Abstract
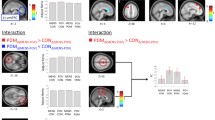
Primary dysmenorrhea (PDM), characterized by cramping pain in the lower abdomen, is a common gynecological disorder in women of child-bearing age. An increasing number of neuroimaging studies have emphasized that PDM is associated with functional and structural abnormalities in the regions related to the default mode network (DMN). Based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), the aim of this study was to use amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and functional connectivity (FC) to investigate changes of the intrinsic brain activity in the DMN in PDM. Pearson correlation analysis was conducted to assess relationships between the neuroimaging findings and clinical symptoms. Forty-eight PDM patients and thirty-eight matched healthy controls participated in this study. Compared to healthy controls, PDM patients had increased ALFF in the precuneus, dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and decreased ALFF in the thalamus. PDM patients also had decreased connectivity between the precuneus and left dmPFC and right ACC, while increased connectivity between the precuneus and left thalamus. In addition, the ALFF in the left dmPFC in PDM patients positively correlated with disease duration. Our findings provide further evidence of the DMN-related abnormalities in PDM patients which might contribute to a better understanding of the pathophysiology of this disease.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apkarian, A. V., Bushnell, M. C., Treede, R. D., & Zubieta, J. K. (2005). Human brain mechanisms of pain perception and regulation in health and disease. European Journal of Pain, 9(4), 463–484.
As-Sanie, S., Harris, R. E., Napadow, V., Kim, J., Neshewat, G., Kairys, A., et al. (2012). Changes in regional gray matter volume in women with chronic pelvic pain: a voxel-based morphometry study. Pain, 153(5), 1006–1014.
Baliki, M. N., Geha, P. Y., Apkarian, A. V., & Chialvo, D. R. (2008). Beyond feeling: chronic pain hurts the brain, disrupting the default-mode network dynamics. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28(6), 1398–1403.
Bantick, S. J., Wise, R. G., Alexander, P., Stuart, C., Smith, S. M., & Irene, T. (2002). Imaging how attention modulates pain in humans using functional MRI. Brain, 125(Pt 2), 310–319.
Berkley, K. J. (2013). Primary dysmenorrhea: an urgent mandate. Pain, 1, 1–8.
Bluhm, R. L., Williamson, P. C., Osuch, E. A., Frewen, P. A., Stevens, T. K., Boksman, K., et al. (2009). Alterations in default network connectivity in posttraumatic stress disorder related to early-life trauma. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience Jpn, 34(3), 187–194.
Cavanna, A. E., & Trimble, M. R. (2006). The precuneus: a review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain, 129(Pt 3), 564–583.
Cox, D. J., & Meyer, R. G. (1978). Behavioral treatment parameters with primary dysmenorrhea. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 1(3), 297–310.
Dante, M., Massimo, C., Antonio, F., Gian Luca, R., & Armando, T. (2009). Noxious somatosensory stimulation affects the default mode of brain function: evidence from functional MR imaging. Radiology, 253(3), 797–804.
Davis, A. R., & Westhoff, C. L. (2001). Primary dysmenorrhea in adolescent girls and treatment with oral contraceptives. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology, 14(1), 3–8.
Davis, K. D., Taylor, K. S., Hutchison, W. D., Dostrovsky, J. O., Mcandrews, M. P., Richter, E. O., et al. (2005). Human anterior cingulate cortex neurons encode cognitive and emotional demands. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25(37), 8402–8406.
Dawood, M. Y. (2006). Primary dysmenorrhea: advances in pathogenesis and management. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 108(2), 428–441.
Durain, D. (2004). Primary dysmenorrhea: assessment and management update. Journal of Midwifery & Womens Health, 49(6), 520–528.
Fallon, N., Alghamdi, J., Chiu, Y., Sluming, V., Nurmikko, T., & Stancak, A. (2012). Structural alterations in brainstem of fibromyalgia syndrome patients correlate with sensitivity to mechanical pressure. Neurologic Clinics, 3(3), 163–170.
