Abstract
Mediation analysis was used to investigate the role of white matter integrity in the relationship between injury severity and verbal memory performance in participants with chronic pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI). DTI tractography was used to measure fractional anisotropy (FA) within the corpus callosum, fornix, cingulum bundles, perforant pathways, and uncinate fasciculi. Injury severity was indexed using Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) scores obtained at the time of the injury. Verbal memory was measured by performance on the long-delay free recall (LDFR) trial of the California Verbal Learning Test–Children’s version. Participants were between the ages of 10–18 and included 21 children with TBI (injured before age 9) and 19 typically-developing children (TDC). Children with TBI showed lower FA across all pathways and poorer LDFR performance relative to TDC. Within the TBI group, mediation analysis revealed neither a significant total effect of GCS on LDFR nor significant direct effects of GCS on LDFR across pathways; however, the indirect effects of GCS on LDFR through FA of the corpus callosum, left perforant pathway, and left uncinate fasciculus were significant and opposite in sign to their respective direct effects. These results suggests that the predictive validity of GCS for LDFR is initially suppressed by the substantial variance accounted for by FA, which is uncorrelated with GCS, and the predictive validity of GCS increases only when FA is considered, and the opposing path is controlled. These findings illustrate the complex associations between acute injury severity, white matter pathways, and verbal memory several years following pediatric TBI.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnan, A., Crawley, A., Mikulis, D., Moscovitch, M., Colella, B., & Green, R. (2013). Moderate-severe traumatic brain injury causes delayed loss of white matter integrity: Evidence of fornix deterioration in the chronic stage of injury. Brain Injury, 27(12), 1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2013.823659.
Alexander, A. L., Lee, J. E., Lazar, M., & Field, A. S. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics, 4(3), 316–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2007.05.011.
Anderson, V., & Catroppa, C. (2007). Memory outcome at 5 years post-childhood traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 21(13–14), 1399–1409. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699050701785070.
Anderson, V., Godfrey, C., Rosenfeld, J. V., & Catroppa, C. (2012). Predictors of cognitive function and recovery 10 years after traumatic brain injury in young children. Pediatrics, 129(2), e254–e261. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-0311.
Augustinack, J. C., Helmer, K., Huber, K. E., Kakunoori, S., Zollei, L., & Fischl, B. (2010). Direct visualization of the perforant pathway in the human brain with ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 4, 42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2010.00042.
Baek, S. O., Kim, O. L., Kim, S. H., Kim, M. S., Son, S. M., Cho, Y. W., et al. (2013). Relation between cingulum injury and cognition in chronic patients with traumatic brain injury: Diffusion tensor tractography study. NeuroRehabilitation, 33(3), 465–471. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-130979.
Bigler, E. D. (2007). Anterior and middle cranial fossa in traumatic brain injury: Relevant neuroanatomy and neuropathology in the study of neuropsychological outcome. Neuropsychology, 21(5), 515–531. https://doi.org/10.1037/0894-4105.21.5.515.
Christidi, F., Bigler, E. D., McCauley, S. R., Schnelle, K. P., Merkley, T. L., Mors, M. B., Li, X., Macleod, M., Chu, Z., Hunter, J. V., Levin, H. S., Clifton, G. L., & Wilde, E. A. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging of the perforant pathway zone and its relation to memory function in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 28(5), 711–725. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2010.1644.
Conger, A. J. (1974). A revised definition for suppressor variables: A guide to their identification and interpretation. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 34(1), 35–46.
Cuff, S., DiRusso, S., Sullivan, T., Risucci, D., Nealon, P., Haider, A., & Slim, M. (2007). Validation of a relative head injury severity scale for pediatric trauma. Journal of Trauma, 63(1), 172–177; discussion 177-178. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31805c14b1.
Davis, J. A. (1985). The logic of causal order (Vol. 55). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publishing.
de Heus, P. (2012). R squared effect-size measures and overlap between direct and indirect effect in mediation analysis. Behavior Research Methods, 44, 213–221.
Delis, D., Kramer, J., Kaplan, E., & Ober, B. (1994). Manual for the California verbal learning test-Children's version. San Antonio, Texas: The Psychological Corporation.
Dennis, E. L., Jin, Y., Villalon-Reina, J. E., Zhan, L., Kernan, C. L., Babikian, T., Mink, R. B., Babbitt, C. J., Johnson, J. L., Giza, C. C., Thompson, P. M., & Asarnow, R. F. (2015). White matter disruption in moderate/severe pediatric traumatic brain injury: Advanced tract-based analyses. Neuroimage Clin, 7, 493–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.02.002.
