Abstract
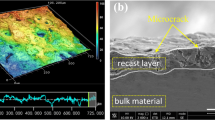
Titanium alloys, in particularly Ti-6Al-4V alloy is used enormously in many high-tech sectors specially in aerospace industries due to its superior properties. Machining process (for example wire electrical discharge machining) to reshape this alloy affects the integrity of the newly generated surfaces. This experimental study has identified three affected layers using scanning electron microscopy on the cross section of the machined titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) alloy surface generated from wire electrical discharge machining (WEDM). This study also explained the formation mechanism of those three layers as no detail investigation is available in this area so far. It was found that the top flaky layers are formed due to the highest cooling rate at the outermost surface, which is induced due to the low thermal conductivity of the titanium alloy as well as the quenching effect because of the existence of dielectric. The recast layer is formed at a cooling rate lower than that at the outer surface, where the melted material is resolidified very quickly without having any grain boundaries. The heat-affected zone appears at a slightly different color, which does not melt but experience heat treatment during the machining process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Bisaria and P. Shandilya, Surface Integrity Aspects for NiTi Shape Memory Alloys During Wire Electric Discharge Machining: A Review, J. Mater. Res., 2020, 35(6), p 537–558.
A. Smirnov, P. Peretyagin and J. Bartolomé, Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of 3Y-TZP/Ta Ceramic-Metal Composites, J. Alloy. Compd., 2018, 739, p 62–68.
H. Bisaria and P. Shandilya, Experimental Studies on Electrical Discharge Wire Cutting of Ni-Rich NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2018, 33(9), p 977–985.
E.K. Mussada, C.C. Hua and A.K.P. Rao, Surface Hardenability Studies of the Die Steel Machined by WEDM, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 1, p 1–6.
S. Kar and P.K. Patowari, Electrode Wear Phenomenon and Its Compensation in Micro Electrical Discharge Milling: A Review, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 1, p 1–27.
A. Pramanik et al., Processing of Duplex Stainless Steel by WEDM, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2018, 1, p 1–9.
A. Pramanik and A. Basak, Sustainability in Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Titanium Alloy: Understanding Wire Rupture, J. Clean. Prod., 2018, 198, p 472–479.
N. Varote and S.S. Joshi, Microstructural Analysis of Machined Surface Integrity in Drilling a Titanium Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(9), p 4391–4401.
L.D. Frame et al., Impacts of Machining and Heat Treating Practices on Residual Stresses in Alpha-Beta Titanium Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(6), p 3626–3637.
D.P. Yan and X. Jin, Characterization of Shear Band Formation and Microstructure Evolution during Orthogonal Cutting of Ti-5553: Part I—Shear Angle, Strain and Strain Rate, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(6), p 4063–4074.
S. Sartori et al., Surface Integrity Analysis of Ti6Al4V After Semi-finishing Turning Under Different Low-Temperature Cooling Strategies, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2018, 27(9), p 4810–4818.
A. Pramanik, Problems and Solutions in Machining of Titanium Alloys, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, 70(5–8), p 919–928.
A. Pramanik et al., Machining and Tool Wear Mechanisms During Machining Titanium Alloys. Advanced Materials Research, Trans Tech Publications, 2013.
A. Pramanik et al., Burr Formation During Drilling of Mild Steel at Different Machining Conditions, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2019, 34(7), p 726–735.
A. Pramanik and G. Littlefair, Machining of Titanium Alloy (Ti-6Al-4V)—Theory to Application, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2015, 19(1), p 1–49.
S. Pradhan et al., Investigation of Machining Characteristics of Hard-to-Machine Ti-6Al-4V-ELI Alloy for Biomedical Applications, J. Market. Res., 2019, 8(5), p 4849–4862.
N.M. Kumar, S.S. Kumaran and L. Kumaraswamidhas, An Investigation of Mechanical Properties and Material Removal Rate, Tool Wear Rate in EDM Machining Process of AL2618 Alloy Reinforced with Si3N4, AlN and ZrB2 Composites, J. Alloy. Compd., 2015, 650, p 318–327.
Y.C. Lin, B.H. Yan and Y.S. Chang, Machining Characteristics of Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) Using a Combination Process of EDM with USM, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 104(3), p 171–177.
M. Kunieda, S. Furuoya and N. Taniguchi, Improvement of EDM Efficiency by Supplying Oxygen Gas into Gap, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 1991, 40(1), p 215–218.
