Abstract
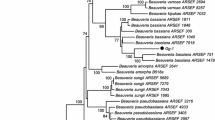
Developing appropriate control measures for the Mahogany shoot borer, Hypsipyla robusta Moore has become increasingly important due to the severe damaging effect of the pest on the establishment of the saplings of Swietenia mahagoni Jacq (Sapindales: Meliaceae). Existing management methods are largely limited to silvicultural practices and spraying of chemical insecticides. To identify a potential fungal biocontrol agent, we compared the virulence of six native and two standard ARSEF isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae Metsch. against this pest. The average survival time and conidial yield of IWST-Ma7 was higher (6.2 to 7.3 days and 4.9 to 4.7×105 conidia/ml) than the standards. Significant difference in sporulation on the cadavers between isolates, doses and incubation periods were substantiated for the selection of potential strain. The mycotoxic effects of crude soluble protein extract when incorporated in the artificial diet, the ARSEF 2596 and ARSEF 3603 showed LD50 value of 3.7% and 5.6%. However, IWST-Ma7 was highly lethal with significant lowest LD50 value of 2.6%. The enzyme activity of IWST-Ma7 was highest for chitinase, CDA, protease and lipase viz., 1.90 U/mg, 1.80 U/mg, 0.98 U/mg and 0.80 U/mg respectively. However the enzyme activity of chitinase and Chitin deacetylase assay for all the isolates was significantly higher than protease and lipase activity. The ITS regions (5.8S rDNA and 28S rDNA) of seven isolates of M. anisopliae were amplified using the ITS1 and ITS4 primers which was a unique fragment of approximately 550 bp. Based on ITS regions, phylogenetic tree have been constructed and the isolates have been grouped in to 5 clades. The virulence and mycotoxic effects of different isolates could rationally be used to employ them for the management of the mahogany borer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS. 1925. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. Journal Economic Entomology, 18: 265–267.
Ahmed SI, Leather SR. 1994. Suitability and potential of entomopathogenic microgranism for forest pest management some points for consideration. International Journal of Pest Management, 40: 287–292.
Anand R, Prasad B, Tiwary BN. 2009. Relative susceptibility of Spodoptera litura pupae to selected entomopathogenic fungi. BioControl 54: 85–92.
Beeson CFC. 1941. The Ecology and Control of the Forest Insects of India and Neighboring Countries, Dehra Dun: Vasant Press, p. 678.
Bischoff JF, Rehner SA, Humber RA. 2009. A multilocus phylogeny of the Metarhizium anisopliae lineage. Mycologia 101: 512–530
Bygrave FL, Bygrave PL. 2001. Host preference of the Meliaceae shootborer Hypsipyla: further information from grafting Cedrela odorata and Cedrela fissilis on Toona ciliata (Australian red cedar). Austrialian Forestry 64(4): 216–219.
Cipiao L, Bandeira RR, Sitoe SM. 2009. Incidence of Hypsipyla sp. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and its population distribution on Khaya anthoteca (Meliaceae) stands in the Manica Province, (Central Mozambique). In: Proceedings of XIII World Forestry Congress, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 18 October–23 October.
Cornelius JP, Watt AD. 2003. Genetic variation in a Hypsipyla-attacked clonal trial of Cedrela odorata under two pruning regimes. Forest Ecology and Management, 183: 341–349.
Cornelius JP. 2009. The utility of the predictive decapitation test as a tool for early genetic selection for Hypsipyla tolerance in big-leaf mahogany (Swietenia macrophylla King). Forest Ecology and Management, 257: 1815–1821.
Coudron TA, Kroha MJ, Ignoffo CM. 1984. Levels of chitinilytic activity during development of three entomopathogenic fungi. Comparative Biochemistry and Physics, 796: 339–348.
Cunningham SA, Floyd RB, Griffiths MW, Wylie FR. 2005. Patterns of host use by the shoot-borer Hypsipyla robusta (Pyralidae: Lepidoptera) comparing five Meliaceae tree species in Asia and Australia. Forest Ecology and Management, 205: 351–357.
Destéfano RHR, Destéfano SAL, Messias CL. 2004. Detection of Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae within infected sugarcane borer Diatraea saccharalis (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae) using specific primers. Genetics and Molecular Biology, 27: 245–252.