Dewan, M. C., Mummareddy, N., Wellons, J. C., 3rd, & Bonfield, C. M. (2016). Epidemiology of global pediatric traumatic brain injury: Qualitative review. World Neurosurgery, 91, 497–509 e491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.03.045.
Ewing-Cobbs, L., Prasad, M. R., Swank, P., Kramer, L., Cox, C. S., Jr., Fletcher, J. M., Barnes, M., Zhang, X., & Hasan, K. M. (2008). Arrested development and disrupted callosal microstructure following pediatric traumatic brain injury: Relation to neurobehavioral outcomes. NeuroImage, 42(4), 1305–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.06.031.
Ewing-Cobbs, L., Johnson, C. P., Juranek, J., DeMaster, D., Prasad, M., Duque, G., Kramer, L., Cox, C. S., & Swank, P. R. (2016). Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging after pediatric traumatic brain injury: Impact of age at injury and time since injury on pathway integrity. Human Brain Mapping, 37(11), 3929–3945. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23286.
Faber, J., Wilde, E. A., Hanten, G., Ewing-Cobbs, L., Aitken, M. E., Yallampalli, R., MacLeod, M. C., Mullins, S. H., Chu, Z. D., Li, X., Hunter, J. V., Noble-Haeusslein, L., & Levin, H. S. (2016). Ten-year outcome of early childhood traumatic brain injury: Diffusion tensor imaging of the ventral striatum in relation to executive functioning. Brain Injury, 30(13–14), 1635–1641. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2016.1199910.
Fairchild, A. J., Mackinnon, D. P., Taborga, M. P., & Taylor, A. B. (2009). R2 effect-size measures for mediation analysis. Behavior Research Methods, 41(2), 486–498. https://doi.org/10.3758/BRM.41.2.486.
Ghosh, A., Wilde, E. A., Hunter, J. V., Bigler, E. D., Chu, Z., Li, X., et al. (2009). The relation between Glasgow coma scale score and later cerebral atrophy in paediatric traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury, 23(3), 228–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699050802672789.
Hasan, K. M., Iftikhar, A., Kamali, A., Kramer, L. A., Ashtari, M., Cirino, P. T., Papanicolaou, A. C., Fletcher, J. M., & Ewing-Cobbs, L. (2009). Development and aging of the healthy human brain uncinate fasciculus across the lifespan using diffusion tensor tractography. Brain Research, 1276, 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.025.
Hedges, L. V. (1981). Distribution theory for glass's estimator of effect size and related estimators. Journal of Educational Statistics, 6(2), 107–128.
Hunter, J. V., Wilde, E. A., Tong, K. A., & Holshouser, B. A. (2012). Emerging imaging tools for use with traumatic brain injury research. Journal of Neurotrauma, 29(4), 654–671. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2011.1906.
Kalus, P., Slotboom, J., Gallinat, J., Mahlberg, R., Cattapan-Ludewig, K., Wiest, R., Nyffeler, T., Buri, C., Federspiel, A., Kunz, D., Schroth, G., & Kiefer, C. (2006). Examining the gateway to the limbic system with diffusion tensor imaging: The perforant pathway in dementia. NeuroImage, 30(3), 713–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.10.035.
Keselman, H. J., Algina, J., Lix, L. M., Wilcox, R. R., & Deering, K. N. (2008). A generally robust approach for testing hypotheses and setting confidence intervals for effect sizes. Psychological Methods, 13(2), 110–129. https://doi.org/10.1037/1082-989X.13.2.110.
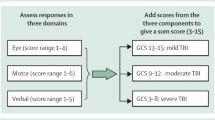
Kirkham, F. J., Newton, C. R., & Whitehouse, W. (2008). Paediatric coma scales. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 50(4), 267–274.
Lajiness-O'Neill, R., Erdodi, L., & Bigler, E. D. (2011). Demographic and injury-related moderators of memory and achievement outcome in pediatric TBI. Applied Neuropsychology, 18(4), 298–308. https://doi.org/10.1080/09084282.2011.595457.
Levin, H. S. (1993). Head trauma. Current Opinion in Neurology, 6(6), 841–846.
Levin, H. S., Song, J., Scheibel, R. S., Fletcher, J. M., Harward, H. N., & Chapman, S. B. (2000). Dissociation of frequency and recency processing from list recall after severe closed head injury in children and adolescents. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 22(1), 1–15.
Levin, H. S., Wilde, E. A., Chu, Z., Yallampalli, R., Hanten, G. R., Li, X., Chia, J., Vasquez, A. C., & Hunter, J. V. (2008). Diffusion tensor imaging in relation to cognitive and functional outcome of traumatic brain injury in children. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 23(4), 197–208. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.HTR.0000327252.54128.7c.
