Abstract
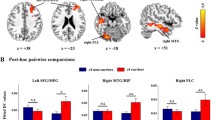
Apolipoprotein E (APOE) ε4 allele is the best established genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, there is a need to understand the effects of this genotype on the brain by simultaneously assessing intrinsic brain network and cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers changes in healthy older ε4 carriers. Thirteen cognitively intact, elderly APOE ε4 carriers and 22 ε3 homozygotes were included in the present study. Eigenvector centrality mapping (ECM) was used to identify brain network hub organization based on resting-state functional MRI (rsfMRI). We evaluated comprehensive cognitive ability and tested levels of Aβ1–42, total-tau (t-tau) and phosphorylated-tau (p-tau181) in CSF. Comparisons of ECM between two groups were conducted, followed by correlations analyses between EC values with significant group differences and cognitive ability/CSF biomarkers. APOE ε4 carriers showed significantly decreased EC values in left medial temporal lobe (MTL), left lingual gyrus (LG) and increased EC values in left middle frontal gyrus (MFG) as compared to non-carriers. Correlation analysis demonstrated that left LG EC value correlated with Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test total learning (RAVLT, r = 0.57, p < 0.05) and t-tau level (r = −0.57, p < 0.05), while left MFG EC values correlated with log-transformed Trail-Making Test B (TMT-B, r = −0.67, p < 0.05) in APOE ε4 carriers. This study suggests the APOE ε4 allele contributes to disruption of brain connectedness in certain functional nodes, which may result from neuronal death caused by toxicity of neurofibrillary tangles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriaanse, S. M., Wink, A. M., Tijms, B. M., Ossenkoppele, R., Verfaillie, S. C., Lammertsma, A. A., Boellaard, R., Scheltens, P., van Berckel, B. N., & Barkhof, F. (2016). The Association of Glucose Metabolism and Eigenvector Centrality in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Connectivity, 6, 1–8.
Alexander, D. M., Williams, L. M., Gatt, J. M., Dobson-Stone, C., Kuan, S. A., Todd, E. G., Schofield, P. R., Cooper, N. J., & Gordon, E. (2007). The contribution of apolipoprotein E alleles on cognitive performance and dynamic neural activity over six decades. Biological Psychology, 75, 229–238.
Babic, M., Svob, S. D., Muck-Seler, D., Pivac, N., Stanic, G., Hof, P. R., & Simic, G. (2014). Update on the core and developing cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer disease. Croatian Medical Journal, 55, 347–365.
Beckmann, C. F., & Smith, S. M. (2003). Probabilistic ICA for FMRI-noise and inference. In Fourth Int. Symp. On Independent Component Analysis and Blind Signal Separation. ISBN (Vol. 695185812).
Binnewijzend, M. A., Adriaanse, S. M., Van der Flier, W. M., Teunissen, C. E., de Munck, J. C., Stam, C. J., Scheltens, P., van Berckel, B. N., Barkhof, F., & Wink, A. M. (2014). Brain network alterations in Alzheimer’s disease measured by eigenvector centrality in fMRI are related to cognition and CSF biomarkers. Human Brain Mapping, 35, 2383–2393.
Blennow, K., & Hampel, H. (2003). CSF markers for incipient Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurology, 2, 605–613.
Bogousslavsky, J., Miklossy, J., Deruaz, J. P., Assal, G., & Regli, F. (1987). Lingual and fusiform gyri in visual processing: a clinico-pathologic study of superior altitudinal hemianopia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 50, 607–614.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1991). Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathologica, 82, 239–259.
Braak, H., & Braak, E. (1997). Diagnostic criteria for neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 18, S85–S88.
Braak, H., Alafuzoff, I., Arzberger, T., Kretzschmar, H., & Del, T. K. (2006). Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathologica, 112, 389–404.
Cho, S., Metcalfe, A. W., Young, C. B., Ryali, S., Geary, D. C., & Menon, V. (2012). Hippocampal-prefrontal engagement and dynamic causal interactions in the maturation of children’s fact retrieval. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 24, 1849–1866.
Cipolotti, L., & Bird, C. M. (2006). Amnesia and the hippocampus. Current Opinion in Neurology, 19, 593–598.
