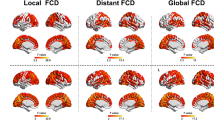
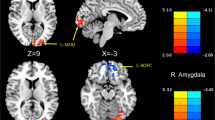
Abstract
Because of the unique position of the topologically central role of densely interconnected brain hubs, our study aimed to investigate whether these regions and their related connections would be particularly vulnerable to migraine. In our study, we explored the rich club structure and its role in global functional dynamics in 30 patients with migraine without aura and 30 healthy controls. DTI and resting fMRI were used to construct structural connectivity (SC) and functional connectivity (FC) networks. An independent replication data set of 26 patients and 26 controls was included to replicate and validate significant findings. As compared with the controls, the structural networks of patients exhibited altered rich club organization with higher level of feeder connection density, abnormal small-world organization with increased global efficiency and decreased strength of SC-FC coupling. As these abnormal topological properties and headache attack duration exhibited a significant association with increased density of feeder connections, our results indicated that migraine may be characterized by a selective alteration of the structural connectivity of the rich club regions, tending to have higher ‘bridgeness’ with non-rich club regions, which may increase the integration among pain-related brain circuits with more excitability but less inhibition for the modulation of migraine.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achard, S., & Bullmore, E. (2007). Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks. PLoS Computational Biology, 3(2), e17.
Achard, S., Salvador, R., Whitcher, B., Suckling, J., & Bullmore, E. (2006). A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(1), 63–72.
Alexander-Bloch, A. F., Vértes, P. E., Stidd, R., Lalonde, F., Clasen, L., Rapoport, J., et al. (2012). The anatomical distance of functional connections predicts brain network topology in health and schizophrenia. Cerebral Cortex, 23, 127–138.
Antal, A., & Paulus, W. (2011). A case of refractory orofacial pain treated by transcranial direct current stimulation applied over hand motor area in combination with NMDA agonist drug intake. Brain Stimulation, 4(2), 117–121.
Apkarian, A. V., Baliki, M. N., & Geha, P. Y. (2009). Towards a theory of chronic pain. Progress in Neurobiology, 87(2), 81–97.
Apkarian, A. V., Hashmi, J. A., & Baliki, M. N. (2011). Pain and the brain: specificity and plasticity of the brain in clinical chronic pain. Pain, 152(3), S49–S64.
Bai, F., Shu, N., Yuan, Y., Shi, Y., Yu, H., Wu, D., et al. (2012). Topologically convergent and divergent structural connectivity patterns between patients with remitted geriatric depression and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(12), 4307–4318.
Bashir, A., Lipton, R. B., Ashina, S., & Ashina, M. (2013). Migraine and structural changes in the brain A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology, 81(14), 1260–1268.
Bingel, U., Schoell, E., Herken, W., Büchel, C., & May, A. (2007). Habituation to painful stimulation involves the antinociceptive system. Pain, 131(1), 21–30.
Borsook, D., Upadhyay, J., Chudler, E. H., & Becerra, L. (2010). A key role of the basal ganglia in pain and analgesia-insights gained through human functional imaging. Molecular Pain, 6(1), 27.
Borsook, D., Maleki, N., Becerra, L., & McEwen, B. (2012). Understanding migraine through the lens of maladaptive stress responses: a model disease of allostatic load. Neuron, 73(2), 219–234.
Brummitt, C. D., D’Souza, R. M., & Leicht, E. (2012). Suppressing cascades of load in interdependent networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(12), E680–E689.
Bullmore, E., & Sporns, O. (2012). The economy of brain network organization. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 13(5), 336–349.
Bullmore, E. T., Suckling, J., Overmeyer, S., Rabe-Hesketh, S., Taylor, E., & Brammer, M. J. (1999). Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE T Medical Imaging, 18(1), 32–42.
Cavada, C., Tejedor, J., Cruz-Rizzolo, R. J., & Reinoso-Suárez, F. (2000). The anatomical connections of the macaque monkey orbitofrontal cortex. a review. Cerebral Cortex, 10(3), 220–242.
Colizza, V., Flammini, A., Serrano, M. A., & Vespignani, A. (2006). Detecting rich-club ordering in complex networks. Nature Physics, 2(2), 110–115.
Collin, G., Sporns, O., Mandl, R. C., & van den Heuvel, M. P. (2014). Structural and functional aspects relating to cost and benefit of rich club organization in the human cerebral cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 24(9), 2258–2267.
