Abstract
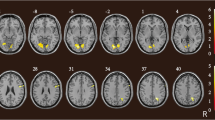
CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy is a rare white-matter encephalopathy characterized by motor and neuropsychiatric symptoms due to colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) gene mutation. Few studies have investigated the intrinsic brain alternations of patients with CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy. We aim to evaluate the structural and functional changes in those patients. Seven patients with CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy and 15 age-matched healthy controls (HCs) underwent multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), including high-resolution T1-weighted imaging, T2-weighted fluid attenuated inversion recovery imaging, diffusion-weighted imaging, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) and resting-state functional MRI. First, to detect structural alterations, the gray matter volumes were compared using voxel-based morphometry analyses. Second, DKI parametric maps were used to evaluate the white matter (WM) connectivity changes. Finally, we constructed a seed-based resting-state functional connectivity matrix based on 90 regions of interest and examined the functional network changes of CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy. Unlike the HCs, patients with CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy predominantly had morphological atrophy in the bilateral thalamus and left hippocampus. In addition, the abnormal diffusivity was mainly distributed in the splenium of the corpus callosum, periventricular regions, centrum semiovale, subcortical U-fibers and midline cortex structures. Moreover, the patients had significantly reduced functional connectivity between the bilateral caudate nucleus and their contralateral hippocampus. Therefore, in addition to hyperintensity on the T2-weighted images, CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy also showed abnormal structural and functional alterations, including subcortical atrophy and reduced functional connectivity, as well as altered diffuse parameters in the WM and subcortical regions. These findings expand our understanding of the potential pathophysiologic mechanism behind this hereditary disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF1R :
-
colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- DKI:
-
diffusion kurtosis imaging
- ALSP:
-
adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids and pigmented glia
- HDLS:
-
hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids
- POLD:
-
pigmented orthochromatic leukodystrophy
- WM:
-
white matter
- DWI:
-
diffusion-weighted imaging
- GM:
-
gray matter
- fMRI:
-
Functional MRI
- FC:
-
functional connectivity
- HCs:
-
healthy controls
- MMSE :
-
Mini-Mental State Examination
- MoCA:
-
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- T2-FLAIR:
-
T2-weighted fluid attenuated inversion recovery imaging
- TR :
-
repetition time
- TE :
-
echo time
- FOV :
-
field of view
- NEX :
-
number of excitations
- EPI :
-
echo planar imaging
- VBM :
-
voxel-based morphometry
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- MNI :
-
Montreal Neurological Institute
- MK :
-
mean kurtosis
- AK :
-
axial kurtosis
- RK :
-
radial kurtosis
- FA:
-
fractional anisotropy
- MD:
-
mean diffusivity
- AD:
-
axial diffusivity
- RD:
-
radial diffusivity
- DKE:
-
Diffusion Kurtosis Estimator
- VBA :
-
voxel-based analysis
- TIV:
-
total intracranial volume
- FDR:
-
false discovery rate
- ROIs:
-
regions of interest
- NBS :
-
network-based statistic
- DTI:
-
diffusion tensor imaging
References
Adams, S. J., & Kirk AAuer, R. N. (2018). Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia (ALSP): Integrating the literature on hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids (HDLS) and pigmentary orthochromatic leukodystrophy (POLD). Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 48, 42–49.
Balevich, E. C., Haznedar, M. M., Wang, E., Newmark, R. E., Bloom, R., Schneiderman, J. S., Aronowitz, J., Tang, C. Y., Chu, K. W., Byne, W., Buchsbaum, M. S., & Hazlett, E. A. (2015). Corpus callosum size and diffusion tensor anisotropy in adolescents and adults with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research, 231, 244–251.
Battisti, C., Di Donato, I., Bianchi, S., Monti, L., Formichi, P., Rufa, A., et al. (2014). Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids: Three patients with stroke-like presentation carrying new mutations in the CSF1R gene. Journal of Neurology, 261, 768–772.
Chao-Gan, Y., & Yu-Feng, Z. (2010). DPARSF: A MATLAB toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13.
Cheng, J. X., Zhang, H. Y., Peng, Z. K., Xu, Y., Tang, H., Wu, J. T., & Xu, J. (2018). Divergent topological networks in Alzheimer's disease: A diffusion kurtosis imaging analysis. Transl Neurodegener, 7, 10.
