Abstract
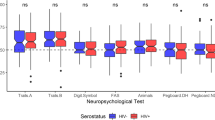
Postural instability occurs in HIV infection, but quantitative balance tests in conjunction with neuroimaging are lacking. We examined whether infratentorial brain tissue volume would be deficient in nondemented HIV-infected individuals and whether selective tissue deficits would be related to postural stability and psychomotor speed performance. The 123 participants included 28 men and 12 women with HIV infection without dementia or alcohol use disorders, and 40 men and 43 women without medical or psychiatric conditions. Participants completed quantitative balance testing, Digit Symbol test, and a test of finger movement speed and dexterity. An infratentorial brain region, supratentorial ventricular system, and corpus callosum were quantified with MRI-derived atlas-based parcellation, and together with archival DTI-derived fiber tracking of pontocerebellar and internal and external capsule fiber systems, brain measures were correlated with test performance. The tissue ratio of the infratentorium was ~3% smaller in the HIV than control group. The HIV group exhibited performance deficits in balancing on one foot, walking toe-to-heel, Digit Symbol substitution task, and time to complete all Digit Symbol grid boxes. Total infratentorial tissue ratio was a significant predictor of balance and Digit Symbol scores. Balance scores did not correlate significantly with ventricular volumes, callosal size, or internal or external capsule fiber integrity but did so with indices of pontocerebellar tract integrity. HIV-infected individuals specifically recruited to be without complications from alcohol use disorders had pontocerebellar tissue volume deficits with functional ramifications. Postural stability and psychomotor speed were impaired and attributable, at least in part, to compromised infratentorial brain systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, H., Mehraein, P., & Weis, S. (1996). Degeneration of the cerebellar dentate nucleus and the inferior olivary nuclei in hiv-1-infected brains: a morphometric analysis. Acta Neuropathologica, 92, 150–155.
Ances, B. M., Vaida, F., Rosario, D., Marquie-Beck, J., Ellis, R. J., Simpson, D. M., et al. (2009). Role of metabolic syndrome components in hiv-associated sensory neuropathy. AIDS, 23, 2317–2322.
Anders, K. H., Becker, P. S., Holden, J. K., Sharer, L. R., Cornford, M. E., Hansen, L. A., et al. (1993). Multifocal necrotizing leukoencephalopathy with pontine predilection in immunosuppressed patients: a clinicopathologic review of 16 cases. Human Pathology, 24, 897–904.
Antinori, A., Arendt, G., Becker, J. T., Brew, B. J., Byrd, D. A., Cherner, M., et al. (2007). Updated research nosology for hiv-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neurology, 69, 1789–1799.
Archibald, S. L., Masliah, E., Fennema-Notestine, C., Marcotte, T. D., Ellis, R. J., McCutchan, J. A., et al. (2004). Correlation of in vivo neuroimaging abnormalities with postmortem human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis and dendritic loss. Archivesof Neurology, 61, 369–376.
Arendt, G., Maecker, H. P., Purrmann, J., & Homberg, V. (1994). Control of posture in patients with neurologically asymptomatic hiv infection and patients with beginning hiv-1-related encephalopathy. Archives of Neurology, 51, 1232–1235.
Bauer, L. O., Ceballos, N. A., Shanley, J. D., & Wolfson, L. I. (2005). Sensorimotor dysfunction in hiv/aids: effects of antiretroviral treatment and comorbid psychiatric disorders. AIDS, 19, 495–502.
Beck, A. T., Steer R. A., & Brown G. K. (1996). Manual for the beck depression inventory-ii. Psychological Corporation, Psychological Corporation.
Beckley, D. J., Bloem, B. R., Martin, E. M., Panzer, V. P., & Remler, M. P. (1998). Postural reflexes in patients with hiv-1 infection. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 109, 402–408.
Benton, A. L., & Hamsher K. D. (1976). Multilingual aphasia examination (manual, revised 1978). University of Iowa, University of Iowa.
Bodammer, N., Kaufmann, J., Kanowski, M., & Tempelmann, C. (2004). Eddy current correction in diffusion-weighted imaging using pairs of images acquired with opposite diffusion gradient polarity. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 51, 188–193.
Brew, B. J. (1999). Aids dementia complex. Neurologic Clinics, 17, 861–881.
Butters, N., Grant, I., Haxby, J., Judd, L. L., Martin, A., McClelland, J., et al. (1990). Assessment of aids-related cognitive changes: recommendations of the nimh workshop on neuropsychological assessment approaches. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 12, 963–978.
