult bone mineral density: the Midlife in the U.S. Study. Bone 2012; 51(1): 107–113
Navarro MC, Saavedra P, Jódar E, Gómez de Tejada MJ, Mirallave A, Sosa M. Osteoporosis and metabolic syndrome according to socio-economic status, contribution of PTH, vitamin D and body weight: the Canarian Osteoporosis Poverty Study (COPS). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013; 78(5): 681–686
Du Y, Zhao LJ, Xu Q, Wu KH, Deng HW. Socioeconomic status and bone mineral density in adults by race/ethnicity and gender: the Louisiana osteoporosis study. Osteoporos Int 2017; 28(5): 1699–1709
Brennan SL, Henry MJ, Wluka AE, Nicholson GC, Kotowicz MA, Williams JW, Pasco JA. BMD in population-based adult women is associated with socioeconomic status. J Bone Miner Res 2009; 24 (5): 809–815
Myong JP, Kim HR, Choi SE, Koo JW. The effect of socio-economic position on bone health among Koreans by gender and menopausal status. Calcif Tissue Int 2012; 90(6): 488–495
Brennan SL, Winzenberg TM, Pasco JA, Wluka AE, Dobbins AG, Jones G. Social disadvantage, bone mineral density and vertebral wedge deformities in the Tasmanian Older Adult Cohort. Osteoporos Int 2013; 24(6): 1909–1916
Brennan SL, Henry MJ, Kotowicz MA, Nicholson GC, Zhang Y, Pasco JA. Incident hip fracture and social disadvantage in an Australian population aged 50 years or greater. Bone 2011; 48(3): 607–610
Quah C, Boulton C, Moran C. The influence of socioeconomic status on the incidence, outcome and mortality of fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2011; 93 (6): 801–805
Brennan SL, Henry MJ, Wluka AE, Nicholson GC, Kotowicz MA, Pasco JA. Socioeconomic status and bone mineral density in a population-based sample of men. Bone 2010; 46(4): 993–999
Aggarwal N, Raveendran A, Khandelwal N, Sen RK, Thakur JS, Dhaliwal LK, Singla V, Manoharan SR. Prevalence and related risk factors of osteoporosis in peri- and postmenopausal Indian women. J Midlife Health 2011; 2(2): 81–85
Vaidya SV, Ekbote VH, Khadilkar AV, Chiplonkar SA, Pillay D, Divate U. Bone status of women over 40 years of age from two socioeconomic strata. Endocr Res 2012; 37(1): 25–34
Elliot JR, Gilchrist NL, Wells JE. The effect of socioeconomic status on bone density in a male Caucasian population. Bone 1996; 18(4): 371–373
Karlamangla AS, Mori T, Merkin SS, Seeman TE, Greendale GA, Binkley N, Crandall CJ. Childhood socioeconomic status and adult femoral neck bone strength: findings from the Midlife in the United States Study. Bone 2013; 56(2): 320–326
Lim JS, Lee HS, Kim EY, Yi KH, Hwang JS. Early menarche increases the risk of type 2 diabetes in young and middle-aged Korean women. Diabet Med 2015; 32(4): 521–525
Ritte R, Lukanova A, Tjønneland A, Olsen A, Overvad K, Mesrine S, Fagherazzi G, Dossus L, Teucher B, Steindorf K, Boeing H, Aleksandrova K, Trichopoulou A, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, Palli D, Grioni S, Mattiello A, Tumino R, Sacerdote C, Quirós JR, Buckland G, Molina-Montes E, Chirlaque MD, Ardanaz E, Amiano P, Bueno-de-Mesquita B, van Duijnhoven F, van Gils CH, Peeters PHM, Wareham N, Khaw KT, Key TJ, Travis RC, Krum-Hansen S, Gram IT, Lund E, Sund M, Andersson A, Romieu I, Rinaldi S, McCormack V, Riboli E, Kaaks R. Height, age at menarche and risk of hormone receptor-positive and-negative breast cancer: a cohort study. Int J Cancer 2013; 132(11): 2619–2629
Gong TT, Wang YL, Ma XX. Age at menarche and endometrial cancer risk: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Sci Rep 2015; 5(1): 14051
Ito M, Yamada M, Hayashi K, Ohki M, Uetani M, Nakamura T. Relation of early menarche to high bone mineral density. Calcif Tissue Int 1995; 57(1): 11–14
