Abstract
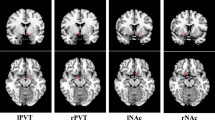
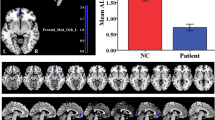
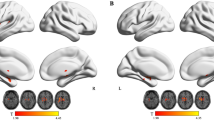
Primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE) is characterized by a low cure rate and a high reoccurrence rate, since its underlying mechanism remains unclear. Based on the recent studies that thalamus plays an important role in waking up a sleeping person, here we further investigate the functional connectivity (FC) information between thalamus and other brain regions, in order to make better understanding of the PNE’s pathogenesis. In this study, we enrolled 30 children diagnosed with PNE and 30 typically developing children that are age and sex matched, the thalamus-based FC estimates were extracted at the resting-state. Experiments showed that for children with PNE, there were four brain regions found with a reduced connection efficiency with thalamus, that were cerebellum posterior lobe, frontal lobe, parietal lobe and precentral gyrus. It can be concluded that these relevant regions might induce an arousal disorder, and therefore further lead to PNE. This finding also provides a new insight in the pathophysiology of PNE.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikins, D., & Ray, W. J. (2001). Frontal lobe contributions to hypnotic susceptibility: a neuropsychological screening of executive functioning. The International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis, 49(4), 320–329.
Allen, G., & Courchesne, E. (2003). Differential effects of developmental cerebellar abnormality on cognitive and motor functions in the cerebellum: an fMRI study of autism. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 160(2), 262–273.
Caldwell, P. H., Deshpande, A. V., Von, G., & A. (2013). Management of nocturnal enuresis. BMJ, 237, f6259.
Carlesimo, G. A., Lombardi, M. G., Caltagirone, C., & Barban, F. (2015). Recollection and familiarity in the human thalamus. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 54, 18–28.
Chao-Gan, Y., & Yu-Feng, Z. (2010). DPARSF: a matlab toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13.
Coenen, A. M., & Drinkenburg, W. H. (2002). Animal models for information processing during sleep. International Journal of Psychophsiology, 46(3), 163–175.
Courchesne, E., Townsend, J., Akshoomoff, N. A., Saitoh, O., Yeung-Courchesne, R., Lincoln, A. J., James, H. E., Haas, R. H., Schreibman, L., & Lau, L. (1994). Impairment in shifting attention in autistic and cerebellar patients. Behavioral Neuroscience, 108(5), 848–865.
Curtis, C. E. (2006). Prefrontal and parietal contributions to spatial working memory. Neuroscience, 139(1), 173–180.
Dai, X., Liu, C., Zhou, R., Gong, H., Wu, B., Gao, L., & Wang, Y. X. (2015). Long-term total sleep deprivation decreases the default spontaneous activity and connectivity pattern in healthy male subjects: a resting-state fMRI study. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 11, 761–772.
Davidson, P. S., Troyer, A. K., & Moscovitch, M. (2006). Frontal lobe contributes to recognition and recall: linking basic research with clinical evaluation and remediation. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12(2), 210–223.
Dhondt, K., Baert, E., Van Herzeele, C., Raes, A., Groen, L. A., Hoebeke, P., et al. (2014). Sleep fragmentation and increased periodic limb movements are more common in children with nocturnal enuresis. Acta Paediatrica, 103(6), e268–e272.
Farvolden, P., & Woody, E. Z. (2004). Hypnosis, memory and frontal executive functioning. The International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hypnosis, 52(1), 3–26.
Fogassi, L., Ferrari, P. F., Gesierich, B., Rozzi, S., Chersi, F., & Rizzolatti, G. (2005). Parietal lobe: from action organization to intention understanding. Science, 308(5722), 662–667.
Freitag, C. M., Rohling, D., Seifen, S., Pukrop, R., & von, Gontard, A. (2006). Neurophysiology of nocturnal enuresis: evoked potentials and prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 48(4), 278–284.
Hallioglu, O., Ozge, A., Comelekoglu, U., Topaloglu, A. K., Kanik, A., Duzovali, O., et al. (2001). Evaluation of cerebral maturation by visual and quantitative analysis of resting electroencephalography in children with primary nocturnal enuresis. Journal of Child Neurology, 16(10), 714–718.
