Abstract
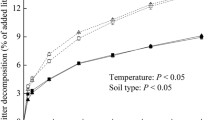
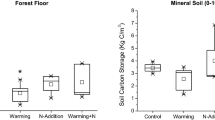
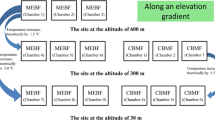
Warming and nitrogen (N) deposition are two important drivers of global climate changes. Coarse woody debris (CWD) contains a large proportion of the carbon (C) in the total global C pool. The composition of soil microbial communities and environmental changes (i.e., N deposition and warming) are the key drivers of CWD decomposition, but the interactive impact between N deposition and warming on the composition of soil microbial communities and CWD decomposition is still unclear. In a laboratory experiment, we study and simulate respiration during decomposition of the CWD (C98) of Cryptomeria japonica (CR) and Platycarya strobilacea (PL) in response to warming and N deposition over 98 days. Resuts show that either warming or N addition significantly accelerated the C98 of the two tree species by altering the soil microbial community (bacterial:fungi and G+:G–). The combined treatment (warming + N) resulted in a decomposition effect equal to the sum of the individual effects. In addition, the species composition of bacteria and fungi was obviously affected by warming. However, N deposition had a remarkable influence on G+:G–. Our results indicated that N deposition and warming will observably alter the composition and growth of the microbial community and thus work synergistically to accelerate CWD decomposition in forest ecosystems. We also present evidence that N deposition and warming influenced the composition and balance of soil microbial communities and biogeochemical cycling of forest ecosystems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin EE (2013) Wood decomposition in a warmer world. PhD dissertation, University of Tennessee
Bao SD (2005) Agriculture chemistry analysis of soil. China Agriculture Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Bebber DP, Watkinson SC, Boddy L, Darrah PR (2011) Simulated nitrogen deposition affects wood decomposition by cord-forming fungi. Oecologia 167(4):1177–1184
Bond-Lamberty B, Wang C, Gower ST (2003) Annual carbon flux from woody debris for a boreal black spruce fire chronosequence. J Geophys Res 107(23):1–10
Bossio DA, Scow KM (1998) Impacts of carbon and flooding on soil microbial communities: phospholipid fatty acid profiles and substrate utilization patterns. Microb Ecol 35:265–278
Cha S, Chae H, Lee S, Shim J (2017) Branch wood decomposition of tree species in a deciduous temperate forest in Korea. Forests 8:176
Chambers JQ, Schimel JP, Nobre AD (2001) Respiration from coarse wood litter in central Amazon forests. Biogeochemistry 52(2):115–131
Chen DM, Lan ZC, Hu SJ, Bai YF (2015) Effects of nitrogen en-richment on belowground communities in grassland: rela-tive role of soil nitrogen availability vs. soil acidification. Soil Biol Biochem 89:99–108
Chen Y, Sayer EJ, Li ZA, Mo QF, Li YW, Ding YZ, Wang J, Lu XK, Tang JW, Wang FM (2016) Nutrient limitation of woody debris decomposition in a tropical forest: contrasting effects of N and P addition. Funct Ecol 30(2):295–304
Chen XP, Wang GX, Zhang T, Mao TX, Wei D, Hu ZY, Song CL (2017) Effects of warming and nitrogen fertilization on GHG flux in the permafrost region of an alpine meadow. Atmos Environ 157:111–124
Contosta AR, Fery SD, Cooper AB (2011) Seasonal dynamics of soil respiration and N mineralization in chronically warmed and fertilized soils. Ecosphere 2(3):36
Crowther TW, Thomas SM, Maynard DS, Baldrian P, Covey K, Frey SD, van Diepen LTA, Bradford MA (2015) Biotic interactions mediate soil microbial feedbacks to climate change. PNAS 112(22):7033–7038
Deng BL, Li Z, Zhang L, Ma YC, Li Z, Zhang WY, Guo XM, Niu DK, Siemann E (2015) Increases in soil CO2 and N2O emissions with warming depend on plant species in restored alpine meadows of Wugong mountain, China. J Soils Sediments 16(3):777–784
Frostegård Å, Bååth E (1996) The use of phospholipid fatty acid analysis to estimate bacterial and fungal biomass in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 22:59–65
Frostegård Å, Bååth E, Tunlio A (1993) Shifts in the structure of soil microbial communities in limited forests as revealed by phospholipids fatty acid analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 25:723–730
Fukasawa Y, Osono T, Takeda H (2011) Wood decomposing abilities of diverse lignicolous fungi on nondecayed and decayed beech wood. Mycologia 103:474–482