Šešelj M, Nahhas RW, Sherwood RJ, Chumlea WC, Towne B, Duren DL. The influence of age at menarche on cross-sectional geometry of bone in young adulthood. Bone 2012; 51(1): 38–45
Chevalley T, Bonjour JP, Ferrari S, Rizzoli R. Influence of age at menarche on forearm bone microstructure in healthy young women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008; 93(7): 2594–2601
Gilsanz V, Chalfant J, Kalkwarf H, Zemel B, Lappe J, Oberfield S, Shepherd J, Wren T, Winer K. Age at onset of puberty predicts bone mass in young adulthood. J Pediatr 2011; 158(1): 100–105. e2
Yoshida S, Ikari K, Furuya T, Toyama Y, Taniguchi A, Yamanaka H, Momohara S. A GC polymorphism associated with serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level is a risk factor for hip fracture in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: 10-year follow-up of the Institute of Rheumatology, Rheumatoid Arthritis cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 2014; 16(2): R75
Roy DK, O’Neill TW, Finn JD, Lunt M, Silman AJ, Felsenberg D, Armbrecht G, Banzer D, Benevolenskaya LI, Bhalla A, Bruges Armas J, Cannata JB, Cooper C, Dequeker J, Diaz MN, Eastell R, Yershova OB, Felsch B, Gowin W, Havelka S, Hoszowski K, Ismail AA, Jajic I, Janott I, Johnell O, Kanis JA, Kragl G, Lopez Vaz A, Lorenc R, Lyritis G, Masaryk P, Matthis C, Miazgowski T, Gennari C, Pols HAP, Poor G, Raspe HH, Reid DM, Reisinger W, Scheidt-Nave C, Stepan JJ, Todd CJ, Weber K, Woolf AD, Reeve J; European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS). Determinants of incident vertebral fracture in men and women: results from the European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS). Osteoporos Int 2003; 14(1): 19–26
Silman AJ. Risk factors for Colles’ fracture in men and women: results from the European Prospective Osteoporosis Study. Osteoporos Int 2003; 14(3): 213–218
Mendoza-Romo MA, Ramírez-Arriola MC, Velasco-Chávez JF, Rivera-Martínez JG, de Jesús RN, Valdez-Jiménez LA. Parity and menarche as risk factors for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Ginecol Obstet Mex 2014; 82(2): 75–82 (in Spanish)
Cashman KD. Calcium intake, calcium bioavailability and bone health. Br J Nutr 2002; 87(Suppl 2): S169–S177
Masuyama R. Bone and Nutrition. Vitamin D independent calcium absorption. Clin Calcium 2015; 25(7): 1023–1028 (in Japanese)
Sahota O. Understanding vitamin D deficiency. Age Ageing 2014; 43(5): 589–591
Munns C, Zacharin MR, Rodda CP, Batch JA, Morley R, Cranswick NE, Craig ME, Cutfield WS, Hofman PL, Taylor BJ, Grover SR, Pasco JA, Burgner D, Cowell CT; Paediatric Endocrine Group; Paediatric Bone Australasia. Prevention and treatment of infant and childhood vitamin D deficiency in Australia and New Zealand: a consensus statement. Med J Aust 2006; 185 (5): 268–272
Kitchin B, Morgan SL. Not just calcium and vitamin D: other nutritional considerations in osteoporosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2007; 9(1): 85–92
Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med 2007; 357(3): 266–281
Dibba B, Prentice A, Ceesay M, Stirling DM, Cole TJ, Poskitt EM. Effect of calcium supplementation on bone mineral accretion in gambian children accustomed to a low-calcium diet. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 71(2): 544–549
Prentice A, Ginty F, Stear SJ, Jones SC, Laskey MA, Cole TJ. Calcium supplementation increases stature and bone mineral mass of 16- to 18-year-old boys. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90(6): 3153–3161
Ho SC, Guldan GS, Woo J, Yu R, Tse MM, Sham A, Cheng J. A prospective study of the effects of 1-year calcium-fortified soy milk supplementation on dietary calcium intake and bone health in Chinese adolescent girls aged 14 to 16. Osteoporos Int 2005; 16 (12): 1907–1916