Hutchinson, J. B., Uncapher, M. R., Weiner, K. S., Bressler, D. W., Silver, M. A., Preston, A. R., & Wagner, A. D. (2014). Functional heterogeneity in posterior parietal cortex across attention and episodic memory retrieval. Cerebral Cortex, 24(1), 49–66.
Ivry, R. B., & Keels, S. W. (1989). Timing functions of the cerebellum. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 1(2), 136–152.
Kamperis, K., Hagstroem, S., Radvanska, E., Rittig, S., & Djurhuus, J. C. (2010). Excess diuresis and natriuresis during acute sleep deprivation in healthy adults. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 299(2), F404–F411.
Kavia, R. B., Dasqupta, R., & Fowler, C. J. (2005). Functional imaging and the central control of the bladder. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 493(1), 27–32.
Kawauchi, A., Imada, N., Tanaka, Y., Minami, M., Watanabe, H., & Shirakawa, S. (1998). Changes in the structure of sleep spindles and delta waves on electroencephalography in patients with nocturnal enuresis. British Journal of Urology, 3, 72–75.
Kiddoo, D. A. (2012). Nocturnal enuresis. CMAJ, 184(8), 980–911.
Kuhtz-Buschbeck, J. P., Gilster, R., van der Horst, C., Hamann, M., Wolff, S., & Jansen, O. (2009). Control of bladder sensations: an fMRI study of brain activity and effective connectivity. Neuroimage, 47(1), 18–27.
Lei, D., Ma, J., Du, X., Shen, G., Tian, M., & Li, G. (2012a). Altered brain activation during response inhibition in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: an fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 33(12), 2913–2919.
Lei, D., Ma, J., Du, X., Shen, G., Tian, M., & Li, G. (2012b). Spontaneous brain activity changes in children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a resting-state fMRI study. Neurourology and Urodynamics, 31(1), 99–104.
Lei, D., Ma, J., Shen, X., Du, X., Shen, G., Liu, W., Yan, X., et al. (2012c). Changes in the brain microstructure of children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a diffusion tensor imaging study. PLoS One, 7(2), e31023.
Lei, D., Ma, J., Zhang, J., Wang, M., Zhang, K., Chen, F., et al. (2015). Connectome-scale assessments of functional connectivity in children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. BioMed Research International, 2015, 463708.
Liu, Z., Xu, C., Xu, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, B., Lv, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, K., & du, C. (2010). Decreased regional homogeneity in insula and cerebellum: a resting-state fMRI study in patients with major depression and subjects at high risk for major depression. Psychiatry Research, 182(3), 211–215.
Liu, X., Yan, Z., Wang, T., Yang, X., Feng, F., Fang, L., Fan, L., et al. (2015). Connectivity pattern differences bilaterally in the cerebellum posterior lobe in healthy subjects after normal sleep and sleep deprivation: a resting-state functional MRI study. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment, 11, 1279–1289.
Logue, S. F., & Gould, T. J. (2014). The neural and genetic basis of executive function: attention, cognitive flexibility, and response inhibition. Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior, 123, 45–54.
Magnotta, V. A., Adix, M. L., Caprahan, A., Lim, K., Gollub, R., & Andreasen, N. C. (2008). Investigation connectivity between the cerebellum and thalamus in schizophrenia using diffusion tensor tractography: a pilot study. Psychiatry Research, 163(3), 193–200.
Mahler, B., Kamperis, K., Schroeder, M., Frøkiær, J., Djurhuus, J. C., & Rittig, S. (2012). Sleep deprivation induces excess diuresis and natriuresis in healthy children. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 302(2), F236–F243.
Middlebrooks, P. G., & Sommer, M. A. (2012). Neuronal correlates of metacognition in primate frontal cortex. Neuron, 75(3), 517–530.
Mitchell, S. A. (2015). The mediodorsal thalamus as a higher order thalamus relay nucleus important for learning and decision-making. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 54, 76–88.
Nakajima, M., & Halassa, M. M. (2017). Thalamus control of cortical connectivity. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 44, 127–131.
Nevéus, T. (2003). The role of sleep and arousal in nocturnal enuresis. Acta Paediatrica, 92(10), 1118–1123.
