Abstract
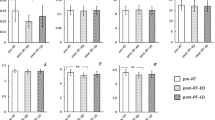
In this study, we seek to longitudinally investigate the network-level functional connectivity (FC) alternations and its association with irradiation dose and cognition changes in the early stage post radiotherapy (RT) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients. We performed independent component analysis (ICA) of resting state blood oxygen level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-fMRI) from 39 newly diagnosed NPC patients before receiving treatment (baseline), and 3 months post-RT. the default mode network (DMN), salience network (SN), and executive control network (ECN) were extracted with well-validated software (GIFT). Inter-network connectivity was assessed using the functional network connectivity (FNC) toolbox. The inter- and intra-network FC was compared between time points, and the z value of FC alternation was correlated with the RT dose value and cognitive changes. Compared with baseline, the FC of the left anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) within the DMN, and the right insular within the SN, significantly reduced 3 months post-RT, with greater effects at higher doses in the right insular. Bilateral ECN FC was also significantly lower 3 months post-RT compared to the baseline. Chemotherapy was not associated with inter- and intra- network FC change. We found intra- and inter-network FC disruption in NPC patients 3 months post-RT, with the right insular showing a dose-dependent effect. Thus, this network-level FC may serve as a potential biomarker of the RT-induced brain functional impairments, and provide valuable targets for further functional recovery treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckmann, C. F., DeLuca, M., Devlin, J. T., & Smith, S. M. (2005). Investigations into resting-state connectivity using independent component analysis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 360(1457), 1001–1013. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2005.1634.
Biswal, B., Yetkin, F. Z., Haughton, V. M., & Hyde, J. S. (1995). Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 34(4), 537–541.
Bressler, S. L., & Menon, V. (2010). Large-scale brain networks in cognition: emerging methods and principles. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(6), 277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.04.004.
Calhoun, V. D., Adali, T., Pearlson, G. D., & Pekar, J. J. (2001). A method for making group inferences from functional MRI data using independent component analysis. Human Brain Mapping, 14(3), 140–151.
Calhoun, V. D., Liu, J., & Adali, T. (2009). A review of group ICA for fMRI data and ICA for joint inference of imaging, genetic, and ERP data. Neuroimage, 45(1 Suppl), 163–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.057.
Damoiseaux, J. S., Rombouts, S. A., Barkhof, F., Scheltens, P., Stam, C. J., Smith, S. M., et al. (2006). Consistent resting-state networks across healthy subjects. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(37), 13848–13853. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601417103.
Dumas, J. A., Makarewicz, J., Schaubhut, G. J., Devins, R., Albert, K., Dittus, K., et al. (2013). Chemotherapy altered brain functional connectivity in women with breast cancer: a pilot study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7(4), 524–532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9244-1.
Ewers, M., Sperling, R. A., Klunk, W. E., Weiner, M. W., & Hampel, H. (2011). Neuroimaging markers for the prediction and early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Trends in Neurosciences, 34(8), 430–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2011.05.005.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., Van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(27), 9673–9678. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504136102.
Greene-Schloesser, D., & Robbins, M. E. (2012). Radiation-induced cognitive impairment–from bench to bedside. Neuro-Oncology, 14 Suppl, 4, 37–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos196.
Greicius, M. D., & Kimmel, D. L. (2012). Neuroimaging insights into network-based neurodegeneration. Current Opinion in Neurology, 25(6), 727–734. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0b013e32835a26b3.
Gusnard, D. A., Raichle, M. E., & Raichle, M. E. (2001). Searching for a baseline: functional imaging and the resting human brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(10), 685–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/35094500.
Hsiao, K. Y., Yeh, S. A., Chang, C. C., Tsai, P. C., Wu, J. M., & Gau, J. S. (2010). Cognitive function before and after intensity-modulated radiation therapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective study. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 77(3), 722–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2009.06.080.
Hyvarinen, A. (1999). Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 626–634. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.761722.
Iyer, N. S., Balsamo, L. M., Bracken, M. B., & Kadan-Lottick, N. S. (2015). Chemotherapy-only treatment effects on long-term neurocognitive functioning in childhood ALL survivors: a review and meta-analysis. Blood, 126(3), 346–353. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-02-627414.
Jafri, M. J., Pearlson, G. D., Stevens, M., & Calhoun, V. D. (2008). A method for functional network connectivity among spatially independent resting-state components in schizophrenia. Neuroimage, 39(4), 1666–1681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.11.001.
Karunamuni, R., Bartsch, H., White, N. S., Moiseenko, V., Carmona, R., Marshall, D. C., et al. (2016). Dose-dependent cortical thinning after partial brain irradiation in high-grade glioma. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 94(2), 297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.10.026.