Lambert HL, Eastell R, Karnik K, Russell JM, Barker ME. Calcium supplementation and bone mineral accretion in adolescent girls: an 18-mo randomized controlled trial with 2-y follow-up. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87(2): 455–462
Du X, Zhu K, Trube A, Zhang Q, Ma G, Hu X, Fraser DR, Greenfield H. School-milk intervention trial enhances growth and bone mineral accretion in Chinese girls aged 10–12 years in Beijing. Br J Nutr 2004; 92(1): 159–168
Winzenberg T, Powell S, Shaw KA, Jones G. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on bone density in healthy children: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2011; 342: c7254
El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Nabulsi M, Tamim H, Maalouf J, Salamoun M, Khalife H, Choucair M, Arabi A, Vieth R. Effect of vitamin D replacement on musculoskeletal parameters in school children: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91(2): 405–412
Khadilkar AV, Sayyad MG, Sanwalka NJ, Bhandari DR, Naik S, Khadilkar VV, Mughal MZ. Vitamin D supplementation and bone mass accrual in underprivileged adolescent Indian girls. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2010; 19(4): 465–472
Al-Shaar L, Nabulsi M, Maalouf J, El-Rassi R, Vieth R, Beck TJ, El-Hajj Fuleihan G. Effect of vitamin D replacement on hip structural geometry in adolescents: a randomized controlled trial. Bone 2013; 56(2): 296–303
Li T. Research progress on pathogenesis of smoking-induced osteoporosis. Chin J Osteoporos (Zhongguo Gu Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi) 2010; 16(5): 381–386 (in Chinese)
Mikosch P. Alcohol and bone. Wien Med Wochenschr 2014; 164 (1-2): 15–24
Suh KT, Kim SW, Roh HL, Youn MS, Jung JS. Decreased osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in alcohol-induced osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005; (431): 220–225
Lorentzon M, Mellström D, Haug E, Ohlsson C. Smoking is associated with lower bone mineral density and reduced cortical thickness in young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92(2): 497–503
Dorn LD, Beal SJ, Kalkwarf HJ, Pabst S, Noll JG, Susman EJ. Longitudinal impact of substance use and depressive symptoms on bone accrual among girls aged 11–19 years. J Adolesc Health 2013; 52(4): 393–399
Rudäng R, Darelid A, Nilsson M, Nilsson S, Mellström D, Ohlsson C, Lorentzon M. Smoking is associated with impaired bone mass development in young adult men: a 5-year longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res 2012; 27(10): 2189–2197
Lucas R, Fraga S, Ramos E, Barros H. Early initiation of smoking and alcohol drinking as a predictor of lower forearm bone mineral density in late adolescence: a cohort study in girls. PLoS One 2012; 7(10): e46940
Winther A, Dennison E, Ahmed LA, Furberg AS, Grimnes G, Jorde R, Gjesdal CG, Emaus N. The Tromsø Study: Fit Futures: a study of Norwegian adolescents’ lifestyle and bone health. Arch Osteoporos 2014; 9(1): 185
Dorn LD, Pabst S, Sontag LM, Kalkwarf HJ, Hillman JB, Susman EJ. Bone mass, depressive, and anxiety symptoms in adolescent girls: variation by smoking and alcohol use. J Adolesc Health 2011; 49(5): 498–504
Lucas R, Fraga S, Ramos E, Barros H. Early initiation of smoking and alcohol drinking as a predictor of lower forearm bone mineral density in late adolescence: a cohort study in girls. PLoS One 2012; 7(10): e46940
Eleftheriou KI, Rawal JS, James LE, Payne JR, Loosemore M, Pennell DJ, World M, Drenos F, Haddad FS, Humphries SE, Sanders J, Montgomery HE. Bone structure and geometry in young men: the influence of smoking, alcohol intake and physical activity. Bone 2013; 52(1): 17–26
