Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role of maspin, p53 and Skp2 expressions in the progression of colorectal tumors, and their clinicopathological significance.
Methods
The expressions of maspin, p53 and Skp2 in colorectal adenocarcinoma (n=50), adenoma (n=20) and normal tissue (n=20) were detected by immunohistochemistry and compared with the clinicopathological tumor parameters. The relationship among maspin, p53 and Skp2 expression was also analyzed in colorectal tumors. The reverse transcriptase PCR was carried out to detect the level of maspin mRNA from 31 colorectal adenocarcinoma and 10 normal control tissues.
Results
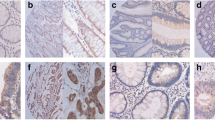
Of 50 cases of colorectal adenocarcinoma, the positive expression rates for maspin, p53 and Skp2 in colorectal adenocarcinoma were 62% (31 of 50 cases), 50% (25 of 50 cases), 48%( 24 of 50 cases), respectively; The positive expression rates for maspin, p53 and Skp2 in adenoma were 90%, 5%, 5%, respectively; The positive expression rates for maspin, p53 and Skp2 in normal control were 95%, 5%, 5%, respectively. Maspin expression was much lower in colorectal adenocarcinoma than in adenoma and normal tissues (both P<0.05). Maspin expression showed a negative association with lymphatic metastasis and higher Dukes’ stage (both P<0.05). Expression of maspin protein was negatively correlated with p53 expression (r =−0.536, P<0.01, in adenocarcinoma; r=−0.668, P<0.01, in adenoma). However, there was no significant correlation between expression of p53 and Skp2 (r=0.000, P>0.05, in adenocarcinoma; r=−0.053, P>0.05, in adenoma).
Conclusion
Maspin might play an important role in tumorigenesis and progression (especially in lymph node metastasis) of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Maspin expression was inversely correlated with mutant p53 expression in colorectal tumors, which suggested that maspin expression was regulated by the p53 pathway. Skp2 might serve as an independent factor which participated in multistage process of colorectal carcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yatabe Y, Mitsudomi T and Takahashi T. Maspin expression in normal lung and non-small cell lung cancers: cellular property-associated expression under the control of promoter DNA methylation [J]. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4041–4049.
Maass N, Hojo T, Zhang M, et al. Maspin-a novel protease inhibitor with tumor-suppressing activity in breast cancer [J]. Acta Oncol 2000; 39: 931–934.
Zhang W, Shi HY, Zhang M. Maspin overpression modulates tumor cell apoptosis through the regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins [J]. BMC Cancer 2005; 5: 50.
Liu J, Yin S, Reddy N, et al. Bax mediates the apoptosis-sensitizing effect of maspin [J]. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 1703–1711.
Odero-Marah VA, Khalkhali-Ellis Z, Chunthapong J, et al. Maspin regulates different signaling pathways for motility and adhesion in aggressive breast cancer cells [J]. Cancer Biol Ther 2003; 2: 389–403.
Ngamkitidechakul C, Warejcka DJ, Burke JM, et al. Sufficiency of the reactive site loop of maspin for induction of cell-matrix adhesion and inhibition of cell invasion. Conversion of ovalbumin to a maspin-like molecule [J]. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 31796–31806.
Maass N, Hojo T, Rosel F, et al. Down regulation of the tumor suppressor gene maspin in breast carcinoma is associated with a higher risk of distant metastasis [J]. Clin Biochem 2001; 34: 303–307.
Machtens S, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, et al. Expression of the p53 and Maspin protein in primary prostate cancer: correlation with clinical feature [J]. Int J Cancer 2001; 95: 337–342.
Maass N, Hojo T, Ueding M, et al. Expression of the tumor suppressor gene Maspin in human pancreatic cancers [J]. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 812–817.
Sood AK, Fletcher MS, Gruman LM, et al. The paradoxical expression of maspin in ovarian carcinoma [J]. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 2924–2932.
Hirai K, Koizumi K, Haraguchi S, et al. Prognostic significance of the tumor suppressor gene maspin in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Ann Thorac Surg 2005; 79: 248–253.
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Tomoda C, et al. Maspin expression is directly associated with biological aggressiveness of thyroid carcinoma [J]. Thyroid 2004; 14: 13–18.