Crossley, N. A., Mechelli, A., Vértes, P. E., Winton-Brown, T. T., Patel, A. X., Ginestet, C. E., et al. (2013). Cognitive relevance of the community structure of the human brain functional coactivation network. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(28), 11583–11588.
Crossley, N. A., Mechelli, A., Scott, J., Carletti, F., Fox, P. T., McGuire, P., et al. (2014). The hubs of the human connectome are generally implicated in the anatomy of brain disorders. Brain, 137(8), 2382–2395.
DaSilva, A. F., Mendonca, M. E., Zaghi, S., Lopes, M., DosSantos, M. F., Spierings, E. L., et al. (2012). tDCS‐induced analgesia and electrical fields in pain‐related neural networks in chronic migraine. Headache, 52(8), 1283–1295.
Draganski, B., Kherif, F., Klöppel, S., Cook, P. A., Alexander, D. C., Parker, G. J., et al. (2008). Evidence for segregated and integrative connectivity patterns in the human basal ganglia. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(28), 7143–7152.
Fair, D. A., Nigg, J. T., Iyer, S., Bathula, D., Mills, K. L., Dosenbach, N. U., et al. (2012). Distinct neural signatures detected for ADHD subtypes after controlling for micro-movements in resting state functional connectivity MRI data. Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience, 6, 80.
Gong, G., He, Y., Concha, L., Lebel, C., Gross, D. W., Evans, A. C., et al. (2009a). Mapping anatomical connectivity patterns of human cerebral cortex using in vivo diffusion tensor imaging tractography. Cerebral Cortex, 19(3), 524–536.
Gong, G., Rosa-Neto, P., Carbonell, F., Chen, Z. J., He, Y., & Evans, A. C. (2009b). Age-and gender-related differences in the cortical anatomical network. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(50), 15684–15693.
Hagmann, P., Cammoun, L., Gigandet, X., Meuli, R., Honey, C. J., Wedeen, V. J., et al. (2008). Mapping the structural core of human cerebral cortex. PLoS Biology, 6(7), e159.
Irfanoglu, M. O., Walker, L., Sarlls, J., Marenco, S., & Pierpaoli, C. (2012). Effects of image distortions originating from susceptibility variations and concomitant fields on diffusion MRI tractography results. NeuroImage, 61(1), 275–288.
Kong, J., & Charlestown, M. (2015). Neuromodulation of conditioned placebo/nocebo in heat pain: anodal vs. cathodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000163.
Leemans, A., & Jones, D. K. (2009). The B‐matrix must be rotated when correcting for subject motion in DTI data. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 61(6), 1336–1349.
Liu, J., Lan, L., Li, G., Yan, X., Nan, J., Xiong, S., et al. (2013a). Migraine-related gray matter and white matter changes at a 1-year follow-up evaluation. The Journal of Pain, 14(12), 1703–1708.
Liu, J., Zhao, L., Nan, J., Li, G., Xiong, S., von Deneen, K. M., et al. (2013b). The trade-off between wiring cost and network topology in white matter structural networks in health and migraine. Experimental Neurology, 248, 196–204.
Liu, J., Lan, L., Mu, J., Zhao, L., Yuan, K., Zhang, Y., et al. (2015a). Genetic contribution of catechol‐O‐methyltransferase in hippocampal structural and functional changes of female migraine sufferers. Human Brain Mapping, 36(5), 1782–1795.
Liu, J., Zhao, L., Lei, F., Zhang, Y., Yuan, K., Gong, Q., et al. (2015b). Disrupted resting‐state functional connectivity and its changing trend in migraine suffers. Human Brain Mapping, 36(5), 1892–1907.
Loher, T., Burgunder, J., Weber, S., Sommerhalder, R., & Krauss, J. (2002). Effect of chronic pallidal deep brain stimulation on off period dystonia and sensory symptoms in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 73(4), 395–399.
Maleki, N., Becerra, L., Nutile, L., Pendse, G., Brawn, J., Bigal, M., et al. (2011). Migraine attacks the basal ganglia. Molecular Pain, 7(71), 8069–8067.
May, A. (2009). New insights into headache: an update on functional and structural imaging findings. Nature Reviews Neurology, 5(4), 199–209.
Mori, S., & van Zijl, P. (2002). Fiber tracking: principles and strategies—a technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15(7–8), 468–480.
