Abstract
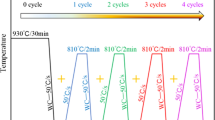
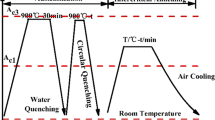
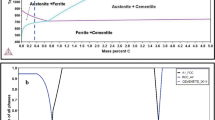
This work elucidated microstructure and mechanical properties of 22MnB5 steel fabricated by cyclic quenching treatment through OM/SEM and tensile tests. The influences of cyclic quenching treatment (CQT) on 22MnB5 steel based on the experimental results can be described as follows: (1) CQT can refine initial austenite grain sizes up to 4.2 μm; (2) CQT can refine lath martensite size, which may be related to the decreased initial austenite grain sizes; (3) 22MnB5 steel after 2 passes cyclic quenching exhibited tensile strength of 1703 MPa and elongation of 20.3% for the ultra-fine microstructure; (4) the vickers hardness of martensite of 22MnB5 increase from 0 pass cyclic quenching to 2 passes cyclic quenching. Therefore, excellent strength-ductility combination of 22MnB5 steel can be achieved by CQT.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.P. Wang, G.X. Wu, R.B. Li, P.G. Jiang, and J.Y. Zhang, Effect of Ni-Interlayer on Zinc Assisted Liquid-Metal-Induced-Embrittlement Susceptibility of 22MnB5 Galvanized Steel, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2021, 422, p 127550.
H. Karbasian and A.E. Tekkayam, A Review on Hot Stamping, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2010, 210, p 2103–2118.
H.J. Pan, M.H. Cai, H. Ding, H.S. Huang, B. Zhu, Y.L. Wang, and Y.S. Zhang, Microstructure Evolution and Enhanced Performance of a Novel Nb-Mo Microalloyed Medium Mn Alloy Fabricated by low-Temperature Rolling and Warm Stamping, Mater. Des., 2017, 134, p 352–360.
H.J. Pan, P. Jiang, Y. Zhang, W.P. Wu, Z.Z. Wang, Q. Wang, and H.Y. Li, Microstructure Evolution and Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Nb-Mo Microalloyed Medium Mn Alloy Fabricated by a Novel Cyclic Quenching Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2020, 797, p 140076.
H.J. Pan, P. Jiang, Y. Zhang, W.P. Wu, Z.Z. Wang, Q. Wang, and H.Y. Li, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Novel Nb-Mo Bearing Medium-Mn Alloy Affected by Intercritical Annealing and Tempering, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2021, 802, p 140680.
K. Nakazawa, Y. Kawabe, and S. Muneki, Grain Refinement of High-Strength Maraging Steels Through Cyclic Heat Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, 33, p 49–56.
A. Saha, D.K. Mondal, K. Biswas, and J. Maity, Microstructural Modifications and Changes in Mechanical Properties During Cyclic Heat Treatment of 0.16% Carbon Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 534, p 465–475.
Z.C. Wang, S.J. Kim, C.G. Lee, and T.H. Lee, Bake-Hardening Behavior of Cold-Rolled CMnSi and CMnSiCu TRIP-Aided Steel Sheets, J. Mater. Process. Techno., 2004, 151, p 141–145.
J.C. Cao, Q.L. Yong, Q.Y. Liu, and X.J. Sun, Precipitation of MC Phase and Precipitation Strengthening in Hot Rolled Nb-Mo and Nb-Ti Steels, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 10080–10084.
J. Shi, X.J. Sun, M.Q. Wang, W.J. Hui, H. Dong, and W.Q. Cao, Enhanced Work-Hardening Behavior and Mechanical Properties in Ultrafine-Grained Steels with Large-Fractioned Metastable Austenite, Scr. Mater., 2010, 63, p 815–818.
D. Embury and O. Bouaziz, Steel-Based Composites: Driving Forces and Classifications, Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2010, 40, p 213–241.
Acknowledgments
The present work was financially supported by the Research Initiation Fund of Changzhou University (No. ZMF20020321 & SIETP-2108), and Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20200985), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51705038 & 51875053).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Wei, C., Yu, W. et al. Achieving Excellent Strength–Ductility Combination by Cyclic Quenching Treatment in 22MnB5 Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 31, 6659–6663 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06737-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-06737-0