Abstract
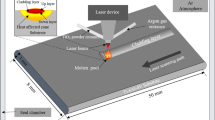
A series of Al2CrFeNiMo x (x = 0 to 2.0 at.%) high-entropy alloys coatings was synthesized on stainless steel by laser cladding. The effect of Mo content on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Al2CrFeNiMo x coatings was studied. The results show that the laser clad layer consists of the cladding zone, bonding zone, and heat-affected zone. The Al2CrFeNiMo x coatings are composed of two simple body-center cubic phases and the cladding zone is mainly composed of equiaxed grains. When the content of Mo reaches 2 at.%, a eutectic structure is found in the interdendritic regions. The surface microhardness of the Al2CrFeNiMo2 coating is 678 HV, which is about three times higher than that of the substrate (243 HV). Compared with stainless steel, the wear resistance of the coatings has been improved greatly. The wear mass loss of the Al2CrFeNiMo alloy is 9.8 mg, which is much less than that of the substrate (18.9 mg) and its wear scar width is the lowest among the Al2CrFeNiMo x coatings, indicating that the wear resistance of the Al2CrFeNiMo is the best.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ashby and A. Greer, Metallic Glasses as Structural Materials, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54(3), p 321-326
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.Y. Gan, T.S. Chin, T.T. Shun, C.H. Tsau, and S.Y. Chang, Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2004, 6, p 299-303
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, Q.J. Zhang, and J. Shi, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CoCrFeNiTiAl x High-Entropy Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2009, 508(1-2), p 214-219
T.K. Chen, T.T. Shun, J.W. Yeh, and M.S. Wong, Nanostructured Nitride Films of Multi-Element High-Entropy Alloys by Reactive DC Sputtering, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2004, 188-189, p 193-200
J.B. Cheng, X.B. Liang, and B.S. Xu, Effect of Nb Addition on the Structure and Mechanical Behaviors of CoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloy Coatings, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014, 240, p 184-190
S.T. Chen, W.Y. Tang, Y.F. Kuo, S.Y. Chen, C.H. Tsau, T.T. Shun, and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Properties of Age-Hardenable Al x CrFe1.5MnNi0.5 Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2010, 527(21-22), p 5818-5825
W. Chen, Z. Fu, S. Fang, H. Xiao, and D. Zhu, Alloying Behavior, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in a FeNiCrCo0.3Al0.7 High Entropy Alloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 51, p 854-860
Y. Wang, S. Ma, X. Chen, J. Shi, Y. Zhang, and J. Qiao, Optimizing Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi x High-Entropy Alloys by Tailoring Microstructures, Acta. Metall. Sin., 2013, 26(3), p 277-284
C.M. Lin, H.L. Tsai, and H.Y. Bor, Effect of Aging Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of High-Entropy Cu0.5CoCrFeNi Alloy, Intermetallics, 2010, 18(6), p 1244-1250
M.H. Chuang, M.H. Tsai, W.R. Wang, S.J. Lin, and J.W. Yeh, Microstructure and Wear Behavior of AlxCo1.5CrFeNi1.5Tiy High-Entropy Alloys, Acta. Mater., 2011, 59(16), p 6308-6317
J.M. Wu, S.J. Lin, J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, Y.S. Huang, and H.C. Chen, Adhesive Wear Behavior of Al x CoCrCuFeNi High-Entropy Alloys as a Function of Aluminum Content, Wear, 2006, 261(5-6), p 513-519
H.B. Cui, L.F. Zheng, and J.Y. Wang, Microstructure Evolution and Corrosion Behavior of Directionally Solidified FeCoNiCrCu High Entropy Alloy, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2011, 66-68, p 146-149
X.W. Qiu, Y.P. Zhang, and C.G. Liu, Effect of Ti Content on Structure and Properties of Al2CrFeNiCoCuTi x High-Entropy Alloy Coatings, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 585, p 282-286
K.B. Zhang, Z.Y. Fu, J.Y. Zhang, J. Shi, W.M. Wang, H. Wang, Y.C. Wang, and Q.J. Zhang, Annealing on the Structure and Properties Evolution of the CoCrFeNiCuAl High-Entropy Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 502(2), p 295-299
W. Ji, W. Wang, H. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Wang, F. Zhang, and Z. Fu, Alloying Behavior and Novel Properties of CoCrFeNiMn High-Entropy Alloy Fabricated by Mechanical Alloying and Spark Plasma Sintering, Intermetallics, 2015, 56, p 24-27
C. Huang, Y. Zhang, R. Vilar, and J. Shen, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Laser Clad TiVCrAlSi High Entropy Alloy Coatings on Ti-6Al-4V Substrate, Mater. Des., 2012, 41, p 338-343
J.H. Chen, P.N. Chen, C.M. Lin, C.M. Chang, Y.Y. Chang, and W. Wu, Microstructure and Wear Properties of Multicomponent Alloy Cladding Formed by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203(20-21), p 3231-3234
P.K. Huang and J.W. Yeh, Effects of Nitrogen Content on Structure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Element (AlCrNbSiTiV)N Coating, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2009, 203(13), p 1891-1896
H. Zhang, Y. Pan, and Y.Z. He, Synthesis and Characterization of FeCoNiCrCu High-Entropy Alloy Coating by Laser Cladding, Mater. Des., 2011, 32(4), p 1910-1915
U. Roy, H. Roy, H. Daoud, U. Glatzel, and K.K. Ray, Fracture Toughness and Fracture Micromechanism in a Cast AlCoCrCuFeNi High Entropy Alloy System, Mater. Lett., 2014, 132, p 186-189
Y.J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, F.J. Wang, Y.L. Wang, and G.L. Chen, Effect of Cu Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi0.5 Solid-Solution Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2008, 466(1-2), p 201-204
W.R. Wang, W.L. Wang, S.C. Wang, Y.C. Tsai, C.H. Lai, and J.W. Yeh, Effects of Al Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Al x CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloys, Intermetallics, 2012, 26, p 44-51
S. Guo and C.T. Liu, Phase Stability in High Entropy Alloys: Formation of Solid-Solution Phase or Amorphous Phase, Prog. Nat. Sci., 2011, 21(6), p 433-446
S. Zhang, C.L. Wu, and C.H. Zhang, Phase Evolution Characteristics of FeCoCrAlCuV x Ni High Entropy Alloy Coatings by Laser High-Entropy Alloying, Mater. Lett., 2015, 141, p 7-9
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue, Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element, Mater. Trans., 2005, 46(12), p 2817-2829
X.W. Qiu and C.G. Liu, Microstructure and Properties of Al2CrFeCoCuTiNi x High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Laser Cladding, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 553, p 216-220
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Nos. (51134013, 51274054, 51375070, 51471044, and U1332115) respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Jiang, L., Jiang, H. et al. Phase Evolution and Properties of Al2CrFeNiMo x High-Entropy Alloys Coatings by Laser Cladding. J Therm Spray Tech 24, 1333–1340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0303-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-015-0303-6