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai Z, Freney JR, Martinelli L, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320(5878):889–892
Guo JF, Chen GS, Xie JS, Yang ZJ, Yang YS (2014) Respiration of downed logs in four natural evergreen broad-leaved forests in subtropical China. Plant Soil 385(1):149–163
Harmon ME, Franklin JF, Swanson FJ, Sollins P, Gregory SV, Lattin JD, Anderson NH, Cline SP, Aumen NG, Sedell JR, Lienkaemper GW, Cromack KJ, Cummins KW (1986) Ecology of coarse woody debris in temperate ecosystems. Adv Ecol Res 15(1):133–302
Herrmann S, Bauhus J (2013) Effects of moisture, temperature and decomposition stage on respirational carbon loss from coarse woody debris (CWD) of important European tree species. Scand J For Res 28(4):346–357
Hoppe B, Purahong W, Wubet T, Kahl T, Bauhus J, Arnstadt T, Hofrichter M, Buscot F, Krüger D (2016) Linking molecular deadwood-inhabiting fungal diversity and community dynamics to ecosystem functions and processes in Central European forests. Fungal Divers 77:367–379
Hu YW, Zhang L, Deng BL, Liu YQ, Liu Q, Zheng X, Zheng LY, Kong FQ, Guo XM, Siemann E (2017) The non-additive effects of temperature and nitrogen deposition on CO2 emissions, nitrification, and nitrogen mineralization in soils mixed with termite nests. CATENA 154:12–20
Idol TW, Figler RA, PopeFP PE Jr (2001) Characterization of coarse woody debris across a 100-year chronosequence of upland oak-hickory forests. For Ecol Manag 149:153–161
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) (2014) Climate change 2014 synthesis report summary for policymakers. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva
IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis-summary for policy makers. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC WGI 4th assessment report
Kim S, Li G, Han SH, Chang H, Kim H, Son YW (2017) Differential effects of coarse woody debris on microbial and soil properties in Pinus densiflora Sieb. et Zucc. Forests 8:292
Lai JS (2013) Canoco 5: a new version of an ecological multivariate data ordination program. Biodivers Sci 21:765–768 (in Chinese)
Liu WJ, Schaefer D, Qiao L, Liu XB (2013) What controls the variability of wood-decay rates? For Ecol Manag 310(1):623–631
Mackensen J, Bauhus J (2003) Density loss and respiration rates in coarse woody debris of Pinus radiata, Eucalyptus regnans and Eucalyptus maculata. Soil Biol Biochem 35(1):177–186
Maestrini B, Abiven S, Singh N, Bird J, Torn MS, Schmidt MWI (2014) Carbon losses from pyrolysed and original wood in a forest soil under natural and increased N deposition. Biogeosciences 11(18):5199
Olsson PA (1999) Signature fatty acids provide tools for determination of the distribution and interactions of mycorrhizal fungi in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:303–310
Pan YD, Birdsey RA, Fang JY, Houghton R, Kauppi PE, Kurz WA, Phillips OL, Shvidenko A, Lewis SL, Canadell JG, Ciais P, Jackson RB, Pacala SW, McGuire AD, Piao SL, Rautiainen A, Sitch S, Hayes D (2011) A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 333(6045):988–993
Perry KI, Herms DA, Klooster WS, Smith A, Hartzler DM, Coyle DR, Gandhi KJ (2018) Downed coarse woody debris dynamics in Ash (Fraxinus spp.) stands invaded by emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire). Forests 9:191
Pietri JCA, Brookes PC (2009) Substrate inputs and pH as factors controlling microbial biomass, activity and community structure in an arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1396–1405
Qiao N, Xu XL, Hu YH, Blagodatskaya E, Liu YW, Schaefer D, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Carbon and nitrogen additions induce distinct priming effects along an organic-matter decay continuum. Sci Rep 6(1):19865
Reay DS, Dentener F, Smith P, Grace J, Feely RA (2008) Global nitrogen deposition and carbon sinks. Nat Geosci 1(7):430–437
Rowland L, Stahl C, Bonal D, Siebicke L, Williams M, Meir P (2013) The response of tropical rainforest dead wood respiration to seasonal drought. Ecosystems 16(7):1294–1309
Russell MB, Woodall CW, Fraver S, D’Amato AW, Domke GM, Skog KE (2014) Residence times and decay rates of downed woody debris biomass/carbon in Eastern US forests. Ecosystems 17(5):765–777
Shorohova E, Kapitsa E (2014) Influence of the substrate and ecosystem attributes on the decomposition rates of coarse woody debris in European boreal forests. For Ecol Manag 315:173–184
Stoklosa AM, Ulyshen MD, Fan Z, Varner M, Seibold S, Mvlle J (2016) Effects of mesh bag enclosure and termites on fine woody debris decomposition in a subtropical forest. Basic Appl Ecol 17:463–470
