Abstract
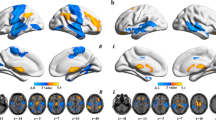
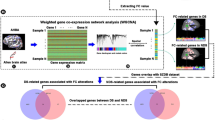
Previous seed- and atlas-based structural covariance/connectivity analyses have demonstrated that patients with schizophrenia is accompanied by aberrant structural connection and abnormal topological organization. However, it remains unclear whether this disruption is present in unbiased whole-brain voxel-wise structural covariance networks (SCNs) and whether brain genetic expression variations are linked with network alterations. In this study, ninety-five patients with schizophrenia and 95 matched healthy controls were recruited and gray matter volumes were extracted from high-resolution structural magnetic resonance imaging scans. Whole-brain voxel-wise gray matter SCNs were constructed at the group level and were further analyzed by using graph theory method. Nonparametric permutation tests were employed for group comparisons. In addition, regression modes along with random effect analysis were utilized to explore the associations between structural network changes and gene expression from the Allen Human Brain Atlas. Compared with healthy controls, the patients with schizophrenia showed significantly increased structural covariance strength (SCS) in the right orbital part of superior frontal gyrus and bilateral middle frontal gyrus, while decreased SCS in the bilateral superior temporal gyrus and precuneus. The altered SCS showed reproducible correlations with the expression profiles of the gene classes involved in therapeutic targets and neurodevelopment. Overall, our findings not only demonstrate that the topological architecture of whole-brain voxel-wise SCNs is impaired in schizophrenia, but also provide evidence for the possible role of therapeutic targets and neurodevelopment-related genes in gray matter structural brain networks in schizophrenia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, A. J., Griss, M. E., Folley, B. S., Hawkins, K. A., & Pearlson, G. D. (2009). Endophenotypes in schizophrenia: A selective review. Schizophrenia Research, 109(1–3), 24–37.
Anderson, V. M., Goldstein, M. E., Kydd, R. R., & Russell, B. R. (2015). Extensive gray matter volume reduction in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 18(7), pyv016.
Ashburner, J. (2007). A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage, 38(1), 95–113.
Alexander-Bloch, A., Giedd, J. N., & Bullmore, E. (2013). Imaging structural co-variance between human brain regions. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14(5), 322–336.
Bassett, D. S., Bullmore, E., Verchinski, B. A., Mattay, V. S., Weinberger, D. R., & Meyer-Lindenberg, A. (2008). Hierarchical organization of human cortical networks in health and schizophrenia. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(37), 9239–9248.
Bhugra, D. (2005). The global prevalence of schizophrenia. PLoS Medicine, 2(5), e151.
Buckner, R. L., Sepulcre, J., Talukdar, T., Krienen, F. M., Liu, H., Hedden, T., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Sperling, R. A., & Johnson, K. A. (2009). Cortical hubs revealed by intrinsic functional connectivity: Mapping, assessment of stability, and relation to Alzheimer's disease. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29(6), 1860–1873.
Chen, J., Cao, F., Liu, L., Wang, L., & Chen, X. (2015). Genetic studies of schizophrenia: An update. Neuroscience Bulletin, 31(1), 87–98.
Chou, K. H., Lin, W. C., Lee, P. L., Tsai, N. W., Huang, Y. C., Chen, H. L., Cheng, K. Y., Chen, P. C., Wang, H. C., Lin, T. K., Li, S. H., Lin, W. M., Lu, C. H., & Lin, C. P. (2015). Structural covariance networks of striatum subdivision in patients with Parkinson's disease. Human Brain Mapping, 36(4), 1567–1584.
Evans, A. C. (2013). Networks of anatomical covariance. NeuroImage, 80, 489–504.
Fatemi, S. H., & Folsom, T. D. (2009). The neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia, revisited. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 35(3), 528–548.
Friston, K. J. (1999). Schizophrenia and the disconnection hypothesis. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum, 395, 68–79.
Friston, K. (2005). Disconnection and cognitive dysmetria in schizophrenia. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(3), 429–432.
