Abstract
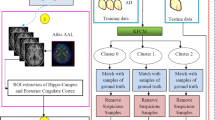
An early intervention of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is highly essential due to the fact that this neuro degenerative disease generates major life-threatening issues, especially memory loss among patients in society. Moreover, categorizing NC (Normal Control), MCI (Mild Cognitive Impairment) and AD early in course allows the patients to experience benefits from new treatments. Therefore, it is important to construct a reliable classification technique to discriminate the patients with or without AD from the bio medical imaging modality. Hence, we developed a novel FCM based Weighted Probabilistic Neural Network (FWPNN) classification algorithm and analyzed the brain images related to structural MRI modality for better discrimination of class labels. Initially our proposed framework begins with brain image normalization stage. In this stage, ROI regions related to Hippo-Campus (HC) and Posterior Cingulate Cortex (PCC) from the brain images are extracted using Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL) method. Subsequently, nineteen highly relevant AD related features are selected through Multiple-criterion feature selection method. At last, our novel FWPNN classification algorithm is imposed to remove suspicious samples from the training data with an end goal to enhance the classification performance. This newly developed classification algorithm combines both the goodness of supervised and unsupervised learning techniques. The experimental validation is carried out with the ADNI subset and then to the Bordex-3 city dataset. Our proposed classification approach achieves an accuracy of about 98.63%, 95.4%, 96.4% in terms of classification with AD vs NC, MCI vs NC and AD vs MCI. The experimental results suggest that the removal of noisy samples from the training data can enhance the decision generation process of the expert systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akgül, C. B., Ünay, D., & Ekin, A. (2009). Automated diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using image similarity and user feedback. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval, 1–34). ACM.
Amadasun, M., & King, R. (1989). Textural features corresponding to textural properties. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 19(5), 1264–1274.
Bay, H., Ess, A., Tuytelaars, T., & Van Gool, L. (2008). Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Computer vision and image understanding, 110(3), pp. 346–359.
Bezdek, J. C., Ehrlich, R., & Full, W. (1984). FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Computers & Geosciences, 10(2–3), 191–203.
Chandrashekar, G., & Sahin, F. (2014). A survey on feature selection methods. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 40(1), 16–28.
Chételat, G., Desgranges, B., Landeau, B., Mezenge, F., Poline, J. B., de La Sayette, V., … & Baron, J. C. (2007). Direct voxel-based comparison between grey matter hypometabolism and atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 131(1), 60–71.
Chu, A., Sehgal, C. M., & Greenleaf, J. F. (1990). Use of gray value distribution of run lengths for texture analysis. Pattern Recognition Letters, 11(6), 415–419.
Chupin, M., Gérardin, E., Cuingnet, R., Boutet, C., Lemieux, L., Lehéricy, S., … & Colliot, O. (2009). Fully automatic hippocampus segmentation and classification in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment applied on data from ADNI. Hippocampus, 19(6), 579–587.
Cocosco, C. A., Zijdenbos, A. P., & Evans, A. C. (2003). A fully automatic and robust brain MRI tissue classification method. Medical Image Analysis, 7(4), 513–527.
Colliot, O., Chételat, G., Chupin, M., Desgranges, B., Magnin, B., Benali, H., … & Lehéricy, S. (2008). Discrimination between Alzheimer disease, mild cognitive impairment, and normal aging by using automated segmentation of the hippocampus. Radiology, 248(1), 194–201.
Cuingnet, R., Gerardin, E., Tessieras, J., Auzias, G., Lehéricy, S., & Habert, M. O. … & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2011). Automatic classification of patients with Alzheimer’s disease from structural MRI: a comparison of ten methods using the ADNI database. Neuroimage, 56(2), 766–781.
Dasarathy, B. V., & Holder, E. B. (1991). Image characterizations based on joint gray level—run length distributions. Pattern Recognition Letters, 12(8), 497–502.
Davatzikos, C., Fan, Y., Wu, X., Shen, D., & Resnick, S. M. (2008). Detection of prodromal Alzheimer’s disease via pattern classification of magnetic resonance imaging. Neurobiology of Aging, 29(4), 514–523.
Dyer, C. R., & Rosenfeld, A. (1976). Fourier texture features- Suppression of aperture effects(Landsat geological terrain image power spectra). IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 6, 703–705.
El-Dahshan, E. A., Salem, A. B. M., & Younis, T. H. (2009). A hybrid technique for automatic MRI brain images classification. Studia Univ. Babes-Bolyai, Informatica, 54(1), 55–67.
El-Dahshan, E. S. A., Hosny, T., & Salem, A. B. M. (2010). Hybrid intelligent techniques for MRI brain images classification. Digital Signal Processing, 20(2), 433–441.
Fan, Y., Batmanghelich, N., Clark, C. M., & Davatzikos, C. & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2008). Spatial patterns of brain atrophy in MCI patients, identified via high-dimensional pattern classification, predict subsequent cognitive decline. Neuroimage, 39(4), 1731–1743.
Frisoni, G. B., Testa, C., Sabattoli, F., Beltramello, A., Soininen, H., & Laakso, M. P. (2005). Structural correlates of early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease: voxel based morphometric study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 76(1), 112–114.
Galloway, M. M. (1975). Texture classification using gray level run length. Comput. Graph. Image Process, 4(2), 172–179.
Gerardin, E., Chételat, G., Chupin, M., Cuingnet, R., Desgranges, B., Kim, H. S., … & Eustache, F. (2009). Multidimensional classification of hippocampal shape features discriminates Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment from normal aging. Neuroimage, 47(4), 1476–1486.
