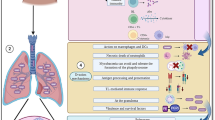
Abstract
The protective ability of host defense system is largely dependent on germ-line encoded pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs). These PRRs respond to a variety of exogenous pathogens or endogenous danger signals, by recognizing some highly conserved structures such as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and danger/damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs). The most studied PRRs are Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Activation of TLRs triggers production of inflammatory cytokines and type I interferons (IFNs) via myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88)-dependent or -independent signaling respectively, thereby modulating innate and adaptive immunity, as well as inflammatory responses. This review introduces the classification, structure, and specific ligands of TLRs, and focuses on their signal pathways and biological activities, as well as clinical relevance. These studies of TLRs in the innate immune system have implications for the prevention and treatment of a variety of infectious diseases, including tuberculosis (TB), microbial keratitis, and hepatitis B and C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Medzhitov R, Janeway C Jr. Innate immunity. N Engl J Med, 2000, 343(5): 338–344
Janeway C A Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol, 2002, 20: 197–216
Medzhitov R, Janeway C A Jr. How does the immune system distinguish self from nonself? Semin Immunol, 2000, 12(3): 185–188, discussion 257–344
Foell D, Wittkowski H, Roth J. Mechanisms of disease: a ‘DAMP’ view of inflammatory arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol, 2007, 3(7): 382–390
Fraser I P, Koziel H, Ezekowitz R A. The serum mannose-binding protein and the macrophage mannose receptor are pattern recognition molecules that link innate and adaptive immunity. Semin Immunol, 1998, 10(5): 363–372
Bowdish D M, Gordon S. Conserved domains of the class A scavenger receptors: evolution and function. Immunol Rev, 2009, 227(1): 19–31
Beutler B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature, 2004, 430(6996): 257–263
Bianchi M E. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol, 2007, 81(1): 1–5
Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol, 2004, 4(7): 499–511
Wheeler D S, Chase M A, Senft A P, Poynter S E, Wong H R, Page K. Extracellular Hsp72, an endogenous DAMP, is released by virally infected airway epithelial cells and activates neutrophils via Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4. Respir Res, 2009, 10: 31
Halayko A J, Ghavami S. S100A8/A9: a mediator of severe asthma pathogenesis and morbidity? Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2009, 87(10): 743–755
Jin M S, Lee J O. Structures of the toll-like receptor family and its ligand complexes. Immunity, 2008, 29(2): 182–191
O’Neill L A, Bowie A G. The family of five: TIR-domaincontaining adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol, 2007, 7(5): 353–364
Dowling D, Hamilton C M, O’Neill S M. A comparative analysis of cytokine responses, cell surface marker expression and MAPKs in DCs matured with LPS compared with a panel of TLR ligands. Cytokine, 2008, 41(3): 254–262
Lien E, Chow J C, Hawkins L D, McGuinness P D, Miyake K, Espevik T, Gusovsky F, Golenbock D T. A novel synthetic acyclic lipid A-like agonist activates cells via the lipopolysaccharide/tolllike receptor 4 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(3): 1873–1880
Wang D, Lou J, Ouyang C, Chen W, Liu Y, Liu X, Cao X, Wang J, Lu L. Ras-related protein Rab10 facilitates TLR4 signaling by promoting replenishment of TLR4 onto the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010, 107(31): 13806–13811