M.-D. Moses and M.P. Jahan, Micro-EDM Machinability of Difficult-to-Cut Ti-6Al-4V Against Soft Brass, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2015, 81(5), p 1345–1361.
H. Huang and J. Yan, Microstructural Changes of Zr-Based Metallic Glass During Micro-electrical Discharge Machining and Grinding by a Sintered Diamond Tool, J. Alloy. Compd., 2016, 688, p 14–21.
S.-L. Chen et al., Effect of Electro-Discharging on Formation of Biocompatible Layer on Implant Surface, J. Alloy. Compd., 2008, 456(1–2), p 413–418.
T.-S. Yang et al., Effect of Electrical Discharging on Formation of Nanoporous Biocompatible Layer on Ti-6Al-4V Alloys, Implant Dent., 2013, 22(4), p 374–379.
F. Otsuka, Y. Kataoka and T. Miyazaki, Enhanced Osteoblast Response to Electrical Discharge Machining Surface, Dent. Mater. J., 2012, 31(2), p 309–315.
P.-W. Peng et al., Effect of Electrical-Discharging on Formation of Nanoporous Biocompatible Layer on Titanium, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 492(1–2), p 625–630.
Y.H. Shih et al., Effect of Nano-Titanium Hydride on Formation of Multi-nanoporous TiO2 Film on Ti, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253(7), p 3678–3682.
H.-C. Cheng et al., Titanium Nanostructural Surface Processing for Improved Biocompatibility, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 89(17), p 1702.
S.-L. Chen et al., Research of the Recast Layer on Implant Surface Modified by Micro-current Electrical Discharge Machining Using Deionized Water Mixed with Titanium Powder as Dielectric Solvent, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 311, p 47–53.
A.R. Prasad, K. Ramji and G. Datta, An Experimental Study of Wire EDM on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy, Procedia Mater. Sci., 2014, 5, p 2567–2576.
A. Kumar, V. Kumar and J. Kumar, Investigation of machining parameters and surface integrity in wire electric discharge machining of pure titanium, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf., 2013, 227(7), p 972–992.
P. Sivaprakasam, P. Hariharan and S. Gowri, Modeling and Analysis of Micro-WEDM Process of Titanium Alloy (Ti–6Al–4V) Using Response Surface Approach, Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J., 2014, 17(4), p 227–235.
S.P. Arikatla, K.T. Mannan and A. Krishnaiah, Investigations on surface Characterisation of Wire Electric Discharge Machined Surface of Titanium Alloy, Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol., 2013, 6(4), p 663–570.
D. Aspinwall et al., Workpiece Surface Roughness and Integrity After WEDM of Ti–6Al–4V and Inconel 718 Using Minimum Damage Generator Technology, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 2008, 57(1), p 187–190.
M. Manjaiah et al., Wire Electric Discharge Machining Characteristics of Titanium Nickel Shape Memory Alloy, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China, 2014, 24(10), p 3201–3209.
A. Kumar, V. Kumar and J. Kumar, Parametric Effect on Wire Breakage Frequency and Surface Topography in WEDM of Pure Titanium, J. Mech. Eng. Technol., 2013, 1(2), p 51–56.
S.D. Lenin et al., Influence of Pulse-on-Time on the Performance of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Ti-6Al-4V Using Zinc Coated Brass Wire, Appl. Mech. Mater., 2014, 592–594, p 416–420.
M.K. Kuttuboina, A. Uthirapathi and S.D. Lenin, Effect of Process Parameters in Electric Discharge Machining of Ti-6Al–4V Alloy by Three Different Tool Electrode Materials, Adv. Mater. Res., 2012, 488–489, p 876–880.
A. Alias, B. Abdullah and N.M. Abbas, Influence of Machine Feed Rate in WEDM of Titanium Ti-6Al-4 V with Constant Current (6A) Using Brass Wire, Procedia Engineering, 2012, 41, p 1806–1811.
A. Pramanik et al., Optimizing Dimensional Accuracy of Titanium Alloy Features Produced by Wire Electrical Discharge Machining, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2019, 34(10), p 1083–1090.
A. Pramanik, A.K. Basak and C. Prakash, Understanding the wire electrical discharge machining of Ti6Al4V alloy, Heliyon, 2019, 5(4), p e01473.