Coscia, D. M., Narr, K. L., Robinson, D. G., Hamilton, L. S., Sevy, S., Burdick, K. E., Gunduz-Bruce, H., McCormack, J., Bilder, R. M., & Szeszko, P. R. (2009). Volumetric and shape analysis of the thalamus in first-episode schizophrenia. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 1236–1245.
de Jong, L. W., van der Hiele, K., Veer, I. M., Houwing, J. J., Westendorp, R. G., Bollen, E. L., et al. (2008). Strongly reduced volumes of putamen and thalamus in Alzheimer's disease: An MRI study. Brain, 131, 3277–3285.
Dennis, E. L., & Thompson, P. M. (2014). Functional brain connectivity using fMRI in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychology Review, 24, 49–62.
Di Paola, M., Macaluso, E., Carlesimo, G. A., Tomaiuolo, F., Worsley, K. J., Fadda, L., et al. (2007). Episodic memory impairment in patients with Alzheimer's disease is correlated with entorhinal cortex atrophy. A voxel-based morphometry study. J Neurol, 254, 774–781.
Dubois, B., Feldman, H. H., Jacova, C., Dekosky, S. T., Barberger-Gateau, P., Cummings, J., et al. (2007). Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurology, 6, 734–746.
ES, H., MM, C., Qi, L., & EX, W. (2008). Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis. NeuroImage, 42, 122–134.
Ferrarini, L., Palm, W. M., Olofsen, H., van der Landen, R., Jan, B. G., Westendorp, R. G., et al. (2008). MMSE scores correlate with local ventricular enlargement in the spectrum from cognitively normal to Alzheimer disease. Neuroimage, 39, 1832–1838.
Filippi, M., Agosta, F., Spinelli, E. G., & Rocca, M. A. (2013). Imaging resting state brain function in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 260, 1709–1713.
Gezelius, H., & Lopez-Bendito, G. (2017). Thalamic neuronal specification and early circuit formation. Developmental Neurobiology, 77, 830–843.
Giraldo-Chica, M., & Woodward, N. D. (2017). Review of thalamocortical resting-state fMRI studies in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 180, 58–63.
Houtchens, M. K., Benedict, R. H., Killiany, R., Sharma, J., Jaisani, Z., Singh, B., et al. (2007). Thalamic atrophy and cognition in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 69, 1213–1223.
Jang, S. H., & Kwon, H. G. (2014). Perspectives on the neural connectivity of the fornix in the human brain. Neural Regeneration Research, 9, 1434–1436.
Jayaweera, H. K., Hickie, I. B., Duffy, S. L., Hermens, D. F., Mowszowski, L., Diamond, K., Terpening, Z., Paradise, M., Lewis, S. J. G., Lagopoulos, J., & Naismith, S. L. (2015). Mild cognitive impairment subtypes in older people with depressive symptoms: Relationship with clinical variables and hippocampal change. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry and Neurology, 28, 174–183.
Jayaweera, H. K., Hickie, I. B., Duffy, S. L., Mowszowski, L., Norrie, L., Lagopoulos, J., & Naismith, S. L. (2016). Episodic memory in depression: The unique contribution of the anterior caudate and hippocampus. Psychological Medicine, 46, 2189–2199.
Jensen, J. H., Helpern, J. A., Ramani, A., & Lu HKaczynski, K. (2005). Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 53, 1432–1440.
Kassubek, J., Juengling, F. D., & Ecker DLandwehrmeyer, G. B. (2005). Thalamic atrophy in Huntington's disease co-varies with cognitive performance: A morphometric MRI analysis. Cerebral Cortex, 15, 846–853.
Kinoshita, M., Kondo, Y., Yoshida, K., Fukushima, K., Hoshi, K., Ishizawa, K., Araki, N., Yazawa, I., Washimi, Y., Saitoh, B., Kira, J. I., & Ikeda, S. I. (2014). Corpus callosum atrophy in patients with hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids: An MRI-based study. Internal Medicine, 53, 21–27.
Konno, T., Broderick, D. F., Mezaki, N., Isami, A., Kaneda, D., Tashiro, Y., Tokutake, T., Keegan, B. M., Woodruff, B. K., Miura, T., Nozaki, H., Nishizawa, M., Onodera, O., Wszolek, Z. K., & Ikeuchi, T. (2017). Diagnostic value of brain calcifications in adult-onset Leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 38, 77–83.