Lang L L, Wang L, Liu L. Exogenous MD-2 Confers Lipopolysaccharide Responsiveness to Human Corneal Epithelial Cells with Intracellular Expression of TLR4 and CD14. Inflammation, 2010 Aug 11. doi: 10:1007/s10753-010-9244-x
Aliprantis A O, Yang R B, Mark M R, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf J D, Klimpel G R, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science, 1999, 285(5428): 736–739
Schwandner R, Dziarski R, Wesche H, Rothe M, Kirschning C J. Peptidoglycan- and lipoteichoic acid-induced cell activation is mediated by toll-like receptor 2. J Biol Chem, 1999, 274(25): 17406–17409
Takeda K, Takeuchi O, Akira S. Recognition of lipopeptides by Toll-like receptors. J Endotoxin Res, 2002, 8(6): 459–463
Ozinsky A, Underhill D M, Fontenot J D, Hajjar A M, Smith K D, Wilson C B, Schroeder L, Aderem A. The repertoire for pattern recognition of pathogens by the innate immune system is defined by cooperation between toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000, 97(25): 13766–13771
Nakao Y, Funami K, Kikkawa S, Taniguchi M, Nishiguchi M, Fukumori Y, Seya T, Matsumoto M. Surface-expressed TLR6 participates in the recognition of diacylated lipopeptide and peptidoglycan in human cells. J Immunol, 2005, 174(3): 1566–1573
Henneke P, Morath S, Uematsu S, Weichert S, Pfitzenmaier M, Takeuchi O, Müller A, Poyart C, Akira S, Berner R, Teti G, Geyer A, Hartung T, Trieu-Cuot P, Kasper D L, Golenbock D T. Role of lipoteichoic acid in the phagocyte response to group B streptococcus. J Immunol, 2005, 174(10): 6449–6455
von Aulock S, Morath S, Hareng L, Knapp S, van Kessel K P, van Strijp J A, Hartung T. Lipoteichoic acid from Staphylococcus aureus is a potent stimulus for neutrophil recruitment. Immunobiology, 2003, 208(4): 413–422
Shimizu T, Kida Y, Kuwano K. A triacylated lipoprotein from Mycoplasma genitalium activates NF-kappaB through Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1) and TLR2. Infect Immun, 2008, 76(8): 3672–3678
Shimizu T, Kida Y, Kuwano K. Triacylated lipoproteins derived from Mycoplasma pneumoniae activate nuclear factor-kappaB through toll-like receptors 1 and 2. Immunology, 2007, 121(4): 473–483
Hayashi F, Smith K D, Ozinsky A, Hawn T R, Yi E C, Goodlett D R, Eng J K, Akira S, Underhill D M, Aderem A. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature, 2001, 410(6832): 1099–1103
Yarovinsky F, Zhang D, Andersen J F, Bannenberg G L, Serhan C N, Hayden M S, Hieny S, Sutterwala F S, Flavell R A, Ghosh S, Sher A. TLR11 activation of dendritic cells by a protozoan profilinlike protein. Science, 2005, 308(5728): 1626–1629
Zhang D, Zhang G, Hayden MS, Greenblatt MB, Bussey C, Flavell R A, Ghosh S. A toll-like receptor that prevents infection by uropathogenic bacteria. Science, 2004, 303(5663): 1522–1526
Liu L, Botos I, Wang Y, Leonard J N, Shiloach J, Segal DM, Davies D R. Structural basis of toll-like receptor 3 signaling with doublestranded RNA. Science, 2008, 320(5874): 379–381
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K, Akira S A. A Tolllike receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature, 2000, 408(6813): 740–745
Gantier M P, Tong S, Behlke M A, Xu D, Phipps S, Foster P S, Williams B R. TLR7 is involved in sequence-specific sensing of single-stranded RNAs in human macrophages. J Immunol, 2008, 180(4): 2117–2124
Hammadi A, Billard C, Faussat AM, Kolb J P. Stimulation of iNOS expression and apoptosis resistance in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells through engagement of Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR-7) and NF-kappaB activation. Nitric Oxide, 2008, 19(2): 138–145
Pivarcsi A, Nagy I, Koreck A, Kis K, Kenderessy-Szabo A, Szell M, Dobozy A, Kemeny L. Microbial compounds induce the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and human betadefensin-2 in vaginal epithelial cells. Microbes Infect, 2005, 7(9–10): 1117–1127
