Abstract
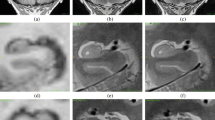
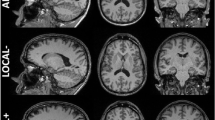
MRI-based hippocampal volume analysis has been extensively employed given its potential as a biomarker for brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), and accurate and efficient determination of hippocampal volumes from brain images is still a challenging issue. We compared an automated method, FreeSurfer (V4), with a published manual protocol for the determination of hippocampal volumes from T1-weighted MRI scans. Our study included MRI data from 125 older adult subjects: healthy controls with no significant cognitive complaints or deficits (HC, n = 38), euthymic individuals with cognitive complaints (CC, n = 39) but intact neuropsychological performance, and patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment (MCI, n = 37) or a clinical diagnosis of probable AD (AD, n = 11). Pearson correlations and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were calculated to evaluate the relationship between results of the manual tracing and FreeSurfer methods and to estimate their agreement. Results indicated that these two methods derived highly correlated results with strong agreement. After controlling for the age, sex and intracranial volume in statistical group analysis, both the manual tracing and FreeSurfer methods yield similar patterns: both the MCI group and the AD group showed hippocampal volume reduction compared to both the HC group and the CC group, and the HC and CC groups did not differ. These comparisons suggest that FreeSurfer has the potential to be used in automated determination of hippocampal volumes for large-scale MCI/AD-related MRI studies, where manual methods are inefficient or not feasible.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreasen, N. C., Cizadlo, T., Harris, G., Swayze, V., O’Leary, D. S., Cohen, G., et al. (1993). Voxel processing techniques for the antemortem study of neuroanatomy and neuropathology using magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Neuropsychiatry, 5, 121–130.
Apostolova, L. G., Dinov, I. D., Dutton, R. A., Hayashi, K. M., Toga, A. W., Cummings, J. L., et al. (2006). 3D comparison of hippocampal atrophy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Brain, 129(Pt 11), 2867–2873.
Apostolova, L. G., Dutton, R. A., Dinov, I. D., Hayashi, K. M., Toga, A. W., Cummings, J. L., et al. (2006). Conversion of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease predicted by hippocampal atrophy maps. Archives of Neurology, 63(5), 693–699.
Becker, J. T., Davis, S. W., Hayashi, K. M., Meltzer, C. C., Toga, A. W., Lopez, O. L., et al. (2006). Three-dimensional patterns of hippocampal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment. Archives of Neurology, 63(1), 97–101.
Bouix, S., Pruessner, J. C., Louis Collins, D., & Siddiqi, K. (2005). Hippocampal shape analysis using medial surfaces. Neuroimage, 25(4), 1077–1089.
Buckner, R. L., Head, D., Parker, J., Fotenos, A. F., Marcus, D., Morris, J. C., et al. (2004). A unified approach for morphometric and functional data analysis in young, old, and demented adults using automated atlas-based head size normalization: reliability and validation against manual measurement of total intracranial volume. NeuroImage, 23, 724–738.
Csernansky, J. G., Wang, L., Jones, D., Rastogi-Cruz, D., Posener, J. A., Heydebrand, G., et al. (2002). Hippocampal deformities in schizophrenia characterized by high dimensional brain mapping. American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(12), 2000–2006.
Csernansky, J. G., Wang, L., Swank, J., Miller, J. P., Gado, M., McKeel, D., et al. (2005). Preclinical detection of Alzheimer's disease: hippocampal shape and volume predict dementia onset in the elderly. Neuroimage, 25(3), 783–792.
Dale, A. M., Fischl, B., & Sereno, M. I. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. Neuroimage, 9(2), 179–194.
Fischl, B., Salat, D. H., Busa, E., Albert, M., Dieterich, M., Haselgrove, C., et al. (2002). Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron, 33(3), 341–355.
Fischl, B., Sereno, M. I., & Dale, A. M. (1999). Cortical surface-based analysis. II: Inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. Neuroimage, 9(2), 195–207.
FreeSurfer Wiki (2009). eTIV—estimated Total Intracranial Volume, aka ICV. Available at http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/eTIV
Gerig, G., Styner, M., Shenton, M. E., & Lieberman, J. A. (2001, Oct. 14–17). Shape versus size: Improved understanding of the morphology of brain structures. Paper presented at the 4th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2001), Ultrecht, the Netherlands.
Hogan, R. E., Wang, L., Bertrand, M. E., Willmore, L. J., Bucholz, R. D., Nassif, A. S., et al. (2006). Predictive value of hippocampal MR imaging-based high-dimensional mapping in mesial temporal epilepsy: preliminary findings. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 27(10), 2149–2154.
Iowa Mental Health Clinical Research Center (2008). BRAINS Software Package. Available at http://www.psychiatry.uiowa.edu/mhcrc/IPLpages/BRAINS.htm
Jack, C. R. J. (1994). MRI-based hippocampal volume measurements in epilepsy. Epilepsia, 35(Suppl 6), S21–S29.