Driver F, Milner RJ, Trueman JWH 2000. A taxonomic revision of Metarhizium based on a phylogenetic analysis of rDNA sequence data. Mycological Research, 104: 134–150.
Doberski JW. 1981. Comparative laboratory studies on three fungal pathogens of the elm bark beetle Scolytus scolytus: Effect of temperature and humidity on infection by Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces farinosus. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 37: 195-200.
Fang W, Feng J, Fan Y, Zhang Y, Bidochka MJ, St. Leger RJ, Pei Y. 2009. Expressing a fusion protein with protease and chitinase activities increases the virulence of the insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 102: 155–159.
Goulet E, Rueda A, Shelton A. 2005. Management of the mahogany shoot borer, Hypsipyla grandella (Zeller) (Lepidoptera:Pyralidae), through weed management and insecticidal sprays in 1- and 2-year-old Swietenia humilis Zucc. Plantations. Crop Protection, 24: 821–828.
Guimaraes NAB, Felfili JM, Da Silva FG, Mazzei L, Fagg CW, Nogueira PE. 2004. Evaluation of mahogany homogenous stands, Swietenia macrophylla King, compared with mixed stands with Eucalyptus urophylla S.T. Blake, 40 months after planting. Arv Brazilian Journal, 28: 777–784.
Hauxwell C, Vargas C, Opuni Frimpong E. 2001. Entomopathogen for control of Hypsipyla spp., pp.131–139. In: Proceedings, International Workshop on ACIAR, 20–23 August 1996, Canberra, Australia
Hossain MA, Islam MA, Hossain MM. 2004. Rooting ability of cuttings of Swietenia macrophylla King and Chukrasia velutina Wight etal Arn as influenced by exogenous hormone. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 6: 560–564.
Hossain MDT, Das F, Marzan LW, Rahman MDS, Anwar MN. 2006. Some properties of protease of the fungal strain Aspergillus flavus. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 8(2): 162–164.
Kulkarni SA, Ghormade V, Kulkarni G, Kapoor M, Chavan SB, Rajendran A, Patil SK, Shouche Y, Deshpande MV. 2008. Comparison of Metarhizium isolates for biocontrol of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in chickpea. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 18(8): 809–828.
Lauma-aho T. 2003. Natural regeneration of African mahogany (Khaya ivorensis) in the moist semi-deciduous forest in Ghana. M.Sc. Thesis. University of Helsiki, Helsiki.
Lim GT, Kirton LG, Salom SM, Kok LT, Fell RD, Pfeiffer DG. 2008. Mahogany shoot borer control in Malaysia and prospects for biocontrol using weaver ants. Journal of Tropical Forest Science, 20(3): 147–155.
Lopes J. do. CA, Jennings SB, Matni NM. 2008. Planting mahogany in canopy gaps created by commercial harvesting. Forest Ecology and Management, 255: 300–307.
Mayhew JE, Newton AC. 1998. The Silviculture of Mahogany, Oxon: CABI Publishing, p. 226
Mavridou A, Typas MA. 1998. Intraspecific polymorphism in Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae revealed by analysis of rRNA gene complex and mtDNA RFLPs. Mycological Research, 102: 1233–1241
McCoy CW, Samson RA, Bovcias DG. 1988. Entomogenous fungi, CRC Handbook of Natural Pesticides Microbial Insecticides Part-A, Entomogenous Protozoa and Fungi, Vol 5, (Ignoffo, C. M., ed.), BocaRaton, FL. pp. 151–236.
Misra RM. 1993. Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) Vuillemin, a fungal pathogen of Hypsipyla robusta Moore (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Indian Journal of Forest, 16: 236–238.
Murad AM, Laumann RA, Mehta A, Noronha EF, Franco OL. 2007. Screening and secretomic analysis of entomopatogenic Beauveria bassiana isolates in response to cowpea weevil (Callosobruchus maculatus) exoskeleton. Comparative Biocheistry and Physics, 145: 333–338.
Mustafa U, Kaur G. 2009. Extra cellular enzyme production in Metarhizium anisopliae isolates. Foliarida Microbiology, 54(6): 499–504.
Nahar P, Ghormade V, Deshpande MV. 2004. The extracellular constitutive production of chitin deacetylase in Metarhizium anisopliae: possible edge to entomopathogenic fungi in the biological control of insect pests. Journal of Invertebrate of Pathology, 85: 80-88.