Mabbott, D. J., Rovet, J., Noseworthy, M. D., Smith, M. L., & Rockel, C. (2009). The relations between white matter and declarative memory in older children and adolescents. Brain Research, 1294, 80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.046.
MacKinnon, D. P., Krull, J. L., & Lockwood, C. M. (2000). Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect. Prevention Science, 1(4), 173–181.
Mori, S., Crain, B. J., Chacko, V. P., & van Zijl, P. C. (1999). Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology, 45(2), 265–269.
Mottram, L., & Donders, J. (2005). Construct validity of the California verbal learning test–Children's version (CVLT-C) after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Psychological Assessment, 17(2), 212–217. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.17.2.212.
Mottram, L., & Donders, J. (2006). Cluster subtypes on the California verbal learning test–Children's version after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Developmental Neuropsychology, 30(3), 865–883. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15326942dn3003_6.
Netsch, T. (2001). Towards real-time multi-modality 3-D medical image registration. In Paper presented at the international conference on computer vision. Vancouver: Canada.
Niogi, S. N., & Mukherjee, P. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging of mild traumatic brain injury. The Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 25(4), 241–255. https://doi.org/10.1097/HTR.0b013e3181e52c2a.
Palacios, E. M., Fernandez-Espejo, D., Junque, C., Sanchez-Carrion, R., Roig, T., Tormos, J. M., Bargallo, N., & Vendrell, P. (2011). Diffusion tensor imaging differences relate to memory deficits in diffuse traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurology, 11, 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-11-24.
Palacios, E. M., Sala-Llonch, R., Junque, C., Fernandez-Espejo, D., Roig, T., Tormos, J. M., Bargallo, N., & Vendrell, P. (2013). Long-term declarative memory deficits in diffuse TBI: Correlations with cortical thickness, white matter integrity, and hippocampal volume. Cortex, 49(3), 646–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2012.02.011.
Paulhus, D. L., Robins, R. W., Trzesniewski, K. H., & Tracy, J. L. (2004). Two replicable suppressor situations in personality research. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39(2), 303–328. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327906mbr3902_7.
Peng, C.-Y. J., & Chen, L.-T. (2014). Beyond Cohen's d: Alternative effect size measures for between-subject designs. The Journal of Experimental Education, 82(1), 22–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745471.
Rogalski, E. J., Murphy, C. M., deToledo-Morrell, L., Shah, R. C., Moseley, M. E., Bammer, R., & Stebbins, G. T. (2009). Changes in parahippocampal white matter integrity in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A diffusion tensor imaging study. Behavioral Neurology, 21(1), 51–61. https://doi.org/10.3233/BEN-2009-0235.
Roman, M. J., Delis, D. C., Willerman, L., Magulac, M., Demadura, T. L., de la Peña, J. L., Loftis, C., Walsh, J., & Kracun, M. (1998). Impact of pediatric traumatic brain injury on components of verbal memory. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 20(2), 245–258.
Ruxton, G. D. (2006). The unequal variance t-test is an underused alternative to Student's t-test and the Mann–Whitney U test. Behavioral Ecology, 17(4), 688–690.
Schonberger, M., Ponsford, J., Reutens, D., Beare, R., & O'Sullivan, R. (2009). The relationship between age, injury severity, and MRI findings after traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 26, 2157–2167, 10.1089=neu.2009.0939.
Sepulcre, J., Masdeu, J. C., Sastre-Garriga, J., Goni, J., Velez-de-Mendizabal, N., Duque, B., et al. (2008). Mapping the brain pathways of declarative verbal memory: Evidence from white matter lesions in the living human brain. NeuroImage, 42(3), 1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.05.038.
Shrout, P. E., & Bolger, N. (2002). Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychological Methods, 7(4), 422–445.
Shrout, P. E., & Fleiss, J. L. (1979). Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychological Bulletin, 86(2), 420–428.
Teasdale, G., & Jennett, B. (1974). Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. A practical scale. Lancet, 2(7872), 81–84.
Tofighi, D., & MacKinnon, D. P. (2011). RMediation: An R package for mediation analysis confidence intervals. Behavior Research Methods, 43(3), 692–700. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-011-0076-x.
Tomaiuolo, F., Worsley, K. J., Lerch, J., Di Paola, M., Carlesimo, G. A., Bonanni, R., et al. (2005). Changes in white matter in long-term survivors of severe non-missile traumatic brain injury: A computational analysis of magnetic resonance images. Journal of Neurotrauma, 22(1), 76–82.
Tzelgov, J., & Henik, A. (1991). Suppression situations in psychological research: Definitions, implications, and applications. Psychological Bulletin, 109(3), 524–536.
