Abstract
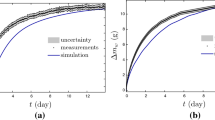
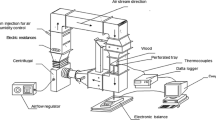
Two analytical procedures (Crank’s method and Dincer’s method) for porous solid materials were reevaluated and used to determine moisture diffusion coefficients and moisture transfer coefficients for larch lumber subjected to drying. A diffusion-like equation was used to describe drying process data. The lumber was idealized in the modeling as infinite plates. The moisture transport process inside the board was assumed to be one-dimensional. The macroscopic drying kinetics curves of larch timber at particular conditions were determined experimentally. Based on these data, calculation for both the moisture diffusion coefficients and moisture transfer coefficients by the Dincer’s analytical procedure were made. The dynamic moisture diffusion coefficients by the traditional Crank’s method were calculated. In general, diffusion coefficients calculated by the Dincer’s method were all higher than those by Crank’s method. These results could be due to the differences between two analytical methods and also different characteristics between solid moisture diffusion process and heat transfer process. Therefore the analysis and solution procedures of moisture diffusion differential equations need to be adapted in the future. With drying temperature’s increasing moisture diffusion coefficient (D) and moisture transfer coefficient (k) increases accordingly. Also the relationships between diffusion coefficients and temperature as well as material moisture contents were analyzed by using Arrhenius equation and bound water transport theory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dincer, I. and Dost, S. 1995. An analytical model for moisture diffusion in solid objects during drying. Drying Technology, 13(1&2): 425–435.
Dincer, I. 1998. Moisture loss from wood products during drying — Part I: Moisture diffusivities and moisture transfer coefficients. Energy Sources, 20(1): 67–75.
Simpson, W.T. 1993. Determination and use of moisture diffusion coefficients to characterize drying of northern red oak (Quercus rubra). Wood Science and Technology, 27(6): 409–420.
Siau, J.F. 1984. Transport processes in wood. Springer, New york: Berlin Heidelberg New york, pp184–187
Miao Ping and Gu Lianbai. 2002. Moisture unsteady-state diffusion during high temperature drying of masson pine timber. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 38(2): 103–107. (in Chinese)
Cai, L.P. 2005. Determination of diffusion coefficients for sub-alpine fir. Wood Science and Technology, 39(2): 153–162.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: ZHAN Jian-feng (1974–), male, Ph.D. Candidate and Lecturer in College of Material Science and Engineering, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin 150040, P. R. China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, Jf., Gu, Jy. & Cai, Yc. Analysis of moisture diffusivity of larch timber during convective drying condition by using Crank’s method and Dincer’s method. J. of For. Res. 18, 199–202 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-007-0040-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-007-0040-x