Canalis E, Mazziotti G, Giustina A, Bilezikian JP. Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: pathophysiology and therapy. Osteoporos Int 2007; 18(10): 1319–1328
Aimaretti G, Corneli G, Rovere S, Croce CG, Ghigo E, Procopio M. Is GH therapy useful to preserve bone mass in transition-phase patients with GH deficiency? J Endocrinol Invest 2005; 28(10 Suppl): 28–32
Antonopoulou M, Bahtiyar G, Banerji MA, Sacerdote AS. Diabetes and bone health. Maturitas 2013; 76(3): 253–259
Mirza F, Canalis E. Management of endocrine disease: secondary osteoporosis: pathophysiology and management. Eur J Endocrinol 2015; 173(3): R131–R151
Duerksen DR, Leslie WD. Positive celiac disease serology and reduced bone mineral density in adult women. Can J Gastroenterol 2010; 24(2): 103–107
Heikkilä K, Pearce J, Mäki M, Kaukinen K. Celiac disease and bone fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015; 100(1): 25–34
Di Stefano M, Mengoli C, Bergonzi M, Corazza GR. Bone mass and mineral metabolism alterations in adult celiac disease: pathophysiology and clinical approach. Nutrients 2013; 5(11): 4786–4799
Laakso S, Valta H, Verkasalo M, Toiviainen-Salo S, Makitie O. Compromised peak bone mass in patients with inflammatory bowel disease—a prospective study. J Pediatr 2014; 164(6): 1436–1443.e1
Faje AT, Karim L, Taylor A, Lee H, Miller KK, Mendes N, Meenaghan E, Goldstein MA, Bouxsein ML, Misra M, Klibanski A. Adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa have impaired cortical and trabecular microarchitecture and lower estimated bone strength at the distal radius. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2013; 98(5): 1923–1929
Geusens PP, Landewé RB, Garnero P, Chen D, Dunstan CR, Lems WF, Stinissen P, van der Heijde DM, van der Linden S, Boers M. The ratio of circulating osteoprotegerin to RANKL in early rheumatoid arthritis predicts later joint destruction. Arthritis Rheum 2006; 54(6): 1772–1777
Magrey MN, Khan MA. The paradox of bone formation and bone loss in ankylosing spondylitis: evolving new concepts of bone formation and future trends in management. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2017; 19(4): 17
Gupta S, Ahsan I, Mahfooz N, Abdelhamid N, Ramanathan M, Weinstock-Guttman B. Osteoporosis and multiple sclerosis: risk factors, pathophysiology, and therapeutic interventions. CNS Drugs 2014; 28(8): 731–742
Ye S, Wu R, Wu J. Multiple sclerosis and fracture. Int J Neurosci 2013; 123(9): 609–616
Coe FL, Worcester EM, Evan AP. Idiopathic hypercalciuria and formation of calcium renal stones. Nat Rev Nephrol 2016; 12(9): 519–533
Khairallah P, Nickolas TL. Updates in CKD-associated osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 2018; 16(6): 712–723
Sharma S, Gupta A, Saxena S. Comprehensive clinical approach to renal tubular acidosis. Clin Exp Nephrol 2015; 19(4): 556–561
Fitzpatrick LA. Pathophysiology of bone loss in patients receiving anticonvulsant therapy. Epilepsy Behav 2004; 5(Suppl 2): 3–15
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (No. LR17H070001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81871831). The funding agencies had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, and decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. We thank the peer reviewers for their thorough and helpful review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Xiaowei Zhu and Houfeng Zheng declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This manuscript is a review article and does not involve a research protocol requiring approval by the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Zheng, H. Factors influencing peak bone mass gain. Front. Med. 15, 53–69 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0748-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0748-y