Cole, D. M., Smith, S. M., & Beckmann, C. F. (2010). Advances and pitfalls in the analysis and interpretation of resting-state FMRI data. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 8.
Corder, E. H., Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D. E., Gaskell, P. C., Small, G. W., Roses, A. D., Haines, J. L., & Pericak-Vance, M. A. (1993). Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science, 261, 921–923.
Corder, E. H., Ghebremedhin, E., Taylor, M. G., Thal, D. R., Ohm, T. G., & Braak, H. (2004). The biphasic relationship between regional brain senile plaque and neurofibrillary tangle distributions: modification by age, sex, and APOE polymorphism. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1019, 24–28.
Cox, R. W. (1996). AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Computers and Biomedical Research, 29, 162–173.
Donix, M., Small, G. W., & Bookheimer, S. Y. (2012). Family history and APOE-4 genetic risk in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychology Review, 22, 298–309.
Donix, M., Burggren, A. C., Scharf, M., Marschner, K., Suthana, N. A., Siddarth, P., Krupa, A. K., Jones, M., Martin-Harris, L., Ercoli, L. M., Miller, K. J., Werner, A., von Kummer, R., Sauer, C., Small, G. W., Holthoff, V. A., & Bookheimer, S. Y. (2013). APOE associated hemispheric asymmetry of entorhinal cortical thickness in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Psychiatry Research, 214, 212–220.
Han, S. D., & Bondi, M. W. (2008). Revision of the apolipoprotein E compensatory mechanism recruitment hypothesis. Alzheimers Dement, 4, 251–254.
Huijbers, W., Pennartz, C. M., Rubin, D. C., & Daselaar, S. M. (2011). Imagery and retrieval of auditory and visual information: neural correlates of successful and unsuccessful performance. Neuropsychologia, 49, 1730–1740.
Jak, A. J., Houston, W. S., Nagel, B. J., Corey-Bloom, J., & Bondi, M. W. (2007). Differential cross-sectional and longitudinal impact of APOE genotype on hippocampal volumes in nondemented older adults. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 23, 382–389.
Janke, A. L., de Zubicaray, G., Rose, S. E., Griffin, M., Chalk, J. B., & Galloway, G. J. (2001). 4D deformation modeling of cortical disease progression in Alzheimer’s dementia. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 46, 661–666.
Jiang, Q., Lee, C. Y., Mandrekar, S., Wilkinson, B., Cramer, P., Zelcer, N., Mann, K., Lamb, B., Willson, T. M., Collins, J. L., Richardson, J. C., Smith, J. D., Comery, T. A., Riddell, D., Holtzman, D. M., Tontonoz, P., & Landreth, G. E. (2008). ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron, 58, 681–693.
Joyce, K. E., Laurienti, P. J., Burdette, J. H., & Hayasaka, S. (2010). A new measure of centrality for brain networks. PloS One, 5, e12200.
Kim, J., Basak, J. M., & Holtzman, D. M. (2009). The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron, 63, 287–303.
Klunk, W. E., Engler, H., Nordberg, A., Wang, Y., Blomqvist, G., Holt, D. P., Bergstrom, M., Savitcheva, I., Huang, G. F., Estrada, S., Ausen, B., Debnath, M. L., Barletta, J., Price, J. C., Sandell, J., Lopresti, B. J., Wall, A., Koivisto, P., Antoni, G., Mathis, C. A., & Langstrom, B. (2004). Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease with Pittsburgh compound-B. Annals of Neurology, 55, 306–319.
Koschützki, D., Lehmann, K. A., Peeters, L., Richter, S., Tenfelde-Podehl, D., Zlotowski, O. (2005). Centrality indices. In Network analysis (pp. 16–61). Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Langville, A. N., & Meyer, C. D. (2011). Google’s PageRank and beyond: The science of search engine rankings. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Lech, R. K., & Suchan, B. (2013). The medial temporal lobe: memory and beyond. Behavioural Brain Research, 254, 45–49.
Leshikar, E. D., Duarte, A., & Hertzog, C. (2012). Task-selective memory effects for successfully implemented encoding strategies. PloS One, 7, e38160.