Newton AC, Watt AD, Lopez F, Cornelius JP, Mesen JF, Corea EA. 1999. Genetic variation in host susceptibility to attack by the mahogany shoot borer, Hypsipyla grandella (Zeller). Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 1: 11–18.
Ofori DA, Opuni-Frimpong E, Cobbinah JR. 2007. Provenance variation in Khaya species for growth and resistance to shoot borer Hypsipyla robusta. Forest Ecology and Management, 242: 438–443.
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Garrido-Jurado I., Santiago-Alvarez C, Quesada-Moraga E. 2009. Purification and characterizations of proteins secreted by the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae with insecticidal activity against adults of the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). Pest Management Sciences, 65(10): 1130–1139.
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Garrido-Jurado I, Borrego A, Quesada-Moraga E. 2010. Effects of cultural conditions on fungal biomass, blastospore yields and toxicity of fungal secreted proteins in batch cultures of Metarhizium anisopliae (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Pest Management Sciences, 66(7): 725–35.
Perez-Salicrup DR, Esquivel RT. 2008. Tree infection by Hypsipyla grandella in Swietenia macrophylla and Cedrela odorata (Meliaceae) in Mexico’s southern Yucatan Peninsula. Forest Ecology and Management, 255: 324–327.
Pignede G, Wang H, Fudalej F, Gaillardin C, Seman M, Nicaud JM. 2000. Characterization of an Extracellular Lipase Encoded by LIP2 in Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Bacteriology, 182: 2802–2810.
Ramareshiah G, Shankaran T. 1994. Studies on some parasites of the Meliaceae Shoot borer Hypsipyla robusta in South India. Hexpoda, 6(1): 39–46.
Remadevi OK, Sasidharan TO, Balachander M, Sapna Bai N. 2010. Metarhizium based mycoinsecticides for forest pest management. Journal of Biopesticides 3: 470–473.
Robert DW. 1969. Toxin from the entomogenous fungus Metarhizium anisopliae: isolation of destruxins from submerged culture. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 14: 82–88.
Salvatierra HO, Berrios F, Grijipma P. 1972. Studies on the shoot borer Hypsipyla grandella (Zeller) Lep. Pyralidae. XII. Determination of the LC50 of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) Sorokin spores on fifth instar larvae, Turrialbacia, 22: 431–438.
Salvatierra HO, Palm JD. 1972. Studies on the shoot borer Hypipyla grandella (Zeller) Lep. Pyralidae. XIV. Susceptibility of first instar larvae to Bacillus thuringinesis. Turrialbacia, 22: 467–468.
St-Leger RJ, Cooper RM, Charnley AK. 1986. Cuticle-degrading enzyme of entomopathogenic fungi: cuticle degradation in-vitro by enzymes from entomopathogens. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 47: 167-177.
St-Leger RJ, Joshi L, Bidochka MJ, Roberts DW. 1996. Characterization of chitinases from Metarhizium anisopliae, M. flavoviridae and Beauveria bassiana, and ultrastructural localization of chitinase production during invasion of insect cuticle. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 62: 907–912.
Tikhonov VE, Lopez-Llorea LV, Salinas J, Jansson HB 2002. Purification and characterization of chitinases from the nematophagous fungi Verticillium chlamydosporium and Verticillium suchlasporium. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 35: 67–78.
Varma RV. 2001. Hypsipyla shoot borers of Meliaceae in India,. In: R.B. Floyd and C. Hauxwell (eds.), Proceedings, International Workshop ACIAR, 20–23 August 1996, Kandy, Sri Lanka. p.189.
Wylie FR. 2001. Control of Hypsipyla spp. Shoot borers with chemical pesticides: a review in Hypsipyla Shoot Borers in Meliaceae.. In: R.B. Floyd and C. Hauxwell (eds.), Proceedings, International Workshop ACIAR, 20–23 August 1996, Kandy, Sri Lanka, pp. 109–115
Ypsilos IK, Magnan N. 2005. Characterization of optimum cultural environmental conditions for the production of high numbers of Metarhizium anisopliae blastospores with enhanced ecological fitness. Biocontrol Science and Technology, 15(7): 683–699.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balachander, M., Remadevi, O.K., Sasidharan, T.O. et al. Virulence and mycotoxic effects of Metarhizium anisopliae on Mahogany shoot borer, Hypsipyla robusta (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Journal of Forestry Research 23, 651–659 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-012-0306-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-012-0306-9