Voelbel, G. T., Genova, H. M., Chiaravalotti, N. D., & Hoptman, M. J. (2012). Diffusion tensor imaging of traumatic brain injury review: Implications for neurorehabilitation. NeuroRehabilitation, 31(3), 281–293. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-2012-0796.
Weisskoff, R. M. (1996). Simple measurement of scanner stability for functional NMR imaging of activation in the brain. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 36(4), 643–645.
Welch, B. L. (1947). The generalisation of student's problems when several different population variances are involved. Biometrika, 34(1–2), 28–35.
Wilde, E. A., Hunter, J. V., Newsome, M. R., Scheibel, R. S., Bigler, E. D., Johnson, J. L., Fearing, M. A., Cleavinger, H. B., Li, X., Swank, P. R., Pedroza, C., Roberson, G. S., Bachevalier, J., & Levin, H. S. (2005). Frontal and temporal morphometric findings on MRI in children after moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 22(3), 333–344. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2005.22.333.
Wilde, E. A., Chu, Z., Bigler, E. D., Hunter, J. V., Fearing, M. A., Hanten, G., Newsome, M. R., Scheibel, R. S., Li, X., & Levin, H. S. (2006). Diffusion tensor imaging in the corpus callosum in children after moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma, 23(10), 1412–1426. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.23.1412.
Wilde, E. A., McCauley, S. R., Chu, Z., Hunter, J. V., Bigler, E. D., Yallampalli, R., Wang, Z. J., Hanten, G., Li, X., Ramos, M. A., Sabir, S. H., Vasquez, A. C., Menefee, D., & Levin, H. S. (2009). Diffusion tensor imaging of hemispheric asymmetries in the developing brain. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 31(2), 205–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/13803390802098118.
Wilde, E. A., Ramos, M. A., Yallampalli, R., Bigler, E. D., McCauley, S. R., Chu, Z., Wu, T. C., Hanten, G., Scheibel, R. S., Li, X., Vásquez, A. C., Hunter, J. V., & Levin, H. S. (2010). Diffusion tensor imaging of the cingulum bundle in children after traumatic brain injury. Developmental Neuropsychology, 35(3), 333–351. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565641003696940.
Wilde, E. A., Ayoub, K. W., Bigler, E. D., Chu, Z. D., Hunter, J. V., Wu, T. C., McCauley, S. R., & Levin, H. S. (2012). Diffusion tensor imaging in moderate-to-severe pediatric traumatic brain injury: Changes within an 18 month post-injury interval. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 6(3), 404–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-012-9150-y.
Wilde, E. A., McCauley, S. R., Jivani, S., Hanten, G., Faber, J., & Gale, S. D. (2015). Neuropsychological consequences of paediatric brain injury: Executive function. In J. Reed, K. Byard, & H. Fine (Eds.), Neuropsychological rehabilitation of childhood brain injury: A practical guide. New York, NY: MacMillan Publishers.
Williams, D. H., Levin, H. S., & Eisenberg, H. M. (1990). Mild head injury classification. Neurosurgery, 27(3), 422–428.
Yassa, M. A., Muftuler, L. T., & Stark, C. E. (2010). Ultrahigh-resolution microstructural diffusion tensor imaging reveals perforant path degradation in aged humans in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 107(28), 12687–12691. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1002113107.
Yeates, K. O., Blumenstein, E., Patterson, C. M., & Delis, D. C. (1995). Verbal learning and memory following pediatric closed-head injury. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 1(1), 78–87.
Yeates, K. O., Levin, H. S., & Ponsford, J. (2017). The neuropsychology of traumatic brain injury: Looking back, peering ahead. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 23(9–10), 806–817. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617717000686.
Yu, Q., Peng, Y., Mishra, V., Ouyang, A., Li, H., Zhang, H., Chen, M., Liu, S., & Huang, H. (2014). Microstructure, length, and connection of limbic tracts in normal human brain development. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 6, 228. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00228.
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our gratitude to our participants and their family members. The study was funded by the National Institute of Health grant R21 NS065937 (‘Trauma to Developing Brain: Model Refinement and Therapeutic Intervention’; Levin, PI and Noble, PI). The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Hannah M. Lindsey, Sanam Jivani Lalani, Jonathan Mietchen, Shawn D. Gale, Elisabeth A. Wilde, Jessica Faber, Marianne MacLeod, Jill V. Hunter, Zili D. Chu, Mary E. Aitken, Linda Ewing-Cobbs, and Harvey S. Levin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindsey, H.M., Lalani, S.J., Mietchen, J. et al. Acute pediatric traumatic brain injury severity predicts long-term verbal memory performance through suppression by white matter integrity on diffusion tensor imaging. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 1626–1637 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00093-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00093-9