Abstract
Objective
To explore the relationships of the polymorphisms of xeroderma pigmentosum C (XPC) and the susceptibility of esophageal cancer (EC) in Changzhi area, China.
Methods
The study was conducted by a case-control study which included 196 cases of EC and 201 cases of controls. XPC PAT polymorphisms were determined with polymerase chain-restriction on fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP).
Results
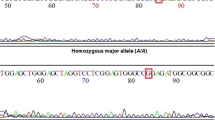
The frequencies of wild homozygote (PAT−/−), mutation heterozygote (PAT−/+) and mutation homozygote (PAT+/+) of XPC were 36.73%, 51.53% and 11.74% in case group, 37.81%, 52.24% and 9.95% in control group, respectively, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (χ2 =0.332, P=0.847). There was no interaction between XPC PAT mutation genotype and xeroderma pigmentosum A (XPA) (S=0.85) and pickled food (S=0.81).
Conclusion
A genetic polymorphism in XPC may be not associated with esophageal cancer in Changzhi population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoeijmakers JH. Genome maintenance mechanisms for preventing cancer [J]. Nature 2001; 411: 366–374.
Wood RD, Mitchell M, Sgouros J, et al. Human DNA repair genes [J]. Science 2001; 291:1284–1289.
Thoma BS, Vasquez KM. Critical DNA damage recognition functions of XPC-hHR23B and XPA-RPA in nucleotide excision repair [J]. Mol Carcinog 2003; 38:1–13.
Larsen LK, Amri EZ, Mandrup S, et al. Genomic organization of the mouse peroxisome proliferators activated receptor beta/delta gene: alternative promoter usage and splicing yield transcripts exhibiting differential translational efficiency [J]. Biochem J 2002; 365:767–775.
Khan SG, Muniz-Medina V, Shahlavi T, et al. The human XPC DNA repair gene: arrangement, splice site information content and influence of a single nucleotide polymorphism in a splice acceptor site on alternative splicing and function [J]. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30:3624–3631.
Zhang D, Chen C, Fu X, et al. A meta-analysis of DNA repair gene XPC polymorphisms and cancer risk [J]. J Hum Genet 2008; 53:18–33.
Blankenburg S, König IR, Moessner R, et al. Assessment of 3 xeroderma pigmentosum group C gene polymorphisms and risk of cutaneous melanoma: a case-control study [J]. Carcinogenesis 2005; 26:1085–1090.
Shen H, Sturgis EM, Khan SG, et al. An introit poly (AT) polymorphism of the DNA repair gene XPC and risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: a case-control study [J]. Cancer Res 2001; 61:3321–3325.
Casson AG, Zheng Z, Evans SC, et al. Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes in the molecular pathogenesis of esophageal (Barrett) adenocarcinoma [J]. Carcinogenesis 2005; 26:1536–1541.
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Yan W. Single nucleotide polymorphisms for DNA repair genes in breast cancer patients [J]. Clin Chim Acta 2005; 359:150–155.
Garcia-Closas M, Malats N, Real FX, et al. Genetic variation in the nucleotide excision repair pathway and bladder cancer risk [J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2006; 15:536–542.
Wang YG, Xin DY, Tan W, et al. Poly (AT) polymorphism in DNA repair gene XPC and lung cancer risk [J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi (in Chinese) 2003; 25:555–557.
Gu J, Zhao H, Dinney CP, et al. Nucleotide excision repair gene polymorphisms and recurrence after treatment for superficial bladder cancer [J]. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11:1408–1415.
Marín MS, López-Cima MF, García-Castro L, et al. Poly (AT) polymorphism in intron 11 of the XPC DNA repair gene enhances the risk of lung cancer [J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2004; 13:1788–1793.
Ruchika Gangwar, Anil Mandhani, Rama Devi Mittal. XPC gene variants: a risk factor for recurrence of urothelial bladder carcinoma in patients on BCG immunotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2009; (Nov) 19, DOI 10.1007/s00432-009-0717-y. [Epub ahead of print].
Qiu L, Wang Z, Shi X, et al. Associations between XPC polymorphisms and risk of cancers: A meta-analysis [J]. Eur J Cancer 2008; 44:2241–2253.
Försti A, Angelini S, Festa F, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in breast cancer [J]. Oncol Rep 2004; 11:917–922.
Qiao Y, Spitz MR, Shen H, et al. Modulation of repair of ultraviolet damage in the host-cell reactivation assay by polymorphic XPC and XPD/ERCC2 genotypes [J]. Carcinogenesis 2002; 23:295–299.
Casson AG, Zheng Z, Evans SC, et al. Polymorphisms in DNA repair genes in the molecular pathogenesis of esophageal (Barrett) adenocarcinoma [J]. Carcinogenesis 2005; 26:1536–1541.
Zambon P, Talamini R, La Vecchia C, et al. Smoking, type of alcoholic beverage and squamous cell of esophageal cancer in northern Italy [J]. Int J Cancer 2000; 86:144–149.
Liu BQ, Jiang JM, Chen ZM, et al. Relationship between smoking and risk of esophageal cancer in 103 areas in China: a large-scale case-control study incorporated into a nationwide survey of mortality [J]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (in Chinese) 2006; 86: 380–385.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from Scholarship Council Fund of Shanxi Province (No.200565).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Xx., Duan, Pf., Wang, Lb. et al. Polymorphisms of XPC gene and susceptibility of esophageal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 22, 49–54 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-010-0049-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-010-0049-0