Li, H. J., Hou, X. H., Liu, H. H., Yue, C. L., He, Y., & Zuo, X. N. (2015a). Toward systems neuroscience in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis of 75 fMRI studies. Human Brain Mapping, 36, 1217–1232.
Li, H. J., Hou, X. H., Liu, H. H., Yue, C. L., Lu, G. M., & Zuo, X. N. (2015b). Putting age-related task activation into large-scale brain networks: a meta-analysis of 114 fMRI studies on healthy aging. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 57, 156–174.
Lohmann, G., Margulies, D. S., Horstmann, A., Pleger, B., Lepsien, J., Goldhahn, D., Schloegl, H., Stumvoll, M., Villringer, A., & Turner, R. (2010). Eigenvector centrality mapping for analyzing connectivity patterns in fMRI data of the human brain. PloS One, 5, e10232.
Lou, Y., Huang, P., Li, D., Cen, Z., Wang, B., Gao, J., Xuan, M., Yu, H., Zhang, M., & Luo, W. (2015). Altered brain network centrality in depressed Parkinson’s disease patients. Movement Disorders, 30, 1777–1784.
Luo, X., Qiu, T., Xu, X., Huang, P., Gu, Q., Shen, Z., Yu, X., Jia, Y., Guan, X., Song, R., & Zhang, M. (2016). Decreased inter-hemispheric functional connectivity in cognitively intact elderly APOE varepsilon4 carriers: a preliminary study. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 50, 1137–1148.
Machulda, M. M., Jones, D. T., Vemuri, P., McDade, E., Avula, R., Przybelski, S., Boeve, B. F., Knopman, D. S., Petersen, R. C., & Jack, C. J. (2011). Effect of APOE epsilon4 status on intrinsic network connectivity in cognitively normal elderly subjects. Archives of Neurology, 68, 1131–1136.
Mendoza, J., & Foundas, A. (2007). Clinical neuroanatomy: A neurobehavioral approach. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Mondadori, C. R., de Quervain, D. J., Buchmann, A., Mustovic, H., Wollmer, M. A., Schmidt, C. F., Boesiger, P., Hock, C., Nitsch, R. M., Papassotiropoulos, A., & Henke, K. (2007). Better memory and neural efficiency in young apolipoprotein E epsilon4 carriers. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 1934–1947.
Newman, M. E. (2008). The mathematics of networks. The NEW Palgrave Encyclopedia of Economics, 2, 1–12.
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Human Brain Mapping, 15, 1–25.
Persson, J., Lind, J., Larsson, A., Ingvar, M., Sleegers, K., Van Broeckhoven, C., Adolfsson, R., Nilsson, L. G., & Nyberg, L. (2008). Altered deactivation in individuals with genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia, 46, 1679–1687.
Pievani, M., Galluzzi, S., Thompson, P. M., Rasser, P. E., Bonetti, M., & Frisoni, G. B. (2011). APOE4 is associated with greater atrophy of the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage, 55, 909–919.
Randall, C., Mosconi, L., de Leon, M., & Glodzik, L. (2013). Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease in healthy elderly. Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Ed), 18, 1150–1173.
Reinvang, I., Espeseth, T., & Westlye, L. T. (2013). APOE-related biomarker profiles in non-pathological aging and early phases of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37, 1322–1335.
Reitan, R. M. (1958). Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 8, 271–276.
Ricci, M., Graef, S., Blundo, C., & Miller, L. A. (2012). Using the Rey auditory verbal learning test (RAVLT) to differentiate Alzheimer’s dementia and behavioural variant fronto-temporal dementia. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 26, 926–941.
Richeson, J. A., Baird, A. A., Gordon, H. L., Heatherton, T. F., Wyland, C. L., Trawalter, S., & Shelton, J. N. (2003). An fMRI investigation of the impact of interracial contact on executive function. Nature Neuroscience, 6, 1323–1328.
Rocchi, A., Pellegrini, S., Siciliano, G., & Murri, L. (2003). Causative and susceptibility genes for Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Brain Research Bulletin, 61, 1–24.
Salminen, L. E., Schofield, P. R., Lane, E. M., Heaps, J. M., Pierce, K. D., Cabeen, R., Laidlaw, D. H., Akbudak, E., Conturo, T. E., Correia, S., & Paul, R. H. (2013). Neuronal fiber bundle lengths in healthy adult carriers of the ApoE4 allele: a quantitative tractography DTI study. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 7, 274–281.