Greenwood, T. A., Braff, D. L., Light, G. A., Cadenhead, K. S., Calkins, M. E., Dobie, D. J., Freedman, R., Green, M. F., Gur, R. E., Gur, R. C., Mintz, J., Nuechterlein, K. H., Olincy, A., Radant, A. D., Seidman, L. J., Siever, L. J., Silverman, J. M., Stone, W. S., Swerdlow, N. R., Tsuang, D. W., Tsuang, M. T., Turetsky, B. I., & Schork, N. J. (2007). Initial heritability analyses of endophenotypic measures for schizophrenia: The consortium on the genetics of schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry, 64(11), 1242–1250.
Guo, W., Hu, M., Fan, X., Liu, F., Wu, R., Chen, J., et al. (2014a). Decreased gray matter volume in the left middle temporal gyrus as a candidate biomarker for schizophrenia: A study of drug naive, first-episode schizophrenia patients and unaffected siblings. Schizophrenia Research, 159(1), 43–50.
Guo, X., Li, J., Wang, J., Fan, X., Hu, M., Shen, Y., et al. (2014b). Hippocampal and orbital inferior frontal gray matter volume abnormalities and cognitive deficit in treatment-naive, first-episode patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 152(2–3), 339–343.
Guo, W., Liu, F., Xiao, C., Liu, J., Yu, M., Zhang, Z., et al. (2015). Increased short-range and long-range functional connectivity in first-episode, medication-naive schizophrenia at rest. Schizophrenia Research, 166(1–3), 144–150.
Hawrylycz, M. J., Lein, E. S., Guillozet-Bongaarts, A. L., Shen, E. H., Ng, L., Miller, J. A., van de Lagemaat, L. N., Smith, K. A., Ebbert, A., Riley, Z. L., Abajian, C., Beckmann, C. F., Bernard, A., Bertagnolli, D., Boe, A. F., Cartagena, P. M., Chakravarty, M. M., Chapin, M., Chong, J., Dalley, R. A., Daly, B. D., Dang, C., Datta, S., Dee, N., Dolbeare, T. A., Faber, V., Feng, D., Fowler, D. R., Goldy, J., Gregor, B. W., Haradon, Z., Haynor, D. R., Hohmann, J. G., Horvath, S., Howard, R. E., Jeromin, A., Jochim, J. M., Kinnunen, M., Lau, C., Lazarz, E. T., Lee, C., Lemon, T. A., Li, L., Li, Y., Morris, J. A., Overly, C. C., Parker, P. D., Parry, S. E., Reding, M., Royall, J. J., Schulkin, J., Sequeira, P. A., Slaughterbeck, C. R., Smith, S. C., Sodt, A. J., Sunkin, S. M., Swanson, B. E., Vawter, M. P., Williams, D., Wohnoutka, P., Zielke, H. R., Geschwind, D. H., Hof, P. R., Smith, S. M., Koch, C., Grant, S. G. N., & Jones, A. R. (2012). An anatomically comprehensive atlas of the adult human brain transcriptome. Nature, 489(7416), 391–399.
Hayasaka, S., & Laurienti, P. J. (2010). Comparison of characteristics between region-and voxel-based network analyses in resting-state fMRI data. NeuroImage, 50(2), 499–508.
Honea, R. A., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., Hobbs, K. B., Pezawas, L., Mattay, V. S., Egan, M. F., Verchinski, B., Passingham, R. E., Weinberger, D. R., & Callicott, J. H. (2008). Is gray matter volume an intermediate phenotype for schizophrenia? A voxel-based morphometry study of patients with schizophrenia and their healthy siblings. Biological Psychiatry, 63(5), 465–474.
Insel, T. R. (2010). Rethinking schizophrenia. Nature, 468(7321), 187–193.
Kay, S. R., Fiszbein, A., & Opler, L. A. (1987). The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 13(2), 261–276.
Kikinis, Z., Fallon, J. H., Niznikiewicz, M., Nestor, P., Davidson, C., Bobrow, L., Pelavin, P. E., Fischl, B., Yendiki, A., McCarley, R. W., Kikinis, R., Kubicki, M., & Shenton, M. E. (2010). Gray matter volume reduction in rostral middle frontal gyrus in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 123(2–3), 153–159.
