Abstract
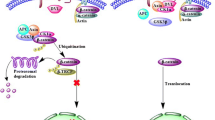
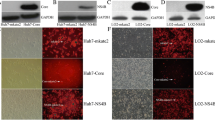
β-catenin is a key molecule involved in both cell-cell adhesion and Wnt signaling pathway. In our study, we found that, in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), β-catenin was correlated with hepatitis B virus (HBV) X gene encoded protein, which is essential for HBV infectivity and is a potential cofactor in viral carcinogenesis. The expression levels of wild-type β-catenin and E-cadherin were decreased in HepG2 cells expressing hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx), accompanied by destabilization of adherens junction. Reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR), Northern and Western blot showed that reduction of wild-type β-catenin expression involved degradation of the protein. However, RNA interference (RNAi) and luciferase assay indicated that HBx enhanced β-catenin mediated signaling in HepG2 cells. In addition, immunohistochemical and Western blot analysis of β-catenin revealed that a decrease in the β-catenin protein level was found in 58.3% of HBV-related HCCs versus 19.2% of non-HBV-related tumors. Our data suggest that the expression of HBx contributed to the development of HCC, in part, by repressing the wild-type β-catenin expression and enforcing β-catenin-dependent signaling pathway, thus inducing cellular changes leading to acquisition of metastatic and/or proliferation properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schafer D F, Sorrell M F. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet, 1999, 353(9160): 1253–1257
Marchio A, Meddeb M, Pineau P, Danglot G, Tiollais P, Bernheim A, Dejean A. Recurrent chromosomal abnormalities in hepatocellular carcinoma detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer, 1997, 18(1): 59–65
Feitelson M A, Duan L X. Hepatitis B virus X antigen in the pathogenesis of chronic infections and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol, 1997, 150(4): 1141–1157
Su Q, Schröder C H, Hofmann W J, Otto G, Pichlmayr R, Bannasch P. Expression of hepatitis B virus X protein in HBV-infected human livers and hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology, 1998, 27(4): 1109–1120
Kim C M, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T, Jay G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature, 1991, 351(6324): 317–320
Slagle B L, Lee T H, Medina D, Finegold M J, Butel J S. Increased sensitivity to the hepatocarcinogen diethylnitrosamine in transgenic mice carrying the hepatitis B virus X gene. Mol Carcinog, 1996, 15(4): 261–269
Terradillos O, Billet O, Renard C A, Levy R, Molina T, Briand P, Buendia M A. The hepatitis B virus X gene potentiates c-mycinduced liver oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Oncogene, 1997, 14(4): 395–404
Benn J, Schneider R J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates Ras-GTP complex formation and establishes a Ras, Raf, MAP kinase signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1994, 91(22): 10350–10354
Natoli G, Avantaggiati M L, Chirillo P, Puri P L, Ianni A, Balsano C, Levrero M. Ras- and Raf-dependent activation of c-jun transcriptional activity by the hepatitis B virus transactivator pX. Oncogene, 1994, 9(10): 2837–2843
Su F, Schneider R J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates transcription factor NF-kappaB by acting on multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors of rel-related proteins. J Virol, 1996, 70(7): 4558–4566
Benn J, Su F, Doria M, Schneider R J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein induces transcription factor AP-1 by activation of extracellular signal-regulated and c-Jun N-terminal mitogen-activated protein kinases. J Virol, 1996, 70(8): 4978–4985
Mahé Y, Mukaida N, Kuno K, Akiyama M, Ikeda N, Matsushima K, Murakami S. Hepatitis B virus X protein transactivates human interleukin-8 gene through acting on nuclear factor kB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-like cis-elements. J Biol Chem, 1991, 266(21): 13759–13763
Gottlob K, Fulco M, Levrero M, Graessmann A. The hepatitis B virus HBx protein inhibits caspase 3 activity. J Biol Chem, 1998, 273(50): 33347–33353
Lee T H, Elledge S J, Butel J S. Hepatitis B virus X protein interacts with a probable cellular DNA repair protein. J Virol, 1995, 69(2): 1107–1114
Ueda H, Ullrich S J, Gangemi J D, Kappel C A, Ngo L, Feitelson M A, Jay G. Functional inactivation but not structural mutation of p53 causes liver cancer. Nat Genet, 1995, 9(1): 41–47
Tlsty T D. Cell-adhesion-dependent influences on genomic instability and carcinogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 1998, 10(5): 647–653
Kemler R. From cadherins to catenins: cytoplasmic protein interactions and regulation of cell adhesion. Trends Genet, 1993, 9(9): 317–321
Kozyraki R, Scoazec J Y, Flejou J F, D’Errico A, Bedossa P, Terris B, Fiorentino M, Bringuier A F, Grigioni W F, Feldmann G. Expression of cadherins and alpha-catenin in primary epithelial tumors of the liver. Gastroenterology, 1996, 110(4): 1137–1149
Wei Y, Van Nhieu J T, Prigent S, Srivatanakul P, Tiollais P, Buendia M A. Altered expression of E-cadherin in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlations with genetic alterations, β-catenin expression, and clinical features. Hepatology, 2002, 36(3): 692–701