Fox, M. D., & Raichle, M. E. (2007). Spontaneous fluctuations in brain activity observed with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 8(9), 700–711.
Fox, M. D., Snyder, A. Z., Vincent, J. L., Corbetta, M., Van Essen, D. C., & Raichle, M. E. (2005). The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(27), 9673–9678.
Fransson, P. (2005). Spontaneous low-frequency BOLD signal fluctuations: an fMRI investigation of the resting-state default mode of brain function hypothesis. Human Brain Mapping, 26(1), 15–29.
Iacovides, S., Baker, F. C., Avidon, I., & Bentley, A. (2013). Women with dysmenorrhea are hypersensitive to experimental deep muscle pain across the menstrual cycle. The Journal of Pain, 14(10), 1066–1076.
Iacovides, S., Avidon, I., & Baker, F. C. (2015). What we know about primary dysmenorrhea today: a critical review. Human Reproduction Update, 21(6), 762–778.
Katja, W., Ben, S., Raffael, K., Klaas Enno, S., Martin, K., Jon, D., et al. (2005). Modulation of pain processing in hyperalgesia by cognitive demand. NeuroImage, 27(1), 59–69.
Kober, H., Barrett, L. F., Joseph, J., Bliss-Moreau, E., Lindquist, K., & Wager, T. D. (2008). Functional grouping and cortical–subcortical interactions in emotion: A meta-analysis of neuroimaging studies. NeuroImage, 42(2), 998–1031.
Lee, M. H., Smyser, C. D., & Shimony, J. S. (2013). Resting-state fMRI: a review of methods and clinical applications. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34(10), 1866–1872.
Li, F., He, N., Li, Y., Chen, L., Huang, X., Lui, S., et al. (2014). Intrinsic brain abnormalities in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: a resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology, 272(2), 514–523.
Liu, P., Yang, J., Wang, G., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Jin, L., et al. (2016). Altered regional cortical thickness and subcortical volume in women with primary dysmenorrhoea. European Journal of Pain, 20(4), 512–520.
Lukas, V. O., Koen, D., Jan, T., & Qasim, A. (2004). Central nervous system involvement in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Best Practice & Research Clinical Gastroenterology, 18(4), 663–680.
Margulies, D. S., Vincent, J. L., Kelly, C., Lohmann, G., Uddin, L. Q., Biswal, B. B., et al. (2009). Precuneus shares intrinsic functional architecture in humans and monkeys. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106(47), 20069–20074.
Martucci, K. T., Shirer, W. R., Bagarinao, E., Johnson, K. A., Farmer, M. A., Labus, J. S., et al. (2015). The posterior medial cortex in urologic chronic pelvic pain syndrome: detachment from default mode network-a resting-state study from the MAPP research network. Pain, 156(9).
Melzack, R. (1987). The short-form McGill pain questionnaire. Pain, 30(2), 191–197.
Napadow, V., Dhond, R. P., Kim, J., Lacount, L., Vangel, M., Harris, R. E., et al. (2009). Brain encoding of acupuncture sensation--coupling on-line rating with fMRI. NeuroImage, 47(3), 1055–1065.
Ortiz, M. I., Rangel-Flores, E., Carrillo-Alarcón, L. C., & Veras-Godoy, H. A. (2009). Prevalence and impact of primary dysmenorrhea among Mexican high school students. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics, 107(3), 240–243.
Qi, R., Liu, C., Ke, J., Xu, Q., Zhong, J., Wang, F., et al. (2015). Intrinsic brain abnormalities in irritable bowel syndrome and effect of anxiety and depression. Brain Imaging & Behavior.
Sigrid, E., Christina, R., Ulrike, B., Michael, F., Manfred, S., & Gizewski, E. R. (2010). Patients with irritable bowel syndrome have altered emotional modulation of neural responses to visceral stimuli. Gastroenterology, 139(4), 1310–1319.
Tu, C. H., Niddam, D. M., Chao, H. T., Liu, R. S., Hwang, R. J., Yeh, T. C., et al. (2009). Abnormal cerebral metabolism during menstrual pain in primary dysmenorrhea. NeuroImage, 47(1), 28–35.