Li, Y. O., Adali, T., & Calhoun, V. D. (2007). Estimating the number of independent components for functional magnetic resonance imaging data. Human Brain Mapping, 28(11), 1251–1266. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20359.
Lin, H., Huang, S., Deng, X., Zhu, J., & Chen, L. (2014). Comparison of 3D anatomical dose verification and 2D phantom dose verification of IMRT/VMAT treatments for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiation Oncology, 9, 71. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-717X-9-71.
Lv, X. F., Qiu, Y. W., Tian, J. Z., Xie, C. M., Han, L. J., Su, H. H., et al. (2013a). Abnormal regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy. Liver International, 33(3), 375–383. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12096.
Lv, X. F., Ye, M., Han, L. J., Zhang, X. L., Cai, P. Q., Jiang, G. H., et al. (2013b). Abnormal baseline brain activity in patients with HBV-related cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Metabolic Brain Disease, 28(3), 485–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-013-9420-4.
Lv, X. F., Wu, H. W., Tian, L., Han, L. J., Li, J., Qiu, Y. W., et al. (2016). Aberrant resting-state functional connectivity density in patients with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis. BioMed Research International, 2016, 4168512, https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4168512.
Ma, Q., Wu, D., Zeng, L.-L., Shen, H., Hu, D., & Qiu, S. (2016). Radiation-induced functional connectivity alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with radiotherapy. Medicine, 95(29), e4275. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000004275.
Ma, X., Qiu, Y., Tian, J., Wang, J., Li, S., Zhan, W., et al. (2015). Aberrant default-mode functional and structural connectivity in heroin-dependent individuals. PLoS One, 10(4), e0120861. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0120861.
Makale, M. T., McDonald, C. R., Hattangadi-Gluth, J. A., & Kesari, S. (2017). Mechanisms of radiotherapy-associated cognitive disability in patients with brain tumours. Nature Reviews Neurology, 13(1), 52–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2016.185.
McDonald, B. C., & Saykin, A. J. (2013). Alterations in brain structure related to breast cancer and its treatment: chemotherapy and other considerations. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7(4), 374–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-013-9256-x.
Menon, V. (2011). Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 15(10), 483–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003.
Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q. (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Structure and Function, 214(5–6), 655–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-010-0262-0.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., Bedirian, V., Charbonneau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., et al. (2005). The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 53(4), 695–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x.
Pospisil, P., Kazda, T., Hynkova, L., Bulik, M., Dobiaskova, M., Burkon, P., et al. (2017). Post-WBRT cognitive impairment and hippocampal neuronal depletion measured by in vivo metabolic MR spectroscopy: results of prospective investigational study. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 122(3), 373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2016.12.013.
Prust, M. J., Jafari-Khouzani, K., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., Polaskova, P., Batchelor, T. T., Gerstner, E. R., et al. (2015). Standard chemoradiation for glioblastoma results in progressive brain volume loss. Neurology, 85(8), 683–691. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001861.
Qiu, Y. W., Han, L. J., Lv, X. F., Jiang, G. H., Tian, J. Z., Zhuo, F. Z., et al. (2011). Regional homogeneity changes in heroin-dependent individuals: resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology, 261(2), 551–559. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11102466.
Qiu, Y. W., Jiang, G. H., Ma, X. F., Su, H. H., Lv, X. F., & Zhuo, F. Z. (2016). Aberrant interhemispheric functional and structural connectivity in heroin-dependent individuals. Addiction Biology. https://doi.org/10.1111/adb.12387.
Qiu, Y. W., Lv, X. F., Jiang, G. H., Su, H. H., Ma, X. F., Tian, J. Z., et al. (2017a). Larger corpus callosum and reduced orbitofrontal cortex homotopic connectivity in codeine cough syrup-dependent male adolescents and young adults. European Radiology, 27(3), 1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-016-4465-5.
Qiu, Y. W., Su, H. H., Lv, X. F., Ma, X. F., Jiang, G. H., & Tian, J. Z. (2017b). Intrinsic brain network abnormalities in codeine-containing cough syrup-dependent male individuals revealed in resting-state fMRI. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 45(1), 177–186. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25352.
Raichle, M. E., MacLeod, A. M., Snyder, A. Z., Powers, W. J., Gusnard, D. A., & Shulman, G. L. (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(2), 676–682. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.98.2.676.
Schaie, K. W. (2005). What can we learn from longitudinal studies of adult development? Research in Human Development, 2(3), 133–158. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15427617rhd0203_4.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., et al. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349–2356. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5587-06.2007.
