Abstract
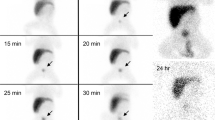
The aim of this study was to investigate the value of technetium etifenin injection (99mTc-EHIDA) hepatobiliary scintigraphy in combination with determination of bilirubin from duodenal drainage in differential diagnosis between infantile hepatitis syndrome and biliary atresia. 99mTc-EHIDA hepatobiliary scintigraphy in combination with duodenal fluid examination was used for evaluation in 84 infants with persistent infantile jaundice. For diagnosing biliary atresia, the sensitivity and specificity of scintigraphy were 100% and 74.5%, respectively; the sensitivity and specificity of scintigraphy in combination with duodenal fluid examination were 100% and 100%, respectively. In conclusion, hepatobiliary scintigraphy, which is a noninvasive, safe, valuable examination method, in combination with examination of duodenal fluid, is of value for the differential diagnosis between infantile hepatitis syndrome and biliary atresia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Z H, Dong Y C. Dynamic duodenal fluid examination for differential diagnosis of infantile continuous obstructive jaundice. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi, 2004, 42(1): 54–56 (in Chinese)
Lee C H, Wang P W, Lee T T, Tiao M M, Huang F C, Chuang J H, Shieh C S, Cheng Y F. The significance of functioning gallbladder visualization on hepatobiliary scintigraphy in infants with persistent jaundice. J Nucl Med, 2000, 41(7): 1209–1213
Gerhold J P, Klingensmith W C 3rd, Kuni C C, Lilly J R, Silverman A, Fritzberg A R, Nixt T L. Diagnosis of biliary atresia with radionuclide hepatobiliary imaging. Radiology, 1983, 146(2): 499–504
Nadel H R. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy in children. Semin Nucl Med, 1996, 26(1): 25–42
Charearnrad P, Chongsrisawat V, Tepmongkol S, Poovorawan Y. The effect of phenobarbital on the accuracy of technetium-99m diisopropyl iminodiacetic acid hepatobiliary scintigraphy in differentiating biliary atresia from neonatal hepatitis syndrome. J Med Assoc Thai, 2003, 86(Suppl 2): S189–S194
Esmaili J, Izadyar S, Karegar I, Gholamrezanezhad A. Biliary atresia in infants with prolonged cholestatic jaundice: diagnostic accuracy of hepatobiliary scintigraphy. Abdom Imaging, 2007, 32(2): 243–247
Poddar U, Bhattacharya A, Thapa B R, Mittal B R, Singh K. Ursodeoxycholic acid-augmented hepatobiliary scintigraphy in the evaluation of neonatal jaundice. J Nucl Med, 2004, 45(9): 1488–1492
Fischler B, Woxenius S, Nemeth A, Papadogiannakis N. Immunoglobulin deposits in liver tissue from infants with biliary atresia and the correlation to cytomegalovirus infection. J Pediatr Surg, 2005, 40(3): 541–546
Fjaer R B, Bruu A L, Nordbø S A. Extrahepatic bile duct atresia and viral involvement. Pediatr Transplant, 2005, 9(1): 68–73
Stipsanelli K, Koutsikos J, Papantoniou V, Arka A, Palestidis C, Tsiouris S, Manolaki A, Zerva C. Hepatobiliary scintigraphy and gamma-GT levels in the differential diagnosis of extrahepatic biliary atresia. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging, 2007, 51(1): 74–81
Greene H L, Helinek G L, Moran R, O’Neill J. A diagnostic approach to prolonged obstructive jaundice by 24-hour collection of duodenal fluid. J Pediatr, 1979, 95(3): 412–414
Faweya A G, Akinyinka O O, Sodeinde O. Duodenal intubation and aspiration test: utility in the differential diagnosis of infantile cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr, 1991, 13(3): 290–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SX., Huang, ZH. The value of radionuclide hepatobiliary scintigraphy in combination with determination of bilirubin from duodenal drainage in differential diagnosis of infantile persistent jaundice. Front. Med. China 4, 342–345 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0099-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-010-0099-1