Gonzalez, R. C., & Woods, R. E. Digital image processing using MATLAB (2nd edn.). Pearson Prentice Hall (Chap. 11), 2010.
Gutman, B., Wang, Y., Morra, J., Toga, A. W., & Thompson, P. M. (2009). Disease classification with hippocampal shape invariants. Hippocampus, 19(6), 572–578.
Haralick, R. M., & Shanmugam, K. (1973). Textural features for image classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, (6), 610–621.
Hu, M. K. (1962). Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 8(2), 179–187.
Kim, Y., Street, W. N., & Menczer, F. (2003). Feature selection in data mining. Data Mining: opportunities and Challenges, 3(9), 80–105.
Klöppel, S., Stonnington, C. M., Chu, C., Draganski, B., Scahill, R. I., Rohrer, J. D., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2008). Automatic classification of MR scans in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 131(3), 681–689.
Kohavi, R. (1995). A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. Ijcai, 14(2) pp. 1137–1145).
Kusy, M., & Kowalski, P. A. (2018). Weighted probabilistic neural network. Information Sciences, 430, 65–76.
Laws, K. I. (1980, July). Rapid texture identification. In” image proc. for missile guid.”. (Vol. 238, pp. 376–381).
Magnin, B., Mesrob, L., Kinkingnéhun, S., Pélégrini-Issac, M., Colliot, O., Sarazin, M., … & Benali, H. (2009). Support vector machine-based classification of Alzheimer’s disease from whole-brain anatomical MRI. Neuroradiology, 51(2), 73–83.
Munteanu, C. R., Fernandez-Lozano, C., Abad, V. M., Fernández, S. P., Álvarez-Linera, J., Hernández-Tamames, J. A., & Pazos, A. (2015). Classification of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease with machine-learning techniques using 1 H magnetic resonance spectroscopy data. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(15), 6205–6214.
Nestor, P. J., Fryer, T. D., Ikeda, M., & Hodges, J. R. (2003). Retrosplenial cortex (BA 29/30) hypometabolism in mild cognitive impairment (prodromal Alzheimer’s disease). European Journal of Neuroscience, 18(9), 2663–2667.
Pan, Y., Huang, W., Lin, Z., Zhu, W., Zhou, J., Wong, J., Ding, Z. (2015). Brain tumor grading based on neural networks and convolutional neural networks. Conference Proceedings: Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. pp. 699–702. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2015.7318458.
Ridha, B. H., Barnes, J., van de Pol, L. A., Schott, J. M., Boyes, R. G., Siddique, M. M., … & Fox, N. C. (2007). Application of automated medial temporal lobe atrophy scale to Alzheimer disease. Archives of Neurology, 64(6), 849–854.
Saad, N. M., Bakar, S. A. R. S. A., Muda, A. S., & Mokji, M. M. (2015). Review of brain lesion detection and classification using neuroimaging analysis techniques. Jurnal Teknologi, 74(6), 73–85.
Shen, K. K., Fripp, J., Mériaudeau, F., Chételat, G., Salvado, O., & Bourgeat, P. & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2012). Detecting global and local hippocampal shape changes in Alzheimer’s disease using statistical shape models. Neuroimage, 59(3), 2155–2166.
Srinivasan, G. N., & Shobha, G. (2008). Statistical texture analysis. In Proceedings of World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 36, 1264–1269.
Stoitsis, J., Golemati, S., & Nikita, K. S. (2006). A modular software system to assist interpretation of medical images—Application to vascular ultrasound images. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 55(6), 1944–1952.
Studholme, C., Drapaca, C., Iordanova, B., & Cardenas, V. (2006). Deformation-based mapping of volume change from serial brain MRI in the presence of local tissue contrast change. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 25(5), 626–639.
Tang, J., Alelyani, S., & Liu, H. (2014). Feature selection for classification: A review. Data Classification: Algorithms and Applications, p. 37.
Toews, M., Wells, W., Collins, D. L., & Arbel, T. (2010). Feature-based morphometry: discovering group-related anatomical patterns. NeuroImage, 49(3), 2318–2327.
Toga, A. W., Thompson, P. M., Mega, M. S., Narr, K. L., & Blanton, R. E. (2001). Probabilistic approaches for atlasing normal and disease-specific brain variability. Anatomy and Embryology, 204(4), 267–282.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., … & Joliot, M. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage, 15(1), 273–289.
Weszka, J. S., Dyer, C. R., & Rosenfeld, A. (1976). A comparative study of texture measures for terrain classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, (4), 269–285.
Wu, C. M., Chen, Y. C., & Hsieh, K. S. (1992). Texture features for classification of ultrasonic liver images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 11(2), 141–152.
Zhang, D., Wang, Y., Zhou, L., Yuan, H., & Shen, D. & Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. (2011). Multimodal classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage, 55(3), 856–867.
Zhang, Y., Dong, Z., Wu, L., & Wang, S. (2011). A hybrid method for MRI brain image classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(8), 10049–10053.
Zöllner, F. G., Emblem, K. E., & Schad, L. R. (2012). SVM-based glioma grading: optimization by feature reduction analysis. Zeitschrift Für Medizinische Physik, 22(3), 205–214.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duraisamy, B., Shanmugam, J.V. & Annamalai, J. Alzheimer disease detection from structural MR images using FCM based weighted probabilistic neural network. Brain Imaging and Behavior 13, 87–110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9831-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-018-9831-2