Castellanos, F., Mallada, J., Ricart, C., & Zabala, J. A. (1994). Ataxic neuropathy associated with human immunodeficiency virus seroconversion. Archives of Neurology, 51, 236.
Chang, L., Ernst, T., Tornatore, C., Aronow, H., Melchor, R., Walot, I., et al. (1997). Metabolite abnormalities in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neurology, 48, 836–845.
Chang, L., Ernst, T., Leonido-Yee, M., & Speck, O. (2000). Perfusion mri detects rcbf abnormalities in early stages of hiv-cognitive motor complex. Neurology, 54, 389–396.
Cherry, C. L., Skolasky, R. L., Lal, L., Creighton, J., Hauer, P., Raman, S. P., et al. (2006). Antiretroviral use and other risks for hiv-associated neuropathies in an international cohort. Neurology, 66, 867–873.
Cooper, J. A., Sagar, H. J., Jordan, N., Harvey, N., & Sullivan, E. V. (1991). Cognitive impairment in early, untreated parkinson’s disease and its relationship to motor disability. Brain, 114, 2095–2122.
Corkin, S., Growdon, J. H., Sullivan, E. V., Nissen, M. J., & Huff, F. J. (1986). Assessing treatment effects from a neuropsychological perspective. In L. Poon (Ed.), Handbook of clinical memory assessment in older adults (pp. 156–167). Washington DC: American Psychological Association.
Crabb, C. (2004). Protease inhibitors and risk of developing hiv-related sensory neuropathy. AIDS, 18, N10.
Crovitz, H. F., & Zener, K. A. (1962). Group test for assessing hand and eye dominance. The American Journal of Psychology, 75, 271–276.
Cysique, L. A., & Brew, B. J. (2009). Neuropsychological functioning and antiretroviral treatment in hiv/aids: a review. Neuropsychology Review.
Dellepiane, M., Medicina, M. C., Mora, R., & Salami, A. (2005). Static and dynamic posturography in patients with asymptomatic hiv-1 infection and aids. Acta Otorhinolaryngologica Italica, 25, 353–358.
Du Pasquier, R. A., Corey, S., Margolin, D. H., Williams, K., Pfister, L. A., De Girolami, U., et al. (2003). Productive infection of cerebellar granule cell neurons by jc virus in an hiv+individual. Neurology, 61, 775–782.
Ellis, R. J., Calero, P., & Stockin, M. D. (2009). Hiv infection and the central nervous system: a primer. Neuropsychology Review.
Ernst, T., Chang, L., Witt, M., Walot, I., Aronow, H., Leonido-Yee, M., et al. (1999). Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and human immunodeficiency virus-associated white matter lesions in aids: magnetization transfer mr imaging. Radiology, 210, 539–543.
Everall, I. P., Hudson, L., al-Sarraj, S., Honavar, M., Lantos, P., & Kerwin, R. (1995). Decreased expression of ampa receptor messenger rna and protein in aids: a model for hiv-associated neurotoxicity. Natural Medicines, 1, 1174–1178.
Fama, R., Eisen, J. C., Rosenbloom, M. J., Sassoon, S. A., Kemper, C. A., Deresinski, S., et al. (2007). Upper and lower limb motor impairments in alcoholism, hiv-infection, and their comorbidity. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 1038–1044.
Flowers, C. H., Mafee, M. F., Crowell, R., Raofi, B., Arnold, P., Dobben, G., et al. (1990). Encephalopathy in aids patients: evaluation with mr imaging. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 11, 1235–1245.
Fregly, A. R., Graybiel, A., & Smith, M. S. (1972). Walk on floor eyes closed (wofec): a new addition to an ataxia test battery. Aerospace Medicine, 43, 395–399.
Galvan, F. H., Bing, E. G., Fleishman, J. A., London, A. S., Caetano, R., Burnam, M. A., et al. (2002). The prevalence of alcohol consumption and heavy drinking among people with hiv in the united states: results from the hiv cost and services utilization study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 63, 179–186.
Gerig, G., Corouge, I., Vachet, C., Krishnan, K. R., & MacFall, J. R. (2005). Quantitative analysis of diffusion properties of white matter fiber tracts: a validation study 13th Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, Miami, FL, pp Abstract no. 1337.
Goodkin, K., Wilkie, F. L., Concha, M., Hinkin, C. H., Symes, S., Baldewicz, T. T., et al. (2001). Aging and neuro-aids conditions and the changing spectrum of hiv-1-associated morbidity and mortality. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, 54(Suppl 1), S35–S43.
