Abstract
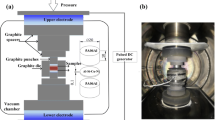
In this study, the spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique was used to join 17-4 martensitic precipitation-hardened stainless steel (17-4PH SS) with Inconel 718, a nickel-based superalloy (IN 718). Spark plasma-assisted diffusion bonding was done at a temperature of 850 °C with a bonding time of 5 min under the pressure of 50 MPa. Ansys simulation was used to examine the temperature distribution and displacement during joule heating, and it was then compared to the experimental data that had been gathered. With the help of a field emission scanning electron microscope, a white conduit at the bonded zone is evident for the diffusion of elements. Electron backscatter diffraction analysis reveals the random and elongated grains, free from local residual plastic strain at the diffusion zone. Electron probe micro-analysis was used to point out the elemental diffusion among dissimilar alloys. It is observed that the elements from IN 718 are diffused to 17-4 PH SS. At the diffusion zone, there is an increment in hardness of 345 ± 10 Hv due to the diffusion of Ni and other elements. The SPS diffusion-bonded samples have an ultimate strength of 708 ± 5 MPa with an elongation of 9 ± 2%. Dissolution of precipitates and M23C6 during diffusion bonding and segregation of Nb; Ti-rich carbide deteriorate the hardness and tensile properties of the bond zone which leads to a strain-free brittle fracture. An electrochemical polarization and impedance study was done in a 3.5% NaCl solution. After SPS diffusion bonding, 17-4 PH has lower corrosion resistance when compared to other regions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Yokokawa, H. Harada, Y. Mori, K. Kawagishi, Y. Koizumi, T. Kobayashi, M. Yuyama, and S. Suzuki, Design of Next Generation Ni-Base Single Crystal Superalloys Containing Ir: Towards 1150 C Temperature Capability. In Superalloys, 2016, p 123–130.
H. Zhang, R. Yan, B. Deng, J. Lin, M. Yang, and F. Peng, Investigation on Surface Integrity in Laser-Assisted Machining of Inconel 718 Based on In-Situ Observation, Procedia CIRP, 2022, 108, p 129–134.
N. Anbarasan, S. Jerome, and S.G.K. Manikandan, Hydrogen and Molybdenum Control on Laves Phase Formation and Tensile Properties of Inconel 718 GTA Welds, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 773, p 138874.
S.G.K. Manikandan, D. Sivakumar, K.P. Rao, and M. Kamaraj, Effect of Weld Cooling Rate on Laves Phase Formation in Inconel 718 Fusion Zone, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2014, 214(2), p 358–364.
S.G.K. Manikandan, D. Sivakumar, K.P. Rao, and M. Kamaraj, Effect of Enhanced Cooling on Microstructure Evolution of Alloy 718 Using the Gas Tungsten Arc Welding Process, Weld. World, 2016, 60(5), p 899–914.
S.G.K. Manikandan, D. Sivakumar, K.P. Rao, and M. Kamaraj, Laves Phase in Alloy 718 Fusion Zone—Microscopic and Calorimetric Studies, Mater. Charact., 2015, 100, p 192–206.
C. Zhong, A. Gasser, G. Backes, J. Fu, and J.H. Schleifenbaum, Laser Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 at Increased Deposition Rates, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2022, 844, p 143196.
D. Sidharth, R. Rajendran, and S. Narayanan, Microstructure and Properties of Inconel 718 and AISI 416 Laser Welded Joints, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, 266, p 52–62.
D. Bridges, C. Ma, S. Zhang, S. Xue, Z. Feng, and A. Hu, Diffusion and Wetting Behaviors of Ag Nanoparticle and Ag Nanowire Pastes for Laser Brazing of Inconel 718, Weld. World, 2018, 62(1), p 169–176.
M.M.Z. Ahmed, B.P. Wynne, and J.P. Martin, Effect of Friction Stir Welding Speed on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Nickel Based Super Alloy Inconel 718, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2013, 18(8), p 680–687.
H.R. Lashgari, S. Li, C. Kong, M. Asnavandi, and S. Zangeneh, Rotary Friction Welding of Additively Manufactured 17-4PH Stainless Steel, J. Manuf. Process., 2021, 64, p 1517–1528.
Z. Guoge, R.S. Chandel, and H.P. Seow, Solid-State Diffusion Bonding of Inconel Alloy 718 to 17-4 PH Stainless Steel, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2001, 16(2), p 265–279.
P. Dong, Z. Wang, W. Wang, S. Chen, and J. Zhou, Understanding the Spark Plasma Sintering from the View of Materials Joining, Scr. Mater., 2016, 123, p 118–121.
T. Nakamura, K. Hayakawa, S. Tanaka, H. Imaizumi, and Y. Nakagawa, Bonding Characteristics of Various Metals by DC Pulse Resistance Heat Pressure Welding, Mater. Trans., 2005, 46(2), p 292–297.
K. Zhao, Y. Liu, L. Huang, B. Liu, and Y. He, Diffusion Bonding of Ti-45Al-7Nb-0.3 W Alloy by Spark Plasma Sintering, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2016, 230, p 272–279.
P. Pripanapong, J. Umeda, H. Imai, M. Takahashi, and K. Kondoh, Bonding Mechanism of Ti/AZ80 Dissimilar Materials Fabricated by Spark Plasma Sintering, J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Stud., 2016, 2(10), p 1009–1013.
K. Ananthakumar and S. Kumaran, Experimental Investigation and Prediction of Optimum Process Parameter for Plasma Assisted Diffusion Bonding of Commercial Pure Titanium and Austenitic Stainless Steel, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2019, 44(2), p 1017–1032.
O. Guillon, J. Gonzalez-Julian, B. Dargatz, T. Kessel, G. Schierning, J. Räthel, and M. Herrmann, Field-Assisted Sintering Technology/Spark Plasma Sintering: Mechanisms, Materials, and Technology Developments, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2014, 16(7), p 830–849.
M. Radajewski, S. Decker, and L. Krüger, Direct Temperature Measurement via Thermocouples Within an SPS/FAST Graphite Tool, Measurement, 2019, 147, p 106863.
U. Anselmi-Tamburini, S. Gennari, J.E. Garay, and Z.A. Munir, Fundamental Investigations on the Spark Plasma Sintering/Synthesis Process: II. Modeling of Current and Temperature Distributions, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 394(1–2), p 139–148.
Y. Mo, D.Z. Wang, B. Jiang, Y.Y. Li, H.D. Liu, C.G. Wang, and J.T. Wang, Influences of Grain Size on Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviors of Nickel-Based Alloy 718. In Materials Science Forum (Vol. 852, pp. 105–112). Trans Tech Publications Ltd. (2016)
R. Baldan, A.A.A.P.D. Silva, T.M. Tanno, E.T.D. Costa, J.V.N. Brentegani, and A.A. Couto, Experimental Investigation of Delta Phase Precipitation in Inconel 625 Superalloy Aged at 550, 625 and 725° C. Mater. Res., 2020, 23(1), e20190546.
S.S.M. Tavares, F.J. Da Silva, C. Scandian, G.F. Da Silva, and H.F.G. De Abreu, Microstructure and Intergranular Corrosion Resistance of UNS S17400 (17-4PH) Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52(11), p 3835–3839.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, D.P., Kumaran, S. Evaluating the Microstructural, Mechanical, and Electrochemical Behavior of Spark Plasma-Assisted Dissimilar Joining of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel to Inconel 718. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 7756–7765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07691-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07691-7