Becker M N, Diamond G, Verghese M W, Randell S H. CD14-dependent lipopolysaccharide-induced beta-defensin-2 expression in human tracheobronchial epithelium. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(38): 29731–29736
Alter G, Suscovich T J, Teigen N, Meier A, Streeck H, Brander C, Altfeld M. Single-stranded RNA derived from HIV-1 serves as a potent activator of NK cells. J Immunol, 2007, 178(12): 7658–7666
Wang J, Shao Y, Bennett T A, Shankar R A, Wightman P D, Reddy L G. The functional effects of physical interactions among Toll-like receptors 7, 8, and 9. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(49): 37427–37434
Yarovinsky F, Sher A. Toll-like receptor recognition of Toxoplasma gondii. Int J Parasitol, 2006, 36(3): 255–259
Hasan U, Chaffois C, Gaillard C, Saulnier V, Merck E, Tancredi S, Guiet C, Brière F, Vlach J, Lebecque S, Trinchieri G, Bates E E. Human TLR10 is a functional receptor, expressed by B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells, which activates gene transcription through MyD88. J Immunol, 2005, 174(5): 2942–2950
Guan Y, Ranoa D R, Jiang S, Mutha S K, Li X, Baudry J, Tapping R I. Human TLRs 10 and 1 share common mechanisms of innate immune sensing but not signaling. J Immunol, 2010, 184(9): 5094–5103
Schnare M, Barton G M, Holt A C, Takeda K, Akira S, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors control activation of adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol, 2001, 2(10): 947–950
Vora P, Youdim A, Thomas L S, Fukata M, Tesfay S Y, Lukasek K, Michelsen K S, Wada A, Hirayama T, Arditi M, Abreu M T. Betadefensin-2 expression is regulated by TLR signaling in intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol, 2004, 173(9): 5398–5405
Wu M, McClellan S A, Barrett R P, Hazlett L D. Beta-defensin-2 promotes resistance against infection with P. aeruginosa. J Immunol, 2009, 182(3): 1609–1616
Wu M, McClellan S A, Barrett R P, Zhang Y, Hazlett L D. Betadefensins 2 and 3 together promote resistance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. J Immunol, 2009, 183(12): 8054–8060
Chen X M, O’Hara S P, Nelson J B, Splinter P L, Small A J, Tietz P S, Limper A H, LaRusso N F. Multiple TLRs are expressed in human cholangiocytes and mediate host epithelial defense responses to Cryptosporidium parvum via activation of NF-kappaB. J Immunol, 2005, 175(11): 7447–7456
Kumar A, Yin J, Zhang J, Yu F S. Modulation of corneal epithelial innate immune response to pseudomonas infection by flagellin pretreatment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2007, 48(10): 4664–4670
Funderburg N, Lederman M M, Feng Z, Drage M G, Jadlowsky J, Harding C V, Weinberg A, Sieg S F. Human-defensin-3 activates professional antigen-presenting cells via Toll-like receptors 1 and 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2007, 104(47): 18631–18635
Biragyn A, Ruffini P A, Leifer C A, Klyushnenkova E, Shakhov A, Chertov O, Shirakawa A K, Farber J M, Segal D M, Oppenheim J J, Kwak L W. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by beta-defensin 2. Science, 2002, 298(5595): 1025–1029
Davila S, Hibberd M L, Hari Dass R, Wong H E, Sahiratmadja E, Bonnard C, Alisjahbana B, Szeszko J S, Balabanova Y, Drobniewski F, van Crevel R, van de Vosse E, Nejentsev S, Ottenhoff T H, Seielstad M. Genetic association and expression studies indicate a role of toll-like receptor 8 in pulmonary tuberculosis. PLoS Genet, 2008, 4(10): e1000218
Ma X, Liu Y, Gowen B B, Graviss E A, Clark A G, Musser J M. Full-exon resequencing reveals toll-like receptor variants contribute to human susceptibility to tuberculosis disease. PLoS One, 2007, 2(12): e1318