Saykin, A. J., Shen, L., Foroud, T. M., Potkin, S. G., Swaminathan, S., Kim, S., Risacher, S. L., Nho, K., Huentelman, M. J., Craig, D. W., Thompson, P. M., Stein, J. L., Moore, J. H., Farrer, L. A., Green, R. C., Bertram, L., Jack, C. J., & Weiner, M. W. (2010). Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative biomarkers as quantitative phenotypes: genetics core aims, progress, and plans. Alzheimers Dement, 6, 265–273.
Schwindt, G. C., & Black, S. E. (2009). Functional imaging studies of episodic memory in Alzheimer’s disease: a quantitative meta-analysis. NeuroImage, 45, 181–190.
Shaw, L. M., Vanderstichele, H., Knapik-Czajka, M., Figurski, M., Coart, E., Blennow, K., Soares, H., Simon, A. J., Lewczuk, P., Dean, R. A., Siemers, E., Potter, W., Lee, V. M., & Trojanowski, J. Q. (2011). Qualification of the analytical and clinical performance of CSF biomarker analyses in ADNI. Acta Neuropathologica, 121, 597–609.
Sheline, Y. I., Morris, J. C., Snyder, A. Z., Price, J. L., Yan, Z., D’Angelo, G., Liu, C., Dixit, S., Benzinger, T., Fagan, A., Goate, A., & Mintun, M. A. (2010). APOE4 allele disrupts resting state fMRI connectivity in the absence of amyloid plaques or decreased CSF Abeta42. Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 17035–17040.
Smith, C. D., Chebrolu, H., Andersen, A. H., Powell, D. A., Lovell, M. A., Xiong, S., & Gold, B. T. (2010). White matter diffusion alterations in normal women at risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of Aging, 31, 1122–1131.
Song, X. W., Dong, Z. Y., Long, X. Y., Li, S. F., Zuo, X. N., Zhu, C. Z., He, Y., Yan, C. G., & Zang, Y. F. (2011). REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PloS One, 6, e25031.
Song, H., Long, H., Zuo, X., Yu, C., Liu, B., Wang, Z., Wang, Q., Wang, F., Han, Y., & Jia, J. (2015). APOE effects on default mode network in Chinese cognitive normal elderly: relationship with clinical cognitive performance. PloS One, 10, e133179.
Sparks, D. L. (1997). Coronary artery disease, hypertension, ApoE, and cholesterol: a link to Alzheimer’s disease? Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 826, 128–146.
Squire, L. R., & Zola-Morgan, S. (1991). The medial temporal lobe memory system. Science, 253, 1380–1386.
Strittmatter, W. J., Saunders, A. M., Schmechel, D., Pericak-Vance, M., Enghild, J., Salvesen, G. S., & Roses, A. D. (1993). Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 90, 1977–1981.
Sulpizio, V., Committeri, G., Lambrey, S., Berthoz, A., & Galati, G. (2013). Selective role of lingual/parahippocampal gyrus and retrosplenial complex in spatial memory across viewpoint changes relative to the environmental reference frame. Behavioural Brain Research, 242, 62–75.
Sunderland, T., Mirza, N., Putnam, K. T., Linker, G., Bhupali, D., Durham, R., Soares, H., Kimmel, L., Friedman, D., Bergeson, J., Csako, G., Levy, J. A., Bartko, J. J., & Cohen, R. M. (2004). Cerebrospinal fluid beta-amyloid1-42 and tau in control subjects at risk for Alzheimer’s disease: the effect of APOE epsilon4 allele. Biological Psychiatry, 56, 670–676.
Suri, S., Heise, V., Trachtenberg, A. J., & Mackay, C. E. (2013). The forgotten APOE allele: a review of the evidence and suggested mechanisms for the protective effect of APOE varepsilon2. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 37, 2878–2886.
Teter, B., Raber, J., Nathan, B., & Crutcher, K. A. (2002). The presence of apoE4, not the absence of apoE3, contributes to AD pathology. Journal of Alzheimers Disease, 4, 155–163.
van Wijk, B. C., Stam, C. J., & Daffertshofer, A. (2010). Comparing brain networks of different size and connectivity density using graph theory. PloS One, 5, e13701.