Konno, T., Kasanuki, K., Ikeuchi, T., Dickson, D. W., & Wszolek, Z. K. (2018a). CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy: A major player in primary microgliopathies. Neurology, 91, 1092–1104.
Konno, T., Yoshida, K., Mizuta, I., Mizuno, T., Kawarai, T., Tada, M., Nozaki, H., Ikeda, S. I., Onodera, O., Wszolek, Z. K., & Ikeuchi, T. (2018b). Diagnostic criteria for adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia due to CSF1R mutation. European Journal of Neurology, 25, 142–147.
Lee, B. Y., Zhu, X. H., & Li XChen, W. (2019). High-resolution imaging of distinct human corpus callosum microstructure and topography of structural connectivity to cortices at high field. Brain Structure & Function, 224, 949–960.
Luo, J., Elwood, F., Britschgi, M., Villeda, S., Zhang, H., Ding, Z., Zhu, L., Alabsi, H., Getachew, R., Narasimhan, R., Wabl, R., Fainberg, N., James, M. L., Wong, G., Relton, J., Gambhir, S. S., Pollard, J. W., & Wyss-Coray, T. (2013). Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling in injured neurons facilitates protection and survival. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210, 157–172.
Marrale, M., Collura, G., Brai, M., Toschi, N., Midiri, F., La Tona, G., et al. (2016). Physics, techniques and review of Neuroradiological applications of diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI). Clinical Neuroradiology, 26, 391–403.
Moon, C. M., Yang, J. C., & Jeong, G. W. (2015). Explicit verbal memory impairments associated with brain functional deficits and morphological alterations in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 186, 328–336.
Muller, N. C. J., Konrad, B. N., Kohn, N., Munoz-Lopez, M., Czisch, M., Fernandez, G., et al. (2018). Hippocampal-caudate nucleus interactions support exceptional memory performance. Brain Structure & Function, 223, 1379–1389.
Newman, J. (1995). Thalamic contributions to attention and consciousness. Consciousness and Cognition, 4, 172–193.
Nicholson, A. M., Baker, M. C., Finch, N. A., Rutherford, N. J., Wider, C., Graff-Radford, N. R., Nelson, P. T., Clark, H. B., Wszolek, Z. K., Dickson, D. W., Knopman, D. S., & Rademakers, R. (2013). CSF1R mutations link POLD and HDLS as a single disease entity. Neurology, 80, 1033–1040.
Poldrack, R. A., & Packard, M. G. (2003). Competition among multiple memory systems: Converging evidence from animal and human brain studies. Neuropsychologia, 41, 245–251.
Prieto-Morin, C., Ayrignac, X., Ellie, E., Tournier-Lasserve, E., & Labauge, P. (2016). CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy mimicking primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, 263, 1864–1865.
Qiu, A., Zhong, J., Graham, S., Chia, M. Y., & Sim, K. (2009). Combined analyses of thalamic volume, shape and white matter integrity in first-episode schizophrenia. Neuroimage, 47, 1163–1171.
Rademakers, R., Baker, M., Nicholson, A. M., Rutherford, N. J., Finch, N., Soto-Ortolaza, A., Lash, J., Wider, C., Wojtas, A., DeJesus-Hernandez, M., Adamson, J., Kouri, N., Sundal, C., Shuster, E. A., Aasly, J., MacKenzie, J., Roeber, S., Kretzschmar, H. A., Boeve, B. F., Knopman, D. S., Petersen, R. C., Cairns, N. J., Ghetti, B., Spina, S., Garbern, J., Tselis, A. C., Uitti, R., Das, P., van Gerpen, J., Meschia, J. F., Levy, S., Broderick, D. F., Graff-Radford, N., Ross, O. A., Miller, B. B., Swerdlow, R. H., Dickson, D. W., & Wszolek, Z. K. (2011). Mutations in the colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) gene cause hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids. Nature Genetics, 44, 200–205.
Richards, S., Aziz, N., Bale, S., Bick, D., Das, S., Gastier-Foster, J., et al. (2015). Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in Medicine, 17, 405–424.
Roland, J. L., Snyder, A. Z., Hacker, C. D., Mitra, A., Shimony, J. S., Limbrick, D. D., Raichle, M. E., Smyth, M. D., & Leuthardt, E. C. (2017). On the role of the corpus callosum in interhemispheric functional connectivity in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114, 13278–13283.