M.N. Islam and A. Pramanik, Comparison of design of experiments via traditional and Taguchi method, J. Adv. Manuf. Syst., 2016, 15(03), p 151–160.
B. Gugulothu, Optimization of Process Parameters on EDM of Titanium Alloy, Mater. Today: Proc., 2020, 27, p 257–262.
M.R. Singh, P.K. Shrivastava and P. Singh, Optimization of EDM Process of Titanium Alloy Using EPSDE Technique, Multisc. Multidiscip. Model. Experim. Des., 2020, 1, p 1–10.
M. Priyadarshini et al., Multi-objective Optimization of EDM Process for Titanium Alloy, Materials Today: Proc., 2020, 33, p 5526–5529.
S. Yeo, W. Kurnia and P. Tan, Critical Assessment and Numerical Comparison of Electro-thermal Models in EDM, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 203(1–3), p 241–251.
H. Bisaria and P. Shandilya, Study on Crater Depth During Material Removal in WEDC of Ni-Rich Nickel–Titanium Shape Memory Alloy, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng., 2019, 41(3), p 1–11.
F.T. Macedo et al., Fundamental Investigation of Dry Electrical Discharge Machining (DEDM) by Optical Emission Spectroscopy and Its Numerical Interpretation, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, 90(9), p 3697–3709.
S. Yeo, W. Kurnia and P. Tan, Electro-thermal Modelling of Anode and Cathode in micro-EDM, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys., 2007, 40(8), p 2513.
H. Singh, Experimental Study of Distribution of Energy During EDM Process for Utilization in Thermal Models, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2012, 55(19–20), p 5053–5064.
A.A. Khan, Role of Heat Transfer on Process Characteristics During Electrical Discharge Machining, Developments in Heat Transfer, InTech, 2011.
K. Salonitis et al., Thermal Modeling of the Material Removal Rate and Surface Roughness for Die-sinking EDM, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, 40(3–4), p 316–323.
M. Kunieda et al., Advancing EDM Through Fundamental Insight into the Process, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol., 2005, 54(2), p 64–87.
A. Basak et al., Chemical Reactivity of Thermo-hardenable Steel Weld Joints Investigated by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(25), p 7575–7582.
A. Pramanik et al., Electrical Discharge Machining of 6061 Aluminium Alloy, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China, 2015, 25(9), p 2866–2874.
A. Pramanik, Electrical Discharge Machining of MMCs Reinforced with Very Small Particles, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2016, 31(4), p 397–404.
A. Mohanty, G. Talla and S. Gangopadhyay, Experimental Investigation and Analysis of EDM Characteristics of Inconel 825, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2014, 29(5), p 540–549.
L. Li et al., Machining Characteristics of Inconel 718 by Sinking-EDM and wire-EDM, Mater. Manuf. Processes, 2015, 30(8), p 968–973.
P. Shandilya, H. Bisaria and P. Jain, Parametric Study on the Recast Layer During EDWC of a Ni-Rich NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, J. Micromanuf., 2018, 1(2), p 134–141.
P. Sharma, D. Chakradhar and S. Narendranath, Effect of wire material on productivity and surface integrity of WEDM-processed Inconel 706 for aircraft application, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25(9), p 3672–3681.
P. Sharma, D. Chakradhar and S. Narendranath, Effect of Wire Diameter on Surface Integrity of Wire Electrical Discharge Machined Inconel 706 for Gas Turbine Application, J. Manuf. Process., 2016, 24, p 170–178.
P. Sharma, D. Chakradhar and S. Narendranath, Evaluation of WEDM Performance Characteristics of Inconel 706 for Turbine Disk Application, Mater. Des., 2015, 88, p 558–566.
A. Pramanik and G. Littlefair, Wire EDM Mechanism of MMCs with the Variation of Reinforced Particle Size, Mater. Manuf. Process., 2016, 31(13), p 1700–1708.
I. Maher, A.A. Sarhan and M. Hamdi, Review of Improvements in Wire Electrode Properties for Longer Working Time and Utilization in Wire EDM Machining, The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 76(1–4), p 329–351.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pramanik, A., Basak, A.K., Prakash, C. et al. Recast Layer Formation during Wire Electrical Discharge Machining of Titanium (Ti-Al6-V4) Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 8926–8935 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06116-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-06116-1