Velez D R, Wejse C, Stryjewski M E, Abbate E, Hulme W F, Myers J L, Estevan R, Patillo S G, Olesen R, Tacconelli A, Sirugo G, Gilbert J R, Hamilton C D, Scott WK. Variants in toll-like receptors 2 and 9 influence susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in Caucasians, African-Americans, and West Africans. Hum Genet, 2010, 127(1): 65–73
Abel B, Thieblemont N, Quesniaux V J, Brown N, Mpagi J, Miyake K, Bihl F, Ryffel B. Toll-like receptor 4 expression is required to control chronic Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in mice. J Immunol, 2002, 169(6): 3155–3162
Yang C S, Shin DM, Lee HM, Son JW, Lee S J, Akira S, Gougerot-Pocidalo M A, El-Benna J, Ichijo H, Jo E K. ASK1-p38 MAPKp47phox activation is essential for inflammatory responses during tuberculosis via TLR2-ROS signalling. Cell Microbiol, 2008, 10(3): 741–754
Castiblanco J, Varela D C, Castaño-Rodríguez N, Rojas-Villarraga A, Hincapié M E, Anaya J M. TIRAP (MAL) S180L polymorphism is a common protective factor against developing tuberculosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Infect Genet Evol, 2008, 8(5): 541–544
Dissanayeke S R, Levin S, Pienaar S, Wood K, Eley B, Beatty D, Henderson H, Anderson S, Levin M. Polymorphic variation in TIRAP is not associated with susceptibility to childhood TB but may determine susceptibility to TBM in some ethnic groups. PLoS One, 2009, 4(8): e6698
Doherty T M, Arditi M T B. TB, or not TB: that is the question — does TLR signaling hold the answer? J Clin Invest, 2004, 114(12): 1699–1703
Hazlett L D. Corneal response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2004, 23(1): 1–30
Jin X, Lin Z, Xie X. The delayed response of Toll-like receptors may relate to Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis exacerbating rapidly at the early stages of infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2010, 29(2): 231–238
Gao N, Kumar A, Jyot J, Yu F S. Flagellin-induced corneal antimicrobial peptide production and wound repair involve a novel NF-kappaB-independent and EGFR-dependent pathway. PLoS One, 2010, 5(2): e9351
Hazlett L D, McClellan S, Kwon B, Barrett R. Increased severity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa corneal infection in strains of mice designated as Th1 versus Th2 responsive. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2000, 41(3): 805–810
Huang X, Barrett R P, McClellan S A, Hazlett L D. Silencing Tolllike receptor-9 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2005, 46(11): 4209–4216
Huang X, Du W, McClellan S A, Barrett R P, Hazlett L D. TLR4 is required for host resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2006, 47(11): 4910–4916
Huang X, Hazlett L D, Du W, Barrett R P. SIGIRR promotes resistance against Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis by downregulating type-1 immunity and IL-1R1 and TLR4 signaling. J Immunol, 2006, 177(1): 548–556
Huang X, Du W, Barrett R P, Hazlett L D. ST2 is essential for Th2 responsiveness and resistance to pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2007, 48(10): 4626–4633
Lok A S, McMahon B J, 0. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology, 2001, 34(6): 1225–1241
Rantala M, van de Laar M J. Surveillance and epidemiology of hepatitis B and C in Europe-a review. Euro Surveill, 2008, 13(21): 13
Brown R A, Gralewski J H, Eid A J, Knoll B M, Finberg R W, Razonable R R. R753Q single-nucleotide polymorphism impairs toll-like receptor 2 recognition of hepatitis C virus core and nonstructural 3 proteins. Transplantation, 2010, 89(7): 811–815
Li Y, Chang M, Abar O, Garcia V, Rowland C, Catanese J, Ross D, Broder S, Shiffman M, Cheung R, Wright T, Friedman S L, Sninsky J. Multiple variants in toll-like receptor 4 gene modulate risk of liver fibrosis in Caucasians with chronic hepatitis C infection. J Hepatol, 2009, 51(4): 750–757