Westlye, E. T., Lundervold, A., Rootwelt, H., Lundervold, A. J., & Westlye, L. T. (2011). Increased hippocampal default mode synchronization during rest in middle-aged and elderly APOE epsilon4 carriers: relationships with memory performance. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 7775–7783.
Wink, A. M., de Munck, J. C., van der Werf, Y. D., van den Heuvel, O. A., & Barkhof, F. (2012). Fast eigenvector centrality mapping of voxel-wise connectivity in functional magnetic resonance imaging: implementation, validation, and interpretation. Brain Connectivity, 2, 265–274.
Yan, C., & Zang, Y. (2010). DPARSF: a MATLAB toolbox for “pipeline” data analysis of resting-state fMRI. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 4, 13.
Yao, Z., Zhang, Y., Lin, L., Zhou, Y., Xu, C., & Jiang, T. (2010). Abnormal cortical networks in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Computational Biology, 6, e1001006.
Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Jiang, T., Zhou, B., An, N., Dai, H., Wang, P., Niu, Y., Wang, L., & Zhang, X. (2012). Altered spontaneous activity in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment revealed by Regional Homogeneity. NeuroImage, 59, 1429–1440.
Zhuang, L., Wen, W., Zhu, W., Trollor, J., Kochan, N., Crawford, J., Reppermund, S., Brodaty, H., & Sachdev, P. (2010). White matter integrity in mild cognitive impairment: a tract-based spatial statistics study. NeuroImage, 53, 16–25.
Zuo, X. N., Ehmke, R., Mennes, M., Imperati, D., Castellanos, F. X., Sporns, O., & Milham, M. P. (2012). Network centrality in the human functional connectome. Cerebral Cortex, 22, 1862–1875.
Acknowledgments
Data collection and sharing for this project was funded by the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (National Institutes of Health Grant U01 AG024904) and DOD ADNI (Department of Defense award number W81XWH-12-2-0012). ADNI is funded by the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, and through generous contributions from the following: AbbVie, Alzheimer’s Association; Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation; Araclon Biotech; Bio Clinica, Inc.; Biogen; Bristol-Myers Squibb Company; Cere Spir, Inc.; Eisai Inc.; Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Eli Lilly and Company; Euro Immun; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. and its affiliated company Genentech, Inc.; Fujirebio; GE Healthcare; IXICO Ltd.; Janssen Alzheimer Immunotherapy Research & Development, LLC.; Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development LLC.; Lumosity; Lundbeck; Merck & Co., Inc.; MesoScale Diagnostics, LLC.; NeuroRx Research; Neurotrack Technologies; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation; Pfizer Inc.; Piramal Imaging; Servier; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company; and Transition Therapeutics. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research is providing funds to support ADNI clinical sites in Canada. Private sector contributions are facilitated by the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (www.fnih.org). The grantee organization is the Northern California Institute for Research and Education, and the study is coordinated by the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study at the University of California, San Diego. ADNI data are disseminated by the Laboratory for Neuro Imaging at the University of Southern California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the 12th Five-year Plan for National Science and Technology Supporting Program of China (Grant No. 2012BAI10B04), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LZ14H180001 and Grant No. Y16H090026).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants and/or authorized representatives and the study partners before any protocol-specific procedures were carried out in the ADNI study.
Additional information
Xiao Luo and Tiantian Qiu contributed equally to this paper.
Data used in preparation of this article were obtained from the Alzheimer’s disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) database (www.adni.loni.usc.edu). As such, the investigators within the ADNI contributed to the design and implementation of ADNI and/or provided data but did not participate in analysis or writing of this report. A complete listing of ADNI investigators can be found at: http://adni.loni.usc.edu/wp-content/uploads/how_to_apply/ADNI_Acknowledgement_List.pdf.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, X., Qiu, T., Jia, Y. et al. Intrinsic functional connectivity alterations in cognitively intact elderly APOE ε4 carriers measured by eigenvector centrality mapping are related to cognition and CSF biomarkers: a preliminary study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 1290–1301 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9600-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9600-z