Rusinek, H., Endo, Y., De Santi, S., Frid, D., Tsui, W. H., Segal, S., et al. (2004). Atrophy rate in medial temporal lobe during progression of Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 63, 2354–2359.
Sundal, C., Van Gerpen, J. A., Nicholson, A. M., Wider, C., Shuster, E. A., Aasly, J., et al. (2012). MRI characteristics and scoring in HDLS due to CSF1R gene mutations. Neurology, 79, 566–574.
Terada, S., Ishizu, H., Yokota, O., Ishihara, T., Nakashima, H., Kugo, A., Tanaka, Y., Nakashima, T., Nakashima, Y., & Kuroda, S. (2004). An autopsy case of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with spheroids, clinically suspected of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathologica, 108, 538–545.
Tian, W. T., Zhan, F. X., Liu, Q., Luan, X. H., Zhang, C., Shang, L., Zhang, B. Y., Pan, S. J., Miao, F., Hu, J., Zhong, P., Liu, S. H., Zhu, Z. Y., Zhou, H. Y., Sun, S., Liu, X. L., Huang, X. J., Jiang, J. W., Ma, J. F., Wang, Y., Chen, S. F., Tang, H. D., Chen, S. D., & Cao, L. (2019). Clinicopathologic characterization and abnormal autophagy of CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy. Transl Neurodegener, 8, 32.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15, 273–289.
van der Knaap, L. J., & van der Ham, I. J. (2011). How does the corpus callosum mediate interhemispheric transfer? A review. Behavioural Brain Research, 223, 211–221.
van der Knaap, M. S., Naidu, S., Kleinschmidt-Demasters, B. K., & Kamphorst WWeinstein, H. C. (2000). Autosomal dominant diffuse leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids. Neurology, 54, 463–468.
Vesely, B., & Antonini ARektor, I. (2016). The contribution of white matter lesions to Parkinson's disease motor and gait symptoms: A critical review of the literature. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna), 123, 241–250.
Voermans, N. C., Petersson, K. M., Daudey, L., Weber, B., Van Spaendonck, K. P., Kremer, H. P., et al. (2004). Interaction between the human hippocampus and the caudate nucleus during route recognition. Neuron, 43, 427–435.
von Gunten, A., Fox, N. C., & Cipolotti LRon, M. A. (2000). A volumetric study of hippocampus and amygdala in depressed patients with subjective memory problems. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 12, 493–498.
Wong, J. C., Chow, T. W., & Hazrati, L. N. (2011). Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia can present as frontotemporal dementia syndrome. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 32, 150–158.
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., & Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics, 14, 339–351.
Zarei, M., Patenaude, B., Damoiseaux, J., Morgese, C., Smith, S., Matthews, P. M., Barkhof, F., Rombouts, S., Sanz-Arigita, E., & Jenkinson, M. (2010). Combining shape and connectivity analysis: An MRI study of thalamic degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage, 49, 1–8.
Study funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81,571,086, 81,870,889 and 81,400,888), National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC1310200), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant (20161401) and Interdisciplinary Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (YG2016MS64).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Zhan: data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, statistical analysis, drafting the manuscript.
Dr. Zhu: data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data.
Dr. Liu: data acquisition.
Dr. Zhou: data acquisition.
Dr. Luan: data acquisition.
Dr. Huang: data acquisition.
Dr. Liu: data acquisition.
Dr. Tian: data acquisition.
Dr. SG Wang: data acquisition.
Dr. Song: data acquisition.
Dr. Chen: data acquisition.
Dr. Zhao: data acquisition.
Dr. Y Wang: data acquisition.
Dr. Tang: data acquisition.
Dr. Chen: data acquisition.
Dr. Hu: data acquisition.
Dr. Li: funding, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting the manuscript, manuscript revision.
Prof. Cao: funding, study design and conceptualization, data acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, statistical analysis, manuscript revision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Dr. BY Li is in charge of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400888).
Prof. L Cao is in charge of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81571086 and 81870889), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission-Gaofeng Clinical Medicine Grant (20161401) and Interdisciplinary Project of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (YG2016MS64).
The other co-authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have potential conflicts of interest to be disclosed. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this paper.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the ethics committee of Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China and was registered at http://www.chictr.org.cn (registration number: ChiCTR1800015295). All participants or their guardians provided written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, FX., Zhu, ZY., Liu, Q. et al. Altered structural and functional connectivity in CSF1R-related leukoencephalopathy. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 1655–1666 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00360-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00360-0