Mayo Clinic (2008). Analyze. Available at http://www.mayo.edu/bir/Software/Analyze/Analyze.html
McGraw, K. O., & Wong, S. P. (1996). Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychological Methods, 1, 30–46.
McHugh, T. L., Saykin, A. J., Wishart, H. A., Flashman, L. A., Cleavinger, H. B., Rabin, L. A., et al. (2007). Hippocampal volume and shape analysis in an older adult population. Clin Neuropsychol, 21(1), 130–145.
Mueller, S. G., Weiner, M. W., Thal, L. J., Petersen, R. C., Jack, C., Jagust, W., et al. (2005). The Alzheimer's disease neuroimaging initiative. Neuroimaging Clinics of North America, 15(4), 869–877. xi–xii.
NAMIC (2008). 3D Slicer Web Page. Available at http://www.slicer.org
Saykin, A. J., Wishart, H. A., Rabin, L. A., Santulli, R. B., Flashman, L. A., West, J. D., et al. (2006). Older adults with cognitive complaints show brain atrophy similar to that of amnestic MCI. Neurology, 67, 834–842.
Shen, D., Moffat, S., Resnick, S. M., & Davatzikos, C. (2002). Measuring size and shape of the hippocampus in MR images using a deformable shape model. Neuroimage, 15(2), 422–434.
Shen, L., Firpi, H. A., Saykin, A. J., & West, J. D. (2009). Parametric surface modeling and registration for comparison of manual and automated segmentation of the hippocampus. Hippocampus, 19(6), 588–595.
Shenton, M. E., Gerig, G., McCarley, R. W., Szekely, G., & Kikinis, R. (2002). Amygdala-hippocampal shape differences in schizophrenia: the application of 3D shape models to volumetric MR data. Psychiatry Research, 115(1–2), 15–35.
Tae, W. S., Kim, S. S., Lee, K. U., Nam, E. C., & Kim, K. W. (2008). Validation of hippocampal volumes measured using a manual method and two automated methods (FreeSurfer and IBASPM) in chronic major depressive disorder. Neuroradiology.
Thompson, P. M., Hayashi, K. M., De Zubicaray, G. I., Janke, A. L., Rose, S. E., Semple, J., et al. (2004). Mapping hippocampal and ventricular change in Alzheimer disease. Neuroimage, 22(4), 1754–1766.
Torres, I. J., Flashman, L. A., O’Leary, D. S., Swayze, V. I., & Andreasen, N. C. (1997). Lack of an association between delayed memory and hippocampal and temporal lobe size in patients with schizophrenia and healthy controls. Biological Psychiatry, 42(12), 1087–1096.
Wang, L., Beg, F., Ratnanather, T., Ceritoglu, C., Younes, L., Morris, J. C., et al. (2007). Large deformation diffeomorphism and momentum based hippocampal shape discrimination in dementia of the Alzheimer type. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 26(4), 462–470.
Wang, L., Joshi, S. C., Miller, M. I., & Csernansky, J. G. (2001). Statistical analysis of hippocampal asymmetry in schizophrenia. Neuroimage, 14(3), 531–545.
Wang, L., Miller, J. P., Gado, M. H., McKeel, D. W., Rothermich, M., Miller, M. I., et al. (2006a). Abnormalities of hippocampal surface structure in very mild dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neuroimage, 30(1), 52–60.
Wang, P., Saykin, A., Flashman, L., Wishart, H., Rabin, L., Santulli, R., et al. (2006b). Regionally specific atrophy of the corpus callosum in AD, MCI and cognitive complaints. Neurobiology of Aging, 27(11), 1613–1617.
Watson, C., Andermann, F., Gloor, P., Jones-Gotman, M., Peters, T., Evans, A., et al. (1992). Anatomic basis of amygdaloid and hippocampal volume measurement by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology, 42(9), 1743–1750.
Yushkevich, P. A., Detre, J. A., Mechanic-Hamilton, D., Fernandez-Seara, M. A., Tang, K. Z., Hoang, A., et al. (2007). Hippocampus-specific fMRI group activation analysis using the continuous medial representation. Neuroimage, 35(4), 1516–1530.
Yushkevich, P. A., Piven, J., Hazlett, H. C., Smith, R. G., Ho, S., Gee, J. C., et al. (2006). User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage, 31(3), 1116–1128.
Acknowledgements
Supported in part by NIA R01 AG19771, NIBIB R03 EB008674-01, NCI R01 CA101318, U54 EB005149 and NIA P30 AG10133 from the NIH, Foundation for the NIH, and grant #87884 from the Indiana Economic Development Corporation (IEDC). We thank Nick Schmansky and Bruce Fischl of Harvard Medical School and Randy Heiland of Indiana University for help with running FreeSurfer on IU’s supercomputers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Saykin, A.J., Kim, S. et al. Comparison of Manual and Automated Determination of Hippocampal Volumes in MCI and Early AD. Brain Imaging and Behavior 4, 86–95 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9088-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9088-x