Abstract
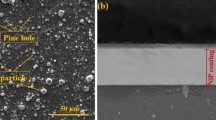
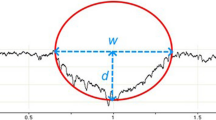
In the present work, 2D wear maps and statistical approaches on commercial samples of AISI 316L stainless steel were obtained to provide a general visualization of response variables and wear regimes under different dry sliding conditions. Dry sliding wear tests on the AISI 316L steel were performed according to the ASTM G133-05 standard procedure guidelines. A linear reciprocating sliding tribometer with a ball-on-flat configuration and a counterpart of Al2O3 was used. Wear tests were performed at room temperature with the following conditions: sliding distance of 100 m, a constant applied load of 5, 10, and 20 N, and sliding speeds of 5, 10, 20, and 30 mm/s. The analysis of variance showed that the load influences the depth, volume, and CoF response variables in a positive way with more than 97% of confidence; while the specific wear rate response variable is mainly affected by the sliding speed with more than 42% of confidence. 2D maps of the response variables were obtained using response surface methodology as a function of the load and sliding speed. The maximum specific wear rate was ~450×10-6 mm3/Nm for the condition of 5 N and 5 mm/s, influenced by the test conditions. From SEM analysis, wear regimes were classified as mild and severe and thus plowing, and material agglomeration predominate as failure mechanisms during mild wear. For severe wear, differences are more evident, with smearing being predominant on the worn tracks.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Gupta, and N. Birbilis, The Influence Of Nanocrystalline Structure and Processing Route on Corrosion of Stainless Steel: A Review, Corros. Sci., 2015, 92, p 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.11.041
A.M. Kumar, and N. Rajendran, Influence of Zirconia Nanoparticles on the Surface and Electrochemical Behaviour of Polypyrrole Nanocomposite Coated 316L SS in Simulated Body Fluid, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 213, p 155–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.10.039
M.A. Hussein, A.S. Mohammed, N. Al-aqeeli, and S. Arabia, Wear Characteristics of Metallic Biomaterials: A Review, Mater. (Basel), 2015, 8(1), p 2749–2768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma8052749
I. Hutchings, and P. Shipway, Sliding Wear, 2nd ed. Elsevier Ltd., Amsterdam, 2017.
B. Bhushan, Principles and Applications of Tribology, Tribology, Wiley, Estados Unidos, 1999.
K. Sadiq, M.M. Stack, and R.A. Black, Wear Mapping of CoCrMo Alloy in Simulated Bio-tribocorrosion Conditions of a Hip Prosthesis Bearing in Calf Serum Solution, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2015, 49, p 452–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.01.004
B. Bhushan, Modern Tribology Handbook, Vol One CRC Press, USA, 2001.
G. Rasool, and M.M. Stack, Wear Maps for TiC Composite Based Coatings Deposited on 303 Stainless Steel, Tribol. Int., 2014, 74, p 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.02.002
M.B. Maros, and A.K. Németh, Wear Maps of HIP Sintered Si3N4/MLG Nanocomposites for Unlike Paired Tribosystems Under Ball-On-Disc Dry Sliding Conditions, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2017, 37(14), p 4357–4369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2017.05.005
M. Davanageri, S. Narendranath,, and R. Kadoli, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Super Duplex Stainless Steel AISI 2507: A Statistical Approach, Arch. Foundry Eng., 2016, 16(4), p 47–56. https://doi.org/10.1515/afe-2016-0082
S. Basavarajappa, and G. Chandramohan, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Metal Matrix Composites: A Statistical Approach, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2006, 15(6), p 656–660. https://doi.org/10.1361/105994906X150731
S. Baskaran, and V. Anandakrishnan, Statistical Analysis of Co-efficient of Friction During Dry Sliding Wear Behaviour of TiC Reinforced Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5(6), p 14273–14280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.03.009
B. Saleh et al., Statistical Analysis of Dry Sliding Wear Process Parameters for AZ91 Alloy Processed by RD-ECAP Using Response Surface Methodology, Met. Mater. Int., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00624-w
P.L. Menezes, S.P. Ingole, M. Nosonovsky, S.V. Kailas, and M.R. Lovell, Tribology for Scientists and Engineers, Springer, New York USA, 2013.