Nevéus, T. (2008). Enuretic sleep: deep, disturbed or just wet? Pediatric Nephrology, 23(8), 1201–1202.
Oedekoven, C. S., Jansen, A., Kircher, T. T., & Leube, D. T. (2013). Age-related changes in parietal lobe activation during an episodic memory retrieval task. Journal of Neural Transmission (Vienna), 120(5), 799–806.
Park, J., Park, D. C., & Polk, T. A. (2013). Parietal functional connectivity innumerical cognition. Cerebral Cortex, 23(9), 2127–2135.
Parvizi, J., Anderson, S. W., Martin, C. O., Damasio, H., & Damasio, A. R. (2001). Pathological laughter and crying: a link to the cerebellum. Brain, 124(pt9), 1708–1719.
Redsell, S. A., & Collier, J. (2001). Bedwetting, behavior and self-esteem: a review of the literature. Child: Care, Health and Development, 27(2), 149–162.
Rizzolatti, G., & Sinigaglia, C. (2010). The functional role of the parieto-frontal mirror circuit: interpretations and misinterpretations. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience, 11(4), 264–274.
Sarici, H., Telli, O., Ozgur, B. C., Demirbas, A., Ozgur, S., & Karagoz, M. A. (2016). Prevalence of nocturnal enuresis and its influence on quality of life in school-aged children. Journal of Pediatric Urology, 12, 159.e1–159.e6.
Seniów, J. (2012). Executive dysfunctions and frontal syndromes. Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience, 30, 50–53.
Soares, J. C., & Mann, J. J. (1997). The anatomy of mood disorders-review of structural neuroimaging studies. Biological Psychiatry, 41(1), 86–106.
Uqur, H. C., Kahiloqullari, G., Coscarella, E., Unlu, A., Tekdemir, I., Morcos, J. J., et al. (2005). Arterial vascularization of primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus). Surgical Neurology, 64(Suppl 2), S48–S52.
Von Gontard, A. (2013). The impact of DSM-5 and guidelines for assessment and treatment of elimination disorders. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 22(Suppl 1), S61–S67.
Watanabe, Y., & Funahashi, S. (2012). Thalamic mediodorsal nucleus and working memory. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 36(1), 134–142.
Yang, Y., Hu, C., Huang, C., & Chou, P. (2014). Thalamic synaptic transmission of sensory information modulated by synergistic interaction of adenosine and serotonin. Journal of Neurochemistry, 128(6), 852–863.
Yu, B., Guo, Q., Fan, G., Ma, H., Wang, L., & Liu, N. (2011). Evaluation of working memory impairment in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: evidence from event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 47(7), 429–435.
Yu, B., Kong, F., Peng, M., Ma, H., Liu, N., & Guo, Q. (2012). Assessment of memory/attention impairment in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: a voxel-based morphometry study. European Journal of Radiology, 81(12), 4119–4122.
Zhang, J., Lei, D., Ma, J., Wang, M., Shen, G., Wang, H., Yang, G., & du, X. (2014). Brain metabolite alterations in children with primary nocturnal enuresis using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurochemical Research, 39(7), 1355–1362.
Zhang, K., Ma, J., Lei, D., Wang, M., Zhang, J., & Du, X. (2015). Task positive and default mode networks during a working memory in children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis and healthy controls. Pediatric Research, 78(4), 422–429.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (Grants 14JC1404600, 16411952800 and 18411960200), the Development of Science and Technology in Pu Dong District (PKJ2017-Y06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Anyi Zhang and Lichi Zhang co-designed the study, conducted the analysis, and drafted the initial manuscript; Mengxing Wang was involved in the acquisition of the data; Yiwen Zhang, Fan Jiang, and Xingming Jin contributed to the conduct of the study; Jun Ma and Xiaoxia Du co-designed the study, reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
We have obtained the ethical approval of the Institutional Review Board of Shanghai Children’s Medical Center affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine (No: SCMC-201014). All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Informed content
All the subjects and their guardians have signed the informed consent. They were informed that the whole survey involvement would be innominate and voluntary, and they could withdraw from the survey at any time.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, A., Zhang, L., Wang, M. et al. Functional connectivity of thalamus in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: results from a resting-state fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 355–363 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00262-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-020-00262-1