Gorman, A. A., Foley, J. M., Ettenhofer, M. L., Hinkin, C. H., & van Gorp, W. G. (2009). Functional consequences of hiv-associated neuropsychological impairment. Neuropsychology Review, 19, 186–203.
Graus, F., Ribalta, T., Abos, J., Alom, J., Cruz-Sanchez, F., Mallolas, J., et al. (1990). Subacute cerebellar syndrome as the first manifestation of aids dementia complex. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 81, 118–120.
Harper, C. G., & Kril, J. J. (1990). Neuropathology of alcoholism. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 25, 207–216.
Heaton, R. K., Grant, I., Butters, N., White, D. A., Kirson, D., Atkinson, J. H., et al. (1995). The hnrc 500--neuropsychology of hiv infection at different disease stages. Hiv neurobehavioral research center. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 1, 231–251.
Heindel, W. C., Jernigan, T. L., Archibald, S. L., Achim, C. L., Masliah, E., & Wiley, C. A. (1994). The relationship of quantitative brain magnetic resonance imaging measures to neuropathologic indexes of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Archives of Neurology, 51, 1129–1135.
Hollingshead, A. (1975). Four-factor index of social status. Yale University, Department of Sociology, Yale University, Department of Sociology.
Karnofsky, D. A. (1949). The clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. In C. M. MacLeod (Ed.), Evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents (pp. 191–205). New York: Columbia University Press.
Kinzel, N., Strike, D., Clark, H. B., & Cavert, W. (2004). Cerebellopontine degeneration as an immune restoration disease in hiv infection. AIDS and Behavior, 18, 2348–2350.
Klunder, A. D., Chiang, M. C., Dutton, R. A., Lee, S. E., Toga, A. W., Lopez, O. L., et al. (2008). Mapping cerebellar degeneration in hiv/aids. NeuroReport, 19, 1655–1659.
Kuchelmeister, K., Bergmann, M., & Gullotta, F. (1993). Cellular changes in the cerebellar granular layer in aids-associated pml. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 19, 398–401.
Lopez, O. L., Becker, J. T., Dew, M. A., & Caldararo, R. (2004). Risk modifiers for peripheral sensory neuropathy in hiv infection/aids. European Journal of Neurology, 11, 97–102.
Maki, P. M., Cohen, M. H., Weber, K., Little, D. M., Fornelli, D., Rubin, L. H., et al. (2009). Impairments in memory and hippocampal function in hiv-positive vs hiv-negative women: a preliminary study. Neurology, 72, 1661–1668.
Mattos, J. P., Rosso, A. L., Correa, R. B., & Novis, S. A. P. (2002). Movement disorders in 28 hiv-infected patients. Arquivos de Neuropsiquiatria, 60, 525–530.
Medana, I. M., & Esiri, M. M. (2003). Axonal damage: a key predictor of outcome in human cns diseases. Brain, 126, 515–530.
Miller, R. F., Harrison, M. J., Hall-Craggs, M. A., & Scaravilli, F. (1998). Central pontine myelinolysis in aids. Acta Neuropathologica (Berlin), 96, 537–540.
Mori, S., & van Zijl, P. C. (2002). Fiber tracking: principles and strategies-a technical review. NMR in Biomedicine, 15, 468–480.
Nath, A. (2010). Human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorder: pathophysiology in relation to drug addiction. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1187, 122–128.
Nath, A., Jankovic, J., & Pettigrew, L. C. (1987). Movement disorders and aids. Neurology, 37, 37–41.
Otis, C. N., & Moral, L. A. (2005). Images in pathology: granule cell loss in aids-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. International Journal of Surgical Pathology, 13, 360.
Pandya, D. N., & Seltzer, B. (1986). The topography of commissural fibers. In F. Lepore, M. Ptito, & H. H. Jasper (Eds.), Two hemispheres-one brain: Functions of the corpus callosum (pp. 47–74). New York: Alan R. Liss, Inc.
Patton, H. K., Chu, W. J., Hetherington, H. P., den Hollander, J., Stewart, K. E., Raper, J. L., et al. (2001). Alkaline ph changes in the cerebellum of asymptomatic hiv-infected individuals. NMR in Biomedicine, 14, 12–18.