Newman, M. E. (2006). Modularity and community structure in networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(23), 8577–8582.
Nitsche, M. A., Cohen, L. G., Wassermann, E. M., Priori, A., Lang, N., Antal, A., et al. (2008). Transcranial direct current stimulation: state of the art 2008. Brain Stimulation, 1(3), 206–223.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2142–2154.
Rubinov, M., & Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage, 52(3), 1059–1069.
Rule, R. R., Shimamura, A. P., & Knight, R. T. (2002). Orbitofrontal cortex and dynamic filtering of emotional stimuli. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 2(3), 264–270.
Schwedt, T. J., Chiang, C.-C., Chong, C. D., & Dodick, D. W. (2015). Functional MRI of migraine. The Lancet Neurology, 14(1), 81–91.
Senden, M., Deco, G., de Reus, M. A., Goebel, R., & van den Heuvel, M. P. (2014). Rich club organization supports a diverse set of functional network configurations. NeuroImage, 96, 174–182.
Shu, N., Liu, Y., Li, K., Duan, Y., Wang, J., Yu, C., et al. (2011). Diffusion tensor tractography reveals disrupted topological efficiency in white matter structural networks in multiple sclerosis. Cerebral Cortex, 21(11), 2565–2577.
Sporns, O., Tononi, G., & Kötter, R. (2005). The human connectome: a structural description of the human brain. PLoS Computational Biology, 1(4), e42.
Supekar, K., Uddin, L. Q., Prater, K., Amin, H., Greicius, M. D., & Menon, V. (2010). Development of functional and structural connectivity within the default mode network in young children. NeuroImage, 52(1), 290–301.
Tomasi, D., Wang, G. J., & Volkow, N. D. (2013). Energetic cost of brain functional connectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(33), 13642–13647.
Tzourio-Mazoyer, N., Landeau, B., Papathanassiou, D., Crivello, F., Etard, O., Delcroix, N., et al. (2002). Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. NeuroImage, 15(1), 273–289.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2011). Rich-club organization of the human connectome. Journal of Neuroscience, 31(44), 15775–15786.
van den Heuvel, M. P., & Sporns, O. (2013). An anatomical substrate for integration among functional networks in human cortex. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(36), 14489–14500.
van den Heuvel, M. P., Kahn, R. S., Goñi, J., & Sporns, O. (2012). High-cost, high-capacity backbone for global brain communication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(28), 11372–11377.
van den Heuvel, M. P., Sporns, O., Collin, G., Scheewe, T., Mandl, R. C., Cahn, W., et al. (2013). Abnormal rich club organization and functional brain dynamics in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry, 70(8), 783–792.
Watts, D. J., & Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 393(6684), 440–442.
Weiland, B. J., Boutros, N. N., Moran, J. M., Tepley, N., & Bowyer, S. M. (2008). Evidence for a frontal cortex role in both auditory and somatosensory habituation: a MEG study. NeuroImage, 42(2), 827–835.
Xia, M., Wang, J., & He, Y. (2013). BrainNet Viewer: a network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS One, 8(7), e68910.
Yuan, K., Zhao, L., Cheng, P., Yu, D., Zhao, L., Dong, T., et al. (2013). Altered structure and resting-state functional connectivity of the basal ganglia in migraine patients without aura. The Journal of Pain, 14(8), 836–844.
Zalesky, A., Fornito, A., & Bullmore, E. T. (2010). Network-based statistic: identifying differences in brain networks. NeuroImage, 53(4), 1197–1207.
Zhang, Z., Liao, W., Chen, H., Mantini, D., Ding, J.-R., Xu, Q., et al. (2011). Altered functional–structural coupling of large-scale brain networks in idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Brain, 134(10), 2912–2928.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81471737, 81571640, and 81371530; and the Basic and Cutting-edge Research (plan) Project of Commission of Science and Technology, Chong Qing (cstc2014jcyjA10120); and the Medical Scientific Research (plan) Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Chong Qing (2012-2-187) (20142089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Kang Li, Lijun Liu, Qin Yin, Wanghuan Dun, Xiaolin Xu, Jixin Liu, Ming Zhang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Ethical statements
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Liu, L., Yin, Q. et al. Abnormal rich club organization and impaired correlation between structural and functional connectivity in migraine sufferers. Brain Imaging and Behavior 11, 526–540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9533-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-016-9533-6