Lichtenstein, P., Yip, B. H., Bjork, C., Pawitan, Y., Cannon, T. D., Sullivan, P. F., et al. (2009). Common genetic determinants of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder in Swedish families: A population-based study. Lancet, 373(9659), 234–239.
Liu, F., Guo, W., Liu, L., Long, Z., Ma, C., Xue, Z., Wang, Y., Li, J., Hu, M., Zhang, J., du, H., Zeng, L., Liu, Z., Wooderson, S. C., Tan, C., Zhao, J., & Chen, H. (2013). Abnormal amplitude low-frequency oscillations in medication-naive, first-episode patients with major depressive disorder: A resting-state fMRI study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 146(3), 401–406.
Liu, F., Guo, W., Fouche, J. P., Wang, Y., Wang, W., Ding, J., Zeng, L., Qiu, C., Gong, Q., Zhang, W., & Chen, H. (2015a). Multivariate classification of social anxiety disorder using whole brain functional connectivity. Brain Structure & Function, 220(1), 101–115.
Liu, F., Zhu, C., Wang, Y., Guo, W., Li, M., Wang, W., Long, Z., Meng, Y., Cui, Q., Zeng, L., Gong, Q., Zhang, W., & Chen, H. (2015b). Disrupted cortical hubs in functional brain networks in social anxiety disorder. Clinical Neurophysiology, 126(9), 1711–1716.
Liu, F., Zhuo, C., & Yu, C. (2016). Altered cerebral blood flow covariance network in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 10, 308.
Liu, F., Wang, Y., Li, M., Wang, W., Li, R., Zhang, Z., Lu, G., & Chen, H. (2017). Dynamic functional network connectivity in idiopathic generalized epilepsy with generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Human Brain Mapping, 38(2), 957–973.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Fornito, A. (2014). Brain networks in schizophrenia. Neuropsychology Review, 24(1), 32–48.
van den Heuvel, M. P., Sporns, O., Collin, G., Scheewe, T., Mandl, R. C., Cahn, W., et al. (2013). Abnormal rich club organization and functional brain dynamics in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(8), 783–792.
Ortiz-Teran, L., Diez, I., Ortiz, T., Perez, D. L., Aragon, J. I., Costumero, V., et al. (2017). Brain circuit-gene expression relationships and neuroplasticity of multisensory cortices in blind children. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(26), 6830–6835.
Ripke, S., Neale, B. M., Corvin, A., Walters, J. T., Farh, K.-H., Holmans, P. A., et al. (2014). Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature, 511(7510), 421.
Romme, I. A., de Reus, M. A., Ophoff, R. A., Kahn, R. S., & van den Heuvel, M. P. (2017). Connectome Disconnectivity and cortical gene expression in patients with schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 81(6), 495–502.
Roshchupkin, G. V., Adams, H. H., van der Lee, S. J., Vernooij, M. W., van Duijn, C. M., Uitterlinden, A. G., van der Lugt, A., Hofman, A., Niessen, W. J., & Ikram, M. A. (2016). Fine-mapping the effects of Alzheimer's disease risk loci on brain morphology. Neurobiology of Aging, 48, 204–211.
Rowland, L. M., Demyanovich, H. K., Wijtenburg, S. A., Eaton, W. W., Rodriguez, K., Gaston, F., Cihakova, D., Talor, M. V., Liu, F., McMahon, R. R., Hong, L. E., & Kelly, D. L. (2017). Antigliadin antibodies (AGA IgG) are related to neurochemistry in schizophrenia. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 8, 104.
Subira, M., Cano, M., de Wit, S. J., Alonso, P., Cardoner, N., Hoexter, M. Q., et al. (2016). Structural covariance of neostriatal and limbic regions in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience, 41(2), 115–123.