Peifer M. β-catenin as oncogene: the smoking gun. Science, 1997, 275(5307): 1752–1753
Moon R T, Bowerman B, Boutros M, Perrimon N. The promise and perils of Wnt signaling through β-catenin. Science, 2002, 296(5573): 1644–1646
He T C, Sparks A B, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa L T, Morin P J, Vogelstein B, Kinzler K W. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science, 1998, 281(5382): 1509–1512
Tetsu O, McCormick F. β-catenin regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature, 1999, 398(6726): 422–426
Liu C, Li Y, Semenov M, Han C, Baeg G H, Tan Y, Zhang Z, Lin X, He X. Control of β-catenin phosphorylation/degradation by a dualkinase mechanism. Cell, 2002, 108(6): 837–847
Bienz M, Clevers H. Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell, 2000, 103(2): 311–320
de La Coste A, Romagnolo B, Billuart P, Renard C A, Buendia M A, Soubrane O, Fabre M, Chelly J, Beldjord C, Kahn A, Perret C. Somatic mutations of the β-catenin gene are frequent in mouse and human hepatocellular carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1998, 95(15): 8847–8851
Samowitz W S, Powers M D, Spirio L N, Nollet F, van Roy F, Slattery M L. β-catenin mutations are more frequent in small colorectal adenomas than in larger adenomas and invasive carcinomas. Cancer Res, 1999, 59(7): 1442–1444
Laurent-Puig P, Legoix P, Bluteau O, Belghiti J, Franco D, Binot F, Monges G, Thomas G, Bioulac-Sage P, Zucman-Rossi J. Genetic alterations associated with hepatocellular carcinomas define distinct pathways of hepatocarcinogenesis. Gastroenterology, 2001, 120(7): 1763–1773
Hsu H C, Jeng YM, Mao T L, Chu J S, Lai P L, Peng S Y. β-catenin mutations are associated with a subset of low-stage hepatocellular carcinoma negative for hepatitis B virus and with favorable prognosis. Am J Pathol, 2000, 157(3): 763–770
Huang H, Fujii H, Sankila A, Mahler-Araujo B M, Matsuda M, Cathomas G, Ohgaki H. β-catenin mutations are frequent in human hepatocellular carcinomas associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Am J Pathol, 1999, 155(6): 1795–1801
Koch A, Denkhaus D, Albrecht S, Leuschner I, von Schweinitz D, Pietsch T. Childhood hepatoblastomas frequently carry a mutated degradation targeting box of the β-catenin gene. Cancer Res, 1999, 59(2): 269–273
Lian Z, Liu J, Pan J, Satiroglu Tufan N L, Zhu M, Arbuthnot P, Kew M, Clayton M M, Feitelson M A. A cellular gene up-regulated by hepatitis B virus-encoded X antigen promotes hepatocellular growth and survival. Hepatology, 2001, 34(1): 146–157
Lian Z, Pan J, Liu J, Zhang S, Zhu M, Arbuthnot P, Kew M, Feitelson M A. The translation initiation factor, hu-Sui1 may be a target of hepatitis B X antigen in hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncogene, 1999, 18(9): 1677–1687
Yan H X, He Y Q, Dong H, Zhang P, Zeng J Z, Cao H F, Wu M C, Wang H Y. Physical and functional interaction between receptorlike protein tyrosine phosphatase PCP-2 and β-catenin. Biochemistry, 2002, 41(52): 15854–15860
Andrews N C, Faller D V. A rapid micropreparation technique for extraction of DNA-binding proteins from limiting numbers of mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res, 1991, 19(9): 2499–2506
Wang H, Lian Z, Lerch M M, Chen Z, Xie W, Ullrich A. Characterization of PCP-2, a novel receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase of the MAM domain family. Oncogene, 1996, 12(12): 2555–2562
Carruba G, Cervello M, Miceli M D, Farruggio R, Notarbartolo M, Virruso L, Giannitrapani L, Gambino R, Montalto G, Castagnetta L. Truncated form of β-catenin and reduced expression of wild-type catenins feature HepG2 human liver cancer cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1999, 886: 212–216
Su Q, Schröder C H, Hofmann W J, Otto G, Pichlmayr R, Bannasch P. Expression of hepatitis B virus X protein in HBV-infected human livers and hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology, 1998, 27(4): 1109–1120
Wang W L, London W T, Feitelson M A. Hepatitis B x antigen in hepatitis B virus carrier patients with liver cancer. Cancer Res, 1991, 51(18): 4971–4977
Huber A H, Stewart D B, Laurents D V, Nelson W J, Weis W I. The cadherin cytoplasmic domain is unstructured in the absence of β-catenin. A possible mechanism for regulating cadherin turnover. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(15): 12301–12309
Polakis P. The oncogenic activation of β-catenin. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 1999, 9(1): 15–21
Gottardi C J, Wong E, Gumbiner B M. E-cadherin suppresses cellular transformation by inhibiting β-catenin signaling in an adhesion-independent manner. J Cell Biol, 2001, 153(5): 1049–1060
Staal F J, Noort Mv M, Strous G J, Clevers H C. Wnt signals are transmitted through N-terminally dephosphorylated β-catenin. EMBO Rep, 2002, 3(1): 63–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Hu, L., Li, L. et al. Dysregulation of β-catenin by hepatitis B virus X protein in HBV-infected human hepatocellular carcinomas. Front. Med. China 4, 399–411 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0170-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0170-y