Abstract
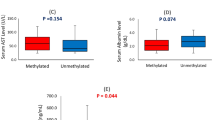
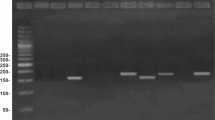
Objective: To analyze the aberrant methylation of p16 gene and DAPK gene in sera from primary liver cancer patients ad to evaluate the clinical significance. Methods: A methylation-specific PCR was performed for the detection of promoter hypermethylation of p16 gene and DAPK gene in blood DNA from 64 cases of HCC patients, and to analyze the relation of the aberrant methylation of p16 gene and KAPK gene and the clinical pathological data. Results: 76.6%(49/64) of the sera from 64 cases of HCC patients showed hypermethylation for p16 promoter and 40.6% (26/64) for KAPK promoter, whereas no methylated p16 gene promoter and DAPK gene promoter were found in sera from benign liver diseases patients and normal control. Methylated p16 gene and KAPK gene promoters in sera did not strongly correlated with HBsAg, stage, metastasis and differentiation in HCC; but strongly correlated with AFP. Conclusion: Detection of the aberrant methylation of p16 gene and KAPK gene in blood DNA from HCC patients might offer an effective means for the earlier auxiliary diagnosis of the malignancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen CJ, Yu MW, Liaw YF. Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gastroenterol Hepatol 1997; 12: S294-S308.
Ng EKO, Tsui NBY, Lam NYL, et al. Presence of filterable and nonfilterable mRNA in the mRNA in the plasma of cancer patients and healthy individuals[J]. Clin Chem 2002; 48: 1212–7.
Qiu W, Zhou B, Zou H, et al. Hypermethylation of growth arrest DNA damage-inducible gene 45 beta promoter in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Am J Pathol 2004; 165: 1689–99.
Herman JG, Graff JR, Myohanen S, et al. Methylation-specific PCR: A novel PCR assay for methylation status of CpG islands[J]. Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93:9821–6.
Gonzalez-Gomez P, Bello MJ, Lomas J, et al. aberrant methylation of multiple genes in neuroblastic tumors: relationship with MYCN amplification and allelic status at 1p[J]. Europ J Cancer 2003; 39: 1478–85.
Hsu HS, Wang YC, Tseng RC, et al. 5′ cytosine-phospho-guanine island methylation is responsible for p14ARF inactivation and inversely correlates with p53 overexpression in resected non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 4734–41.
Yu J, Zhang H, Gu J, et al. Methylation profiles of thirty four promoter-CpG island and concordant methylation behaviors of sixteen genes that may contribute to carcinogenesis of astrocytoma[J]. BMC Cancer 2004; 4: 65.
Yu J, Ni M, Xu J, et al. Methylation profiling of twenty promoter-CpG island of genes which may contribute to hepatocellular carcinogenesis[J]. BMC Cancer 2002; 2: 29.
Anker P, Stroun M. Progress in the knowledge of circulating nucleic acids: plasma RNA is particle associated. Can it become a general detection marker for a cancer blood test[J]? Clin Chem 2002; 49: 1210–1.
Alonso ME, Bello MJ, Gonzalez-Gomez P, et al. Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in oligodendrogliomas and ependymomas[J]. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 2003; 144: 134–42.
Ivy HN, Wong YM, Dennis Lo, et al. Relationship of p16 methylation status and serum α-fetoprotein concentration in hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. Clin Chem 2000; 46: 1420–2.
Pellise M, Castells A, Gines A, et al. Detection of lymph node micrometastases by gene promoter hyper-methylation in samples obtained by endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy[J]. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10: 4444–9.
Schagdarsurengin U, Wilkens L, Steinemann D, et al. Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the RASSF1A gene in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncogene 2003; 22: 1866–71.
Guan XX, Chen LB. A prospect for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients by detection of plasma DNA[J]. Oncol Prog 2003; 1: 187–90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Biography: LIN Qing(1972–), female, master of medicine, physician, General Hospital of Nanjing Command of PLA, majors in medical oncology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Q., Chen, Lb., Tang, Ym. et al. Promoter hypermethylation of p16 gene and DAPK gene in sera from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 17, 250–254 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0020-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-005-0020-7