Tao BX, Song CC, Guo YD (2013) Short-term effects of nitrogen additions and increasing temperature on wetland soil respiration, Sanjiang plain, China. Wetlands 33:727–736
Tao BX, Zhang BH, Dong J, Liu CY, Cui Q (2019) Antagonistic effect of nitrogen additions and warming on litter decomposiiton in the coastal wetlamd of the Yellow River delta, China. Ecol Eng 131:1–8
Valenzuela-Solano C, Crohn DM (2006) Are decomposition and N release from organic mulches determined mainly by their chemical composition? Soil Biol Biochem 38:337–384
Van Geffen KG, Poorter L, Sass-Klaassen U, Van Logtestijn RS, Cornelissen JH (2010) The trait contribution to wood decomposition rates of 15 Neotropical tree species. Ecology 91:3686–3697
Vanderbilt KL, White CS, Hopkins O, Craig JA (2008) Above-ground decomposition in arid environments: results of a long-term study in central New Mexico. J Arid Environ 72:696–709
Wang C, Lu XK, Mori T, Mao QG, Zhou KJ, Zhou GY, Nie YX, Mo JM (2018) Responses of soil microbial community to continuous experimental nitrogen additions for 13 years in a nitrogen-rich tropical forest. Soil Biol Biochem 121:103–112
Warner DL, Villarreal S, McWilliams K, Inamdar S, Vargas R (2017) Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from tree stems, coarse woody debris, and soils in an upland temperate forest. Ecosystems 20(6):1205–1216
Wu JB, Zhang XJ, Wang HL, Shun JW, Guan DX (2010) Respiration of downed logs in an old-growth temperate forest in north-eastern China. Scand J For Res 25(6):500–506
Wu CS, Wang HK, Mo QF, Zhang ZJ, Huang GX, Kong FQ, Liu YQ, Wang GG (2019a) Effects of elevated UV-B radiation and N deposition on the decomposition of coarse woody debris. Sci Total Environ 663:170–176
Wu CS, Zhang ZJ, Wang HK, Huang GX, Shu CJ, Kong FQ, Zhang Y, Wang GG, Liu YQ (2019b) Home-field advantage of CWD decomposition in subtropical forests varied by field sites. For Ecol Manag 444:127–137
Wu CS, Zhang ZJ, Shu CJ, Mo QF, Wang HK, Kong FQ, Wang GG, Liu YQ (2020) The response of coarse woody debris decomposition and microbial community to nutrient additions in a subtropical forest. For Ecol Manag 460:117
Zanne AE, Oberle B, Dunham KM, Milo AM, Walton ML, Young DF (2015) A deteriorating state of affairs: how endogenous and exogenous factors determine plant decay rates. J Ecol 103(6):1421–1431
Zelles L (1999) Fatty acid patterns of phospholipids and lipopolysaccharides in the characterisation of microbial communities in soil: a review. Biol Fertil Soils 29:111–129
Zhang Y, Vogel JG, Meek C, Will R, Wilson D, West J (2016) Wood decomposition by microbes and macroinvertebrates, and soil CO2 efflux vary in response to throughfall reduction and fertilization in a loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) plantation. For Ecol Manag 382(1):10–20
Zhou L, Dai LM, Gu HY, Zhong L (2007) Review on the decomposition and influence factors of coarse woody debris in forest ecosystem. J For Res 18:48–54
Zhou WP, Shen WJ, Li YE, Hui DF (2017) Interactive effects of temperature and moisture on composition of the soil microbial community. Eur J Soil Sci 68:909–918
Zhu XY, Luo CY, Wang SP, Zhang ZH, Cui SJ, Bao XY, Jiang LL, Li YM, Li X, Wang Q, Zhou Y (2015) Effects of warming, grazing/cutting and nitrogen fertilization on greenhouse gas fluxes during growing seasons in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan plateau. Agric For Meteorol 214–215:506–514
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. G. Geoff Wang of Clemson University for reviewing an early draft of this manuscript and for many helpful suggestions for improving the manuscript. We also thank the anonymous reviewers, the Chief Editor and Handling Editor of the journal for their suggestions on improving this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation, HW, CL, QC, and ZY; Formal analysis, HW and CW; Investigation, HW, CW, CL, QC, CS, and YZ; Writing—original draft, CW, HW, QM and YL; Writing—review and editing, HW, JL, CW, and YL.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (3196140162).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com.
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Wu, C., Liu, J. et al. Changes in soil microbial communities induced by warming and N deposition accelerate the CO2 emissions of coarse woody debris. J. For. Res. 34, 1051–1063 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01544-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-022-01544-8