Tam, G. W., van de Lagemaat, L. N., Redon, R., Strathdee, K. E., Croning, M. D., Malloy, M. P., et al. (2010). Confirmed rare copy number variants implicate novel genes in schizophrenia. Biochemical Society Transactions, 38(2), 445–451.
Tregellas, J. R., Shatti, S., Tanabe, J. L., Martin, L. F., Gibson, L., Wylie, K., & Rojas, D. C. (2007). Gray matter volume differences and the effects of smoking on gray matter in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 97(1–3), 242–249.
Wang, J., Wang, L., Zang, Y., Yang, H., Tang, H., Gong, Q., Chen, Z., Zhu, C., & He, Y. (2009). Parcellation-dependent small-world brain functional networks: A resting-state fMRI study. Human Brain Mapping, 30(5), 1511–1523.
Wang, J. H., Zuo, X. N., Gohel, S., Milham, M. P., Biswal, B. B., & He, Y. (2011). Graph theoretical analysis of functional brain networks: Test-retest evaluation on short- and long-term resting-state functional MRI data. PLoS One, 6(7), e21976.
Xia, M., Wang, J., & He, Y. (2013). BrainNet viewer: A network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS One, 8(7), e68910.
Xu, Q., Fu, J., Liu, F., Qin, W., Liu, B., Jiang, T., et al. (2018). Left parietal functional connectivity mediates the association between COMT rs4633 and verbal intelligence in healthy adults. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 12(233). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00233.
Zalesky, A., Fornito, A., Harding, I. H., Cocchi, L., Yucel, M., Pantelis, C., et al. (2010). Whole-brain anatomical networks: Does the choice of nodes matter? NeuroImage, 50(3), 970–983.
Zhang, B., Xu, Y. H., Wei, S. G., Zhang, H. B., Fu, D. K., Feng, Z. F., et al. (2014). Association study identifying a new susceptibility gene (AUTS2) for schizophrenia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(11), 19406–19416.
Zhu, J., Zhuo, C., Xu, L., Liu, F., Qin, W., & Yu, C. (2017). Altered coupling between resting-state cerebral blood flow and functional connectivity in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43(6), 1363–1374.
Zielinski, B. A., Gennatas, E. D., Zhou, J., & Seeley, W. W. (2010). Network-level structural covariance in the developing brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(42), 18191–18196.
Zugman, A., Assuncao, I., Vieira, G., Gadelha, A., White, T. P., Oliveira, P. P., et al. (2015). Structural covariance in schizophrenia and first-episode psychosis: An approach based on graph analysis. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 71, 89–96.
Funding
This study was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501451 to F.L.), the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (16JCYBJC24200 to J.L. and 17JCZDJC35700 to C.Z.), the Tianjin Health Bureau Foundation (2014KR02 to C.Z.), the Tianjin Health Key Program (13KG118 to J.L.), and the “New Century” Talent Training Project of Tianjin Medical University General Hospital (2017 to F.L.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethical committee of the Tianjin Medical University General Hospital.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Electronic supplementary material
Fig. S1
Between-group comparisons of structural covariance strength (SCS) maps (left panel: mean SCS maps subtraction; right panel: raw p values obtained by permutation test) across a range of analytical approaches: (A) weighted network, correlation threshold = 0.2, voxel size = 3 × 3 × 3 mm3; (B) binarized network, correlation threshold = 0.2, voxel size = 3 × 3 × 3 mm3; (C) weighted network, correlation threshold = 0.2, voxel size = 1.5 × 1.5 × 1.5 mm3; (D) weighted network, correlation threshold = 0.1, voxel size = 3 × 3 × 3 mm3; (E) weighted network, correlation threshold = 0.3, voxel size = 3 × 3 × 3 mm3. The SCS maps were visualized with the BrainNet Viewer (Xia et al. 2013). Abbreviation: SCH, schizophrenia; HC, healthy controls; mSCS, mean structural covariance strength; L, left; R, right. (GIF 260 kb)
ESM 1
(XLSX 100 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Tian, H., Li, J. et al. Altered voxel-wise gray matter structural brain networks in schizophrenia: Association with brain genetic expression pattern. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 493–502 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9880-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9880-6