J.L. Montes-Seguedo et al., Mapping the Friction Coefficient of AISI 316L on UHMWPE Lubricated with Bovine Serum to Study the Effect of Loading and Entrainment at High Values of Sliding-to-rolling Ratio, Health Technol. (Berl), 2019, 10, p 385–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12553-019-00355-y
M. Peruzzo, F.L. Serafini, M.F.C. Ordonez, R.M. Souza and M.C.M. Farias, Reciprocating Sliding Wear of the Sintered 316L Stainless Steel with Boron Additions, Wear, 2019, 422–423, p 108–118.
L.J. O’Donnell, G.M. Michal, F. Ernst, H. Kahn, and A.H. Heuer, Wear Maps for Low Temperature Carburised 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel Sliding Against Alumina, Surf. Eng., 2010, 26(4), p 284–292. https://doi.org/10.1179/026708410X12550773057901
M.C.M. Farias, R.M. Souza, A. Sinatora, and D.K. Tanaka, The Influence of Applied Load, Sliding Velocity and Martensitic Transformation on the Unlubricated Sliding Wear of Austenitic Stainless Steels, Wear, 2007, 263(1–6), p 773–781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.12.017
R.A. García-León, J. Martinez-Trinidad, I. Campos-Silva, U. Figueroa-López, and A. Guevara-Morales, Wear Maps of Borided AISI 316L Steel Under Ball-on-Flat Dry Sliding Conditions, Mater. Lett., 2021, 282, p 128842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128842
R.A. García-León et al., Dry Sliding Wear Test on Borided AISI 316L Stainless Steel Under Ball-on-Flat Configuration: A Statistical Analysis, Tribol. Int., 2021, 157, p 106885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2021.106885
R.A. García-Léon, J. Martínez-Trinidad, I. Campos-Silva, and W. Wong-Angel, Mechanical Characterization of the AISI 316L Alloy Exposed to Boriding Process, Dyna (Colombia), 2020, 87(213), p 34–41.
Acequisa, “Aceros y Equipos S.L. Aleación AISI 316L.,” Online, 2018. http://acequisa.com/spanish/inox/316l.html.
A. Jana et al., Severe Wear Behaviour of Alumina Balls Sliding Against Diamond Ceramic Coatings, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2016, 39(2), p 573–586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-016-1166-2
K. Holmberg, and A. Matthews, Coatings Tribology: Properties, Mechanisms, Techniques and Applications in Surface Engineering, Elsevier, United Kingdom, 2009.
G.B. Stachowiak, M. Salasi, W.D.A. Rickard, and G.W. Stachowiak, The Effects of Particle Angularity on Low-Stress Three-Body Abrasion-Corrosion of 316L Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2016, 111, p 690–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2016.06.008
H. Gutiérrez Pulido, and R. De La Vara Salazar, Análisis y Diseño de Experimentos, McGraw-Hil, Mexico, 2015.
D. Montgomery, and G. Runger, Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, WILEY, United States of America, 2018.
S.A. Selvan, and S. Ramanathan, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Hot Extruded ZE41A Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(7–8), p 1815–1820. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2009.11.017
G. Straffelini, Wear Mechanisms. Friction and Wear, Springer Tracts Mech. Eng., 2015, 11, p 85–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-05894-8_4
C.D. Resendiz-Calderon, L.I. Farfan-Cabrera, J.E. Oseguera-Peña, I. Cázares-Ramírez, and E.A. Gallardo-Hernandez, Friction and Wear of Metals Under Micro-abrasion, Wet and Dry Sliding Conditions, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2020, 29(9), p 6228–6238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-05102-3
K. Benarji, Y. Ravi Kumar, A.N. Jinoop, C.P. Paul, and K.S. Bindra, Effect of Heat-Treatment on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behaviour of SS 316 Structures Built by Laser Directed Energy Deposition Based Additive Manufacturing, Met. Mater. Int., 2020 https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-020-00838-y
C. Li, X. Deng, L. Huang, Y. Jia, and Z. Wang, Effect of Temperature on Microstructure, Properties and Sliding Wear Behavior of Low Alloy Wear-Resistant Martensitic Steel, Wear, 2019 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.203125
E. Atar, Sliding wear performances of 316 L, Ti6Al4V, and CoCrMo alloys, Kov. Mater., 2013, 51, p 183–188. https://doi.org/10.4149/km-2013-3.183
K. Holmberg, and A. Matthews, Coatings Tribology, Second Edition: Properties, Mechanisms, Techniques and Applications in Surface Engineering, Elsevier, United Kingdom, 2009.