Tu, C. H., Niddam, D. M., Chao, H. T., Chen, L. F., Chen, Y. S., Wu, Y. T., et al. (2010). Brain morphological changes associated with cyclic menstrual pain. Pain, 150(3), 462–468.
Tu, C. H., Niddam, D. M., Yeh, T. C., Lirng, J. F., Cheng, C. M., Chou, C. C., et al. (2013). Menstrual pain is associated with rapid structural alterations in the brain. Pain, 154(9), 1718–1724.
Usui, C., Hatta, K., Doi, N., Nakanishi, A., Nakamura, H., Nishioka, K., et al. (2010). Brain perfusion in fibromyalgia patients and its differences between responders and poor responders to gabapentin. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 12(2), 1–10.
Utevsky, A. V., Smith, D. V., & Huettel, S. A. (2014). Precuneus is a functional core of the default-mode network. The Journal of Neuroscience, 34(3), 932–940.
Vandenbergh, J., Dupont, P., Fischler, B., Bormans, G., Persoons, P., Janssens, J., et al. (2005). Regional brain activation during proximal stomach distention in humans: a positron emission tomography study. Gastroenterology, 128(3), 564–573.
Wei, S. Y., Chao, H. T., Tu, C. H., Li, W. C., Low, I., Chuang, C. Y., et al. (2016). Changes in functional connectivity of pain modulatory systems in women with primary dysmenorrhea. Pain, 157(1), 92–102.
Witting, N., Dk, K. A., Kupers, R., Svensson, P., Arendt-Nielsen, L., Gjedde, A., et al. (2001). Experimental brush-evoked allodynia activates posterior parietal cortex. Neurology, 57(10), 1817–1824.
Xiao Wei, S., Zhang Ye, D., Xiang Yu, L., Su Fang, L., Xi Nian, Z., Chao Zhe, Z., et al. (2011). REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PloS One, 6(9), e25031.
Yan, C. G., & Zang, Y. F. (2010). DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for "pipeline" data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13.
Zang, Y. F., He, Y., Zhu, C. Z., Cao, Q. J., Sui, M. Q., Liang, M., et al. (2007). Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain & Development, 29(2), 83–91.
Zbys, F., Mona, N., Jagannath, V. A., Beaman, J. H., Kiran, E., & Zuuren, E. J., Van (2012). Beta2-adrenoceptor agonists for dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 5, CD008585.
Zeng, F., Qin, W., Liang, F., Liu, J., Tang, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2011). Abnormal resting brain activity in patients with functional dyspepsia is related to symptom severity. Gastroenterology, 141(2), 499–506.
Zhang, D., & Raichle, M. E. (2010). Disease and the brain’s dark energy. Nature Reviews Neurology, 6(1), 15–28.
Zung, W. W. (1971). A rating instrument for anxiety disorders. Psychosomatics, 12(6), 371–379.
Zung, W. W. K., Richards, C. B., & Short, M. J. (1965). Self-rating depression scale in an outpatient clinic: further validation of the SDS. Archives of General Psychiatry, 13(6), 508–515.
Zyloney, C. E., Jensen, K., Polich, G., Loiotile, R. E., Cheetham, A., Laviolette, P. S., et al. (2010). Imaging the functional connectivity of the periaqueductal gray during genuine and sham electroacupuncture treatment. Molecular Pain, 6, 80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the West China Hospital Subcommittee on Human Studies and was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent after receiving a complete description of the study.
Funding
This study was supported by National Basic Research Program of China under Grant Nos. 2014CB543203, 2015CB856403 and 2012CB518501, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81471738, 81271644, 81471811 and 61401346, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Conflict of interest
Peng Liu, Yanfei Liu, Geliang Wang, Xuejuan Yang, Lingmin Jin, Jinbo Sun and Wei Qin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Liu, Y., Wang, G. et al. Aberrant default mode network in patients with primary dysmenorrhea: a fMRI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1479–1485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9627-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9627-1