Seibert, T. M., Karunamuni, R., Bartsch, H., Kaifi, S., Krishnan, A. P., Dalia, Y., et al. (2017). Radiation dose-dependent hippocampal atrophy detected with longitudinal volumetric magnetic resonance imaging. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 97(2), 263–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.035.
Sestieri, C., Corbetta, M., Romani, G. L., & Shulman, G. L. (2011). Episodic memory retrieval, parietal cortex, and the default mode network: functional and topographic analyses. The Journal of Neuroscience, 31(12), 4407–4420. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3335-10.2011.
Shehzad, Z., Kelly, A. M., Reiss, P. T., Gee, D. G., Gotimer, K., Uddin, L. Q., et al. (2009). The resting brain: unconstrained yet reliable. Cerebral Cortex, 19(10), 2209–2229. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhn256.
Shirer, W. R., Ryali, S., Rykhlevskaia, E., Menon, V., & Greicius, M. D. (2012). Decoding subject-driven cognitive states with whole-brain connectivity patterns. Cerebral Cortex, 22(1), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr099.
Simo, M., Vaquero, L., Ripolles, P., Gurtubay-Antolin, A., Jove, J., Navarro, A., et al. (2016). Longitudinal brain changes associated with prophylactic cranial irradiation in lung cancer. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 11(4), 475–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2015.12.110.
Smith, S. M., Fox, P. T., Miller, K. L., Glahn, D. C., Fox, P. M., Mackay, C. E., et al. (2009). Correspondence of the brain’s functional architecture during activation and rest. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(31), 13040–13045. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0905267106.
Soussain, C., Ricard, D., Fike, J. R., Mazeron, J. J., Psimaras, D., & Delattre, J. Y. (2009). CNS complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Lancet, 374(9701), 1639–1651. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61299-X.
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J., & Menon, V. (2008). A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(34), 12569–12574. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0800005105.
Storey, J. D. (2002). A direct approach to false discovery rates. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B-Statistical Methodology, 64, 479–498. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9868.00346.
Sultanem, K., Shu, H. K., Xia, P., Akazawa, C., Quivey, J. M., Verhey, L. J., et al. (2000). Three-dimensional intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: the University of California-San Francisco experience. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics, 48(3), 711–722.
Tang, Y., Luo, D., Rong, X., Shi, X., & Peng, Y. (2012). Psychological disorders, cognitive dysfunction and quality of life in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with radiation-induced brain injury. PLoS One, 7(6), e36529. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036529.
van de Ven, V. G., Formisano, E., Prvulovic, D., Roeder, C. H., & Linden, D. E. (2004). Functional connectivity as revealed by spatial independent component analysis of fMRI measurements during rest. Human Brain Mapping, 22(3), 165–178. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20022.
Wang, S., Wu, E. X., Qiu, D., Leung, L. H., Lau, H. F., & Khong, P. L. (2009). Longitudinal diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study of radiation-induced white matter damage in a rat model. Cancer Research, 69(3), 1190–1198. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2661.
Wei, W. I., & Kwong, D. L. (2010). Current management strategy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngologica, 3(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2010.3.1.1.
Wei, W. I., & Sham, J. S. (2005). Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet, 365(9476), 2041–2054. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66698-6.
Xu, C., Zhang, L. H., Chen, Y. P., Liu, X., Zhou, G. Q., Lin, A. H., et al. (2017). Chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in stage II nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a systemic review and meta-analysis of 2138 patients. Journal of Cancer, 8(2), 287–297. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.17317.
Yang, M., Kim, J., Kim, J. S., Kim, S. H., Kim, J. C., Kang, M. J., et al. (2014). Hippocampal dysfunctions in tumor-bearing mice. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 36, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.10.022.
Zhang, D., & Raichle, M. E. (2010). Disease and the brain’s dark energy. Nature Reviews Neurology, 6(1), 15–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2009.198.
Zhang, L. Y., Yang, H. Y., & Tian, Y. (2015). Radiation-induced cognitive impairment. Therapeutic Targets for Neurological Diseases, 2, e837. https://doi.org/10.14800/ttnd.837.
Acknowledgements
We thank LetPub (http://www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by grants from the Natural Scientific Foundation of China (grant numbers: 81401399, 81560283, and 81201084), Natural Scientific Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (grant number: 20151BAB205049), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant number: 15ykpy35), and Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant number: B2014162).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Y., Guo, Z., Han, L. et al. Network-level dysconnectivity in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) early post-radiotherapy: longitudinal resting state fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 12, 1279–1289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9801-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-017-9801-0