Paul, R. H., Yiannoutsos, C. T., Miller, E. N., Chang, L., Marra, C. M., Schifitto, G., et al. (2007). Proton mrs and neuropsychological correlates in aids dementia complex: evidence of subcortical specificity. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 19, 283–292.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Rohlfing, T., Adalsteinsson, E., Kemper, C. A., Deresinski, S., et al. (2006). Contribution of alcoholism to brain dysmorphology in hiv infection: effects on the ventricles and corpus callosum. Neuroimage, 33, 239–251.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Adalsteinsson, E., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Diffusion tensor imaging with quantitative fiber tracking in hiv infection and alcoholism comorbidity: synergistic white matter damage. Brain, 130, 48–64.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Rohlfing, T., Kemper, C. A., Deresinski, S., & Sullivan, E. V. (2009). Frontostriatal fiber bundle compromise in hiv infection without dementia. AIDS, 23, 1977–1985.
Pfefferbaum, A., Rosenbloom, M. J., Fama, R., Sassoon, S. A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2010). Transcallosal white matter degradation detected with quantitative fiber tracking in alcoholic men and women: selective relations to dissociable functions. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 34, 1201–1211.
Powell, D., Kaplan, E., Whitla, D., Weintraubm, S., Caitlin, R., & Funkenstein, H. (1993). Microcog assessment of cognitive functioning manual. San Antonio: Psych Corp.
Price, R. L., & Sidtis, J. J. (1993). Evaluation of the aids dementia complex in clinical trials. JAIDS, 3, 551–560.
Ramachandran, G., Glickman, L., Levenson, J., & Rao, C. (1997). Incidence of extrapyramidal syndromes in aids patients and a comparison group of medically ill inpatients. The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 9, 579–583.
Richardson, J. K., & Hurvitz, E. A. (1995). Peripheral neuropathy: a true risk factor for falls. The Journals of Gerontology. Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 50, M211–M215.
Robertson, K. R., Parsons, T. D., Sidtis, J. J., Hanlon Inman, T., Robertson, W. T., Hall, C. D., et al. (2006). Timed gait test: normative data for the assessment of the aids dementia complex. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 28, 1053–1064.
Rohlfing, T., & Maurer, C. R. (2003). Nonrigid image registration in shared-memory multiprocessor environments with application to brains, breasts, and bees. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 7, 16–25.
Rohlfing, T., Zahr, N. M., Sullivan, E. V., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2010). The sri24 multi-channel atlas of normal adult human brain structure. Human Brain Mapping, 31, 798–819.
Ruiz, A., Post, M. J., & Bundschu, C. C. (1997). Dentate nuclei involvement in aids patients with cns cryptococcosis: imaging findings with pathologic correlation. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 21, 175–182.
Sacktor, N., Skolasky, R. L., Tarwater, P. M., McArthur, J. C., Selnes, O. A., Becker, J., et al. (2003). Response to systemic hiv viral load suppression correlates with psychomotor speed performance. Neurology, 61, 567–569.
Samet, J. H., Walley, A. Y., & Bridden, C. (2007). Illicit drugs, alcohol, and addiction in human immunodeficiency virus. Panminerva Medica, 49, 67–77.
Sassoon, S. A., Fama, R., Rosenbloom, M. J., O’Reilly, A., Pfefferbaum, A., & Sullivan, E. V. (2007). Component cognitive and motor processes of the digit symbol test: differential deficits in alcoholism, hiv infection and their comorbidity. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 31, 1315–1324.
Savolainen, V. T., Liesto, K., Mannikko, A., Penttila, A., & Karhunen, P. J. (1993). Alcohol consumption and alcoholic liver disease: evidence of a threshold level of effects of ethanol. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research, 17, 1112–1117.
Scatliff, J. H., Kwock, L., Chancellor, K., Bouldin, T. W., Kapoor, C. C., & Castillo, M. (1997). Postmortem mr imaging of the brains of patients with aids. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 7, 297–320.
Schifitto, G., McDermott, M. P., McArthur, J. C., Marder, K., Sacktor, N., Epstein, L., et al. (2002). Incidence of and risk factors for hiv-associated distal sensory polyneuropathy. Neurology, 58, 1764–1768.
Sclar, G., Kennedy, C. A., Hill, J. M., & McCormack, M. K. (2000). Cerebellar degeneration associated with hiv infection [letter]. Neurology, 54, 1012–1013.
Simioni, S., Cavassini, M., Annoni, J. M., Rimbault Abraham, A., Bourquin, I., Schiffer, V., et al. (2010). Cognitive dysfunction in hiv patients despite long-standing suppression of viremia. AIDS, 24, 1243–1250.
Song, S. K., Sun, S. W., Ramsbottom, M. J., Chang, C., Russell, J., & Cross, A. H. (2002). Dysmyelination revealed through mri as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. NeuroImage, 17, 1429–1436.