S. C. Lim, “Wear Maps.” In ASM Handbook, Volume 18, Friction, Lubrication, and Wear Technology George E. Totten, editor, vol. 18, 2017, pp. 233–243
S. Thapliyal, and D.K. Dwivedi, Study of the Effect of Friction Stir Processing of the Sliding Wear Behavior of Cast NiAl Bronze: A Statistical Analysis, Tribol. Int., 2016, 97, p 124–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.01.008
D.A. Rigney, M.G.S. Naylor, R. Divakar, and L.K. Ives, Low Energy Dislocation Structures Caused by Sliding and by Particle Impact, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1986, 81, p 409–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-5416(86)90279-X
M. Peruzzo, F.L. Serafini, M.F.C. Ordoñez, R.M. Souza, and M.C.M. Farias, Reciprocating Sliding Wear of the Sintered 316L Stainless Steel with Boron Additions, Wear, 2019, 423, p 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2019.01.027
K.-H. Z. B. T.-T. S. Gahr, Ed., “Chapter 5. Grooving Wear” In Microstructure and Wear of Materials, vol. 10, Elsevier, 1987, pp. 132–350.
J.R. Davis, Surface Engineering for Corrosion and Wear Resistance, ASM Intern, United States of America, 2001.
J. Jiang, F.H. Stott, and M.M. Stack, The Role of Triboparticulates in Dry Sliding Wear, Tribol. Int., 1998, 31(5), p 245–256.
K. Kato, and K. Adachi, Wear of Advanced Ceramics, Wear, 2002, 253, p 1097–1104.
B. Bhushan, Introduction to Tribology, Second Ed. New York, USA, 2013.
K. Adachi, K. Kato, and N. Chen, Wear Map of Ceramics, Wear, 1997, 203–204, p 291–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1648(96)07363-2
T.E. Fischer, M.P. Anderson, and S. Jahanmir, Influence of Fracture Toughness on the Wear Resistance of Yttria-Doped Zirconium Oxide, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1989, 72(2), p 252–257. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1989.tb06110.x
H.Y. Lee. Effect of Changing Sliding Speed on Wear Behavior of Mild Carbon Steel, Met. Mater. Int., 2020, 26(12), p 1749–1756. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-019-00417-w
K.-H. Gahr, “Chapter 6. Sliding Wear,” in Microstructure and Wear of Materials, vol. 10, 1987, pp. 351–495.
M.F. Ashby, and S.C. Lim, Wear-Mechanism Maps, Scr. Metall. Mater., 1990, 24(5), p 805–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-716X(90)90116-X
N. Lin et al., A Combined Surface Treatment of Surface Texturing-Double Glow Plasma Surface Titanizing on AISI 316 Stainless Steel to Combat Surface Damage: Comparative Appraisals of Corrosion Resistance and Wear Resistance, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 493, p 747–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.06.028
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research grant 2021111 of the Instituto Politécnico Nacional of México. R.A. García-León thanks Dr. Hugo Martínez (Centro de Nanociencias y Nanotecnologías del IPN) for his support on the SEM-EDS analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.A. García-León, Investigation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Original Draft, Writing-Review & Editing. J. Martínez-Trinidad, Methodology, Project Administration, Supervision, Formal Analysis, Funding Acquisition. A. Guevara-Morales, Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing-Review. I. Campos-Silva, Methodology, Supervision, other contributions. U. Figueroa-López, Methodology, Supervision, other contributions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-León, R.A., Martínez-Trinidad, J., Guevara-Morales, A. et al. Wear Maps and Statistical Approach of AISI 316L Alloy under Dry Sliding Conditions. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 30, 6175–6190 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05822-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05822-0