Sugimoto S, Maass N, Takimoto Y, et al. Expression and regulation of tumor suppressor gene maspin in human bladder cancer [J]. Cancer Lett 2004; 203: 209–215.
Terashima M, Maesawa C, Oyama K, et al. Gene expression profiles in human gastric cancer: expression of maspin correlates with lymph node metastasis [J]. Br J Cancer 2005; 92: 1130–1136.
Doo-Young Lee, Chang-Soo Park, Hyung-Seok Kim, et al. Maspin and p53 protein expression in gastric adenocarcinoma and its clinical applications [J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2008; 16: 14–15.
Sheng S, Pemberton PA, Sager R. Production, purification, and characterization of recombinant maspin proteins [J]. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 30988–30993.
Zou Z, Anisowicz A, Hendrix MJ, et al. Maspin, a serpin with tumor-suppressing activity in human mammary epithelial cells [J]. Science 1994; 263: 526–529.
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Sheng S, et al. Maspin suppresses the invasive phenotype of human breast carcinoma [J]. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 5681–5685.
Umekita Y, Hiipakka RA, Liao S. Rat and human maspins: structures, metastatic suppressor activity and mutation in prostate cancer cells [J]. Cancer Lett 1997; 113: 87–93.
Xia W, Lau YK, Hu MC, et al. High tumoral maspin expression is associated with improved survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma [J]. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2398–2403.
Song SY, Lee SK, Kim DH, et al. Expression of maspin in colon cancers: its relationship with p53 expression and microvessel density [J]. Dig Dis Sci 2002; 47: 1831–1835.
Boltze C. Loss of maspin is a helpful prognosticator in colorectal cancer: a tissue microarray analysis [J]. Pathol Res Pract 2005; 200: 783–790.
Dengfeng Cao, Qian Zhang, Lee Shun-Fune Wu, et al. Prognostic significance of maspin in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: tissue microarray analysis of 223 surgically resected cases [J]. Mod Pathol 2007; 20: 570–578.
Zou Z, Gao C, Nagaich AK, et al. P53 regulates the expression of the tumor suppressor gene maspin [J]. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 6051–6054.
Ito R, Nakayama H, Yoshida K, et al. Loss of maspin expression is associated with development and progression of gastric carcinoma with p53 abnormality [J]. Oncol Rep 2004; 12: 985–990.
Machtens S, Serth J, Bokemeyer C, et al. Expression of the p53 and maspin protein in primary prostate cancer: correlation with clinical features [J]. Int J Cancer 2001; 95: 337–342.
Boltze C, Schneider-Stock R, Meyer F, et al. Maspin in thyroid cancer: its relationship with p53 and clinical outcome [J]. Oncol Rep 2003; 10:1783–1787.
Umekita Y, Ohi Y, Sagara Y, et al. Expression of maspin predicts poor prognosis in breast-cancer patients [J]. Int J Cancer 2002; 100: 452–455.
Catzavelos C, Bhattacharya N, Ung YC, et al. Decreased levels of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 inhibitor protein: prognostic implications in primary breast cancer [J]. Nat Med 1997; 3:227–230.
Esposito V, Baldi A, De Luca A, et al. Prognostic role of the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in non-small lung cancer [J]. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 3382–3385.
Loda M, Cukor B, Tam SW, et al. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas [J]. Nat Med 1997; 3:231–234.
Mori M, Mimori K, Shiraidhi T, et al. p27 expression and gastric carcinoma [J]. Nat Med 1997; 36: 593.
Guo Y, Sklar GN, Borkowsky A, et al. Loss of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 in human prostate cancer correlates with tumor grade [J]. Clin Cancer Res 1997; 3:2269–2274.
Li JQ, Wu F, Masaki T, et al. Correlation of Skp2 with carcinogenesis, invasion, metastasis, and prognosis in colorectal tumors [J]. Int J Oncol 2004; 25: 87–95.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Chongqing Educational Committee Funds (No. 040310)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Jt., Yi, Yf. & Shi, Hp. Expressions of maspin, P53 and Skp2 in colorectal tumors and their clinicopathological significance. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 21, 147–153 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0147-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0147-z