Sullivan, E. V., Deshmukh, A., Desmond, J. E., Lim, K. O., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2000). Cerebellar volume decline in normal aging, alcoholism, and korsakoff’s syndrome: relation to ataxia. Neuropsychology, 14, 341–352.
Sullivan, E. V., Adalsteinsson, E., Hedehus, M., Ju, C., Moseley, M., Lim, K. O., et al. (2001). Equivalent disruption of regional white matter microstructure in aging healthy men and women. NeuroReport, 12, 99–104.
Sullivan, E. V., Harris, R. A., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2010a). Alcohol’s effects on brain and behavior. Alcohol Research & Health, 33, 127–143.
Sullivan, E. V., Rohlfing, T., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2010b). Pontocerebellar volume deficits and ataxia in alcoholic men and women: no evidence for “Telescoping”. Psychopharmacology, 208, 279–290.
Sullivan, E. V., Rohlfing, T., & Pfefferbaum, A. (2010c). Quantitative fiber tracking of lateral and interhemispheric white matter systems in normal aging: relations to timed performance. Neurobiology of Aging, 31, 464–481.
Sun, S. W., Liang, H. F., Trinkaus, K., Cross, A. H., Armstrong, R. C., & Song, S. K. (2006). Noninvasive detection of cuprizone induced axonal damage and demyelination in the mouse corpus callosum. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 55, 302–308.
Tagliati, M., Simpson, D., Morgello, S., Clifford, D., Schwartz, R. L., & Berger, J. R. (1998). Cerebellar degeneration associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Neurology, 50, 244–251.
Tate, D. F., Conley J., Paul R. H., Coop K., Zhang S., Zhou W., et al. (2010). Quantitative diffusion tensor imaging tractrography metrics are associated with cognitive performance among hiv-infected patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior, Epub online.
Trenkwalder, C., Straube, A., Paulus, W., Krafczyk, S., Schielke, E., & Einhaupl, K. M. (1992). Postural imbalance: an early sign in hiv-1 infected patients. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 241, 267–272.
Valcour, V., Watters, M. R., Williams, A. E., Sacktor, N., McMurtray, A., & Shikuma, C. (2008). Aging exacerbates extrapyramidal motor signs in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Journal of Neurovirology, 14, 362–367.
Victor, M., Adams R. D., & Collins G. H. (1989). The wernicke-korsakoff syndrome and related neurologic disorders due to alcoholism and malnutrition (2nd edition). F.A. Davis Co, F.A. Davis Co.
von Giesen, H. J., Wittsack, H. J., Wenserski, F., Koller, H., Hefter, H., & Arendt, G. (2001). Basal ganglia metabolite abnormalities in minor motor disorders associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Archives of Neurology, 58, 1281–1286.
Wechsler, D. (1981). Wechsler adult intelligence scale - revised. The Psychological Corporation, The Psychological Corporation.
Woods, S. P., Moore, D. J., Weber, E., & Grant, I. (2009). Cognitive neuropsychology of hiv-associated neurocognitive disorders. Neuropsychology Review, 19, 152–168.
Wuthrich, C., Cheng, Y. M., Joseph, J. T., Kesari, S., Beckwith, C., Stopa, E., et al. (2009). Frequent infection of cerebellar granule cell neurons by polyomavirus jc in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 68, 15–25.
Xu, D., Mori, S., Solaiyappan, M., van Zijl, P. C., & Davatzikos, C. (2002). A framework for callosal fiber distribution analysis. NeuroImage, 17, 1131–1143.
Xue, R., van Zijl, P. C., Crain, B. J., Solaiyappan, M., & Mori, S. (1999). In vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of rat brain axonal projections by diffusion tensor imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 42, 1123–1127.
Yebra, M., Garcia-Merino, A., Albarran, F., Varela, J. M., & Echevarria, J. M. (1988). Cerebellar disease without dementia and infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (hiv). Annals of Internal Medicine, 108, 310–311.
Acknowledgment
Support for this work was provided by the United States National Institutes of Health grants AA017347, AA017168, EB008381. The registration tools are available as source code in the Computational Morphometry Toolkit: http://nitrc.org/projects/cmtk/. The SRI24 atlas is available from http://nitrc.org/projects/sri24/.
Financial Disclosures
None of the authors have any conflicts to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sullivan, E.V., Rosenbloom, M.J., Rohlfing, T. et al. Pontocerebellar contribution to postural instability and psychomotor slowing in HIV infection without dementia. Brain Imaging and Behavior 5, 12–24 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9107-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9107-y