Askar E, Bregadze R, Mertens J, Schweyer S, Rosenberger A, Ramadori G, Mihm S. TLR3 gene polymorphisms and liver disease manifestations in chronic hepatitis C. J Med Virol, 2009, 81(7): 1204–1211
Schott E, Witt H, Neumann K, Taube S, Oh D Y, Schreier E, Vierich S, Puhl G, Bergk A, Halangk J, Weich V, Wiedenmann B, Berg T A. A Toll-like receptor 7 single nucleotide polymorphism protects from advanced inflammation and fibrosis in male patients with chronic HCV-infection. J Hepatol, 2007, 47(2): 203–211
Zhou J, Huang Y, Tian D, Xu D, Chen M, Wu H. Expression of tolllike receptor 9 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with different hepatitis B and C viral loads. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2009, 29(3): 313–317
Wang J P, Zhang Y, Wei X, Li J, Nan X P, Yu H T, Li Y, Wang P Z, Bai X F. Circulating Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2, TLR4, and regulatory T cells in patients with chronic hepatitis C. APMIS, 2010, 118(4): 261–270
Lester R T, Yao X D, Ball T B, McKinnon L R, Kaul R, Wachihi C, Jaoko W, Plummer F A, Rosenthal K L. Toll-like receptor expression and responsiveness are increased in viraemic HIV-1 infection. AIDS, 2008, 22(6): 685–694
Ahmed N, Hayashi T, Hasegawa A, Furukawa H, Okamura N, Chida T, Masuda T, Kannagi M. Suppression of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) replication in macrophages by commensal bacteria preferentially stimulating toll-like receptor 4. J Gen Virol, 2010, 91(Pt 11): 2804–2813
Pine S O, McElrath M J, Bochud P Y. Polymorphisms in toll-like receptor 4 and toll-like receptor 9 influence viral load in a seroincident cohort of HIV-1-infected individuals. AIDS, 2009, 23(18): 2387–2395
Báfica A, Scanga C A, Schito M, Chaussabel D, Sher A. Influence of coinfecting pathogens on HIV expression: evidence for a role of Toll-like receptors. J Immunol, 2004, 172(12): 7229–7234
Bochud P Y, Hersberger M, Taffé P, Bochud M, Stein C M, Rodrigues S D, Calandra T, Francioli P, Telenti A, Speck R F, Aderem A, 0. Polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor 9 influence the clinical course of HIV-1 infection. AIDS, 2007, 21(4): 441–446
Soriano-Sarabia N, Vallejo A, Ramírez-Lorca R, Rodríguez Mdel M, Salinas A, Pulido I, Sáez M E, Leal M. Influence of the Toll-like receptor 9 1635A/G polymorphism on the CD4 count, HIV viral load, and clinical progression. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr, 2008, 49(2): 128–135
Guillot L, Le Goffic R, Bloch S, Escriou N, Akira S, Chignard M, Si-Tahar M. Involvement of toll-like receptor 3 in the immune response of lung epithelial cells to double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J Biol Chem, 2005, 280(7): 5571–5580
Marshall-Clarke S, Tasker L, Buchatska O, Downes J, Pennock J, Wharton S, Borrow P, Wiseman D Z. Influenza H2 haemagglutinin activates B cells via a MyD88-dependent pathway. Eur J Immunol, 2006, 36(1): 95–106
Wang J P, Bowen G N, Padden C, Cerny A, Finberg R W, Newburger P E, Kurt-Jones E A. Toll-like receptor-mediated activation of neutrophils by influenza A virus. Blood, 2008, 112(5): 2028–2034
Pierik M, Joossens S, Van Steen K, Van Schuerbeek N, Vlietinck R, Rutgeerts P, Vermeire S. Toll-like receptor-1, -2, and-6 polymorphisms influence disease extension in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2006, 12(1): 1–8
Török H P, Glas J, Endres I, Tonenchi L, Teshome M Y, Wetzke M, Klein W, Lohse P, Ochsenkühn T, Folwaczny M, Göke B, Folwaczny C, Müller-Myhsok B, Brand S. Epistasis between Tolllike receptor-9 polymorphisms and variants in NOD2 and IL23R modulates susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol, 2009, 104(7): 1723–1733
Franchimont D, Vermeire S, El Housni H, Pierik M, Van Steen K, Gustot T, Quertinmont E, Abramowicz M, Van Gossum A, Devière J, Rutgeerts P. Deficient host-bacteria interactions in inflammatory bowel disease? The toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 Asp299gly polymorphism is associated with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Gut, 2004, 53(7): 987–992
Gewirtz A T, Vijay-Kumar M, Brant S R, Duerr R H, Nicolae D L, Cho J H. Dominant-negative TLR5 polymorphism reduces adaptive immune response to flagellin and negatively associates with Crohn’s disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2006, 290(6): G1157–G1163
Leoratti F M, Farias L, Alves F P, Suarez-Mútis M C, Coura J R, Kalil J, Camargo E P, Moraes S L, Ramasawmy R. Variants in the toll-like receptor signaling pathway and clinical outcomes of malaria. J Infect Dis, 2008, 198(5): 772–780
Hamann L, Bedu-Addo G, Eggelte T A, Schumann R R, Mockenhaupt F P. The toll-like receptor 1 variant S248N influences placental malaria. Infect Genet Evol, 2010, 10(6): 785–789
Basu M, Maji A K, Chakraborty A, Banerjee R, Mullick S, Saha P, Das S, Kanjilal S D, Sengupta S. Genetic association of Toll-likereceptor 4 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha polymorphisms with Plasmodium falciparum blood infection levels. Infect Genet Evol, 2010, 10(5): 686–696
Chen J, Xu W, Zhou T, Ding Y, Duan J, Huang F. Inhibitory role of toll-like receptors agonists in Plasmodium yoelii liver stage development. Parasite Immunol, 2009, 31(8): 466–473
Greene J A, Moormann AM, Vulule J, Bockarie MJ, Zimmerman P A, Kazura JW. Toll-like receptor polymorphisms in malaria-endemic populations. Malar J, 2009, 8: 50
Crompton P D, Mircetic M, Weiss G, Baughman A, Huang C Y, Topham D J, Treanor J J, Sanz I, Lee F E, Durbin A P, Miura K, Narum D L, Ellis R D, Malkin E, Mullen G E, Miller L H, Martin L B, Pierce S K. The TLR9 ligand CpG promotes the acquisition of Plasmodium falciparum-specific memory B cells in malaria-naive individuals. J Immunol, 2009, 182(5): 3318–3326
Sam-Agudu N A, Greene J A, Opoka R O, Kazura JW, Boivin M J, Zimmerman P A, Riedesel M A, Bergemann T L, Schimmenti L A, John C C. TLR9 polymorphisms are associated with altered IFNgamma levels in children with cerebral malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2010, 82(4): 548–555
Wong S H, Gochhait S, Malhotra D, Pettersson F H, Teo Y Y, Khor C C, Rautanen A, Chapman S J, Mills T C, Srivastava A, Rudko A, Freidin M B, Puzyrev V P, Ali S, Aggarwal S, Chopra R, Reddy B S, Garg V K, Roy S, Meisner S, Hazra S K, Saha B, Floyd S, Keating B J, Kim C, Fairfax B P, Knight J C, Hill P C, Adegbola R A, Hakonarson H, Fine P E, Pitchappan R M, Bamezai R N, Hill A V, Vannberg F O. Leprosy and the adaptation of human toll-like receptor 1. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6: e1000979
Schuring R P, Hamann L, Faber W R, Pahan D, Richardus J H, Schumann R R, Oskam L. Polymorphism N248S in the human Tolllike receptor 1 gene is related to leprosy and leprosy reactions. J Infect Dis, 2009, 199(12): 1816–1819
Krutzik S R, Ochoa MT, Sieling P A, Uematsu S, Ng YW, Legaspi A, Liu P T, Cole S T, Godowski P J, Maeda Y, Sarno E N, Norgard M V, Brennan P J, Akira S, Rea T H, Modlin R L. Activation and regulation of Toll-like receptors 2 and 1 in human leprosy. Nat Med, 2003, 9(5): 525–532
Johnson C M, Lyle E A, Omueti K O, Stepensky V A, Yegin O, Alpsoy E, Hamann L, Schumann R R, Tapping R I. Cutting edge: A common polymorphism impairs cell surface trafficking and functional responses of TLR1 but protects against leprosy. J Immunol, 2007, 178(12): 7520–7524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, MH., Zhang, P. & Huang, X. Toll-like receptors in innate immunity and infectious diseases